Best Calculation Of Maintenance Fluids: Top 5 Tools Compared
Finding the Best Calculation Of Maintenance Fluids: An Introduction
In the fast-paced world of healthcare, accurately calculating maintenance fluids is crucial for patient management, especially in clinical settings where intravenous (IV) fluids are routinely administered. However, with numerous methods and formulas available, healthcare professionals often face the challenge of selecting a reliable and efficient tool to perform these calculations. The task can become overwhelming, particularly for those who may not be familiar with the nuances of fluid management or the specific needs of their patients.
This article aims to simplify that process by reviewing and ranking the top online tools available for the calculation of maintenance fluids. Our goal is to save you time and effort by providing a comprehensive overview of the best options currently on the market. We understand that accuracy in fluid calculations is paramount, as even minor errors can lead to significant clinical consequences. Therefore, our evaluation criteria include not only the accuracy of each tool but also their ease of use, user interface design, and additional features that may enhance the overall user experience.
By focusing on these key aspects, we hope to guide you in choosing the most suitable online calculator for your needs. Whether you are a nurse, physician, or medical student, the right tool can make a substantial difference in your ability to deliver optimal patient care. Join us as we delve into the best resources available for calculating maintenance fluids, ensuring that you are well-equipped to make informed decisions in your clinical practice.
Our Criteria: How We Selected the Top Tools
Accuracy and Reliability
The foremost criterion for selecting the top maintenance fluid calculators is their accuracy and reliability in delivering results. These tools must utilize established medical formulas and guidelines, such as the 4-2-1 rule or variations tailored for specific patient demographics (e.g., pediatric or adult patients). We prioritized calculators that have been validated by healthcare professionals and are widely referenced in clinical settings.
Ease of Use
We believe that a good calculator should be intuitive and user-friendly. The selected tools allow users to input data with minimal effort, ensuring that healthcare providers can quickly calculate maintenance fluid rates without extensive training. Features such as clear instructions, a clean interface, and straightforward navigation were essential in our evaluation.
Key Features
An effective maintenance fluid calculator should include several specific input fields to cater to various patient needs. Key features we looked for include:
– Weight Input: Users should be able to enter the patient’s weight in either pounds or kilograms.
– Age Specifications: Some calculators should adjust for age, particularly for pediatric patients where fluid requirements differ.
– Fluid Type Selection: Options to select the type of IV fluid (e.g., isotonic, hypotonic) based on patient condition.
– Real-Time Calculations: Immediate results that display total maintenance fluid requirements and infusion rates based on the provided inputs.
– Additional Notes or Guidelines: Annotations regarding the formulas used, contraindications, or specific considerations for certain patient groups.
Cost (Free vs. Paid)
Cost is an important factor for many users, especially in a healthcare setting. We prioritized tools that are freely accessible to ensure that all healthcare providers can utilize them without financial constraints. While some paid tools may offer advanced features, our focus was on identifying high-quality free resources that provide essential calculations effectively.
Accessibility
We also considered the accessibility of the calculators across different devices. Tools that are mobile-friendly or available as applications allow healthcare professionals to use them in various settings, whether in a hospital, clinic, or at the bedside.
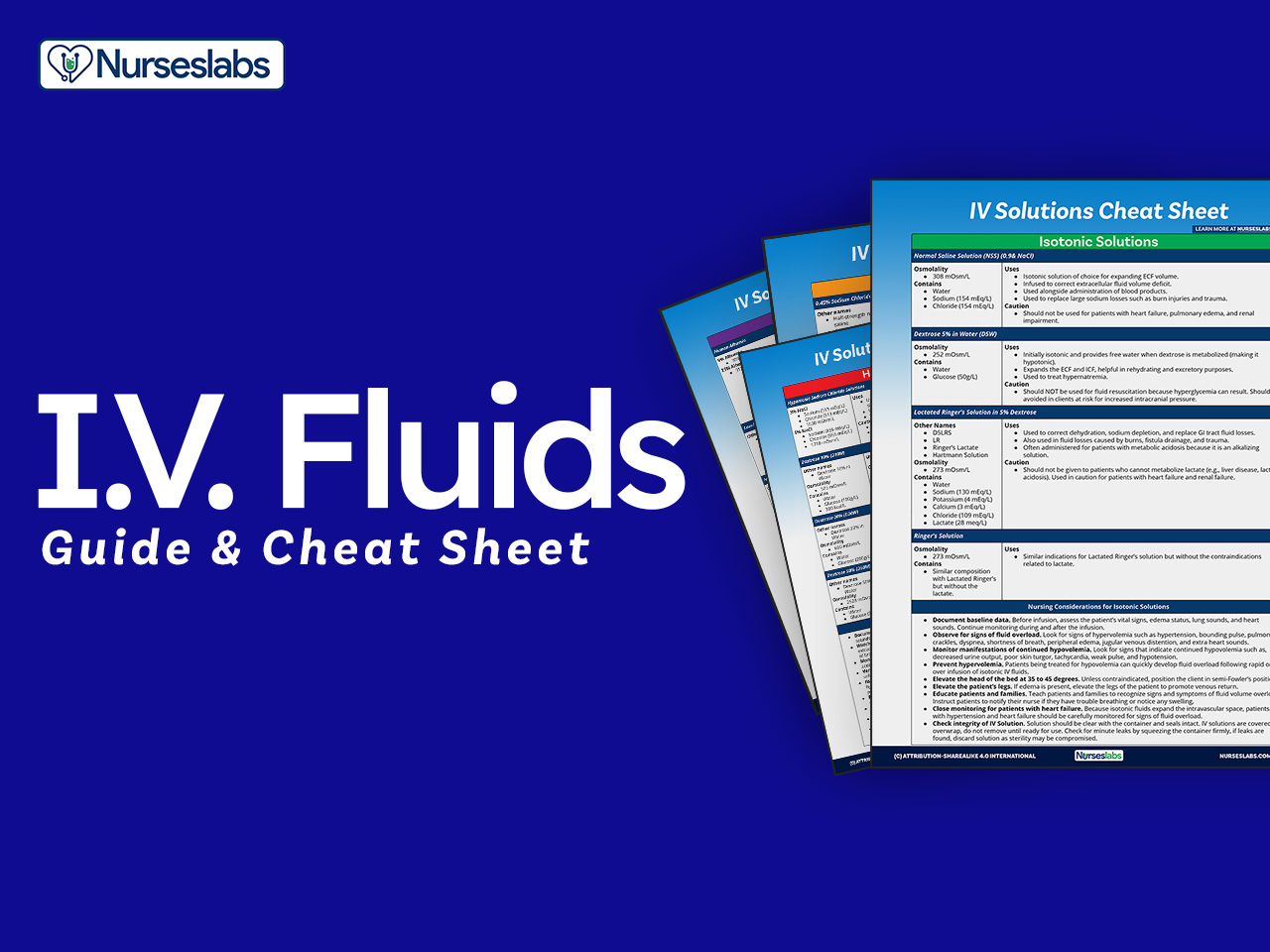
User Reviews and Expert Recommendations
Finally, we took into account user reviews and expert recommendations when selecting the top tools. Feedback from healthcare professionals who regularly use these calculators helps validate their effectiveness and overall user satisfaction. Tools with a strong track record and positive testimonials were given preference in our selection process.
By adhering to these criteria, we aimed to compile a list of maintenance fluid calculators that are not only effective but also user-centric, ensuring that healthcare providers can deliver the best care possible.
The Best Calculation Of Maintenance Fluidss of 2025
2. Fluid Management
The “Fluid Management” resource from StatPearls, available on the NCBI Bookshelf, serves as a comprehensive guide for healthcare professionals managing intravenous fluid therapy. It outlines standard protocols for administering maintenance IV fluids, specifically recommending a baseline of 2 liters of D5 1/2NS daily for adult patients with normal kidney function. The tool emphasizes evidence-based practices, ensuring clinicians can deliver effective and safe fluid management tailored to individual patient needs.
- Website: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Established: Approx. 28 years (domain registered in 1997)
3. Calculating Maintenance IV Fluid Rate
The “Calculating Maintenance IV Fluid Rate” tool from Lippincott NursingCenter provides healthcare professionals with a straightforward method for estimating maintenance fluid requirements. It follows the general guideline of 30-40 mL/kg/day, offering a quick and efficient calculation for determining IV fluid rates. This resource is particularly useful for nurses and clinicians needing to ensure proper hydration and fluid balance in patients, facilitating timely and accurate clinical decision-making.
- Website: nursingcenter.com
- Established: Approx. 28 years (domain registered in 1997)
5. Consensus Guidelines for IV Fluid Management
The “Consensus Guidelines for IV Fluid Management” from UCSF Pediatrics serves as a critical resource for healthcare professionals managing intravenous fluid therapy. Designed primarily for euvolemic patients unable to maintain adequate hydration through oral intake, the guidelines provide essential calculations for determining hourly maintenance fluid rates. This tool emphasizes evidence-based practices to optimize patient care and ensure safe, effective fluid administration in pediatric settings.
- Website: medconnection.ucsfbenioffchildrens.org
- Established: Approx. 15 years (domain registered in 2010)
How to Get the Most Accurate Results
Double-Check Your Inputs
When using online maintenance fluid calculators, the accuracy of your results is heavily dependent on the data you input. Always ensure that you have correctly entered the patient’s weight, age, and any relevant medical history. For pediatric patients, using the correct weight—ideally the ideal body weight (IBW) rather than the actual weight—can significantly impact the fluid calculation. Take a moment to verify each figure before hitting ‘calculate’; even a minor error can lead to significant discrepancies in the recommended fluid rates.
Understand the Underlying Assumptions
Each calculator may use different formulas or assumptions based on clinical guidelines or research studies. Familiarize yourself with the methodology behind the tool you are using. For instance, some calculators might apply the 4-2-1 rule, while others could utilize different parameters based on the patient’s clinical status or specific guidelines. Understanding these assumptions will help you interpret the results better and apply them appropriately to your clinical situation.
Use Multiple Tools for Comparison
No single online calculator is perfect. To enhance accuracy, consider using more than one tool to cross-check your results. This approach can help you identify any outliers or discrepancies in the calculations. If multiple calculators yield similar results, you can have greater confidence in the recommended fluid rates. However, if the results vary significantly, further investigation is warranted to understand why—whether it’s due to differing input parameters or underlying assumptions.
Keep Clinical Context in Mind
Always apply clinical judgment alongside the calculator’s output. Online tools are designed to assist in calculations, but they cannot account for every individual patient’s unique circumstances. Factors such as ongoing fluid losses, electrolyte imbalances, and the patient’s overall clinical picture should guide your final decision on fluid administration. Don’t hesitate to consult clinical guidelines or collaborate with colleagues when faced with complex cases.
Monitor Patient Response
After initiating fluid therapy based on calculator recommendations, closely monitor the patient’s response. Keep an eye on vital signs, fluid intake and output, and laboratory results. Adjustments may be necessary if the patient shows signs of fluid overload or if laboratory values indicate imbalances. Regular monitoring ensures that the fluid regimen remains appropriate as the patient’s condition evolves.
Document Your Process
Finally, document your calculations and the rationale for your chosen fluid regimen. This practice not only supports continuity of care but also provides a reference for future cases. Clear documentation can be invaluable for other healthcare professionals who may be involved in the patient’s care, ensuring that everyone is on the same page regarding the treatment plan.
By following these guidelines, you can maximize the accuracy and efficacy of online maintenance fluid calculators, leading to better patient outcomes.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are maintenance fluids and why are they important?
Maintenance fluids are intravenous (IV) fluids administered to patients to maintain hydration and electrolyte balance when they are unable to consume adequate oral fluids. They are crucial in medical settings, especially for patients who are NPO (nothing by mouth) due to surgery or illness, as they help prevent dehydration, maintain normal physiological functions, and support recovery.
2. How do I calculate maintenance fluid requirements?
Maintenance fluid requirements can be calculated using several formulas, with the most common being the “4-2-1 rule.” This formula allocates fluid needs based on body weight:
– For the first 10 kg of body weight, provide 4 mL/kg/hr.
– For the next 10 kg (11-20 kg), provide 2 mL/kg/hr.
– For any weight above 20 kg, provide 1 mL/kg/hr.
This method ensures that the fluid intake is adjusted according to the patient’s weight, which is vital for effective management.
3. Are there online tools to help with fluid calculations?
Yes, there are several online calculators available that can assist in calculating maintenance fluid requirements. Websites like MDCalc, EBM Consult, and NursingCenter offer user-friendly calculators that allow you to input patient-specific data (like weight) to quickly determine the appropriate fluid rates. These tools are beneficial for healthcare professionals who need to make accurate calculations efficiently.
4. What factors should I consider when selecting maintenance fluids?
When selecting maintenance fluids, several factors should be considered, including:
– Patient’s age and weight
– Current hydration status (euvolemic, hypovolemic)
– Specific medical conditions (e.g., renal disease, cardiac issues)
– Electrolyte imbalances
– Potential ongoing fluid losses (e.g., from vomiting or diarrhea)
Tailoring the fluid choice and rate to the individual patient’s needs is essential to ensure optimal care and avoid complications.
5. What are the risks associated with improper maintenance fluid administration?
Improper administration of maintenance fluids can lead to several complications, including:
– Electrolyte imbalances (e.g., hyponatremia or hypernatremia)
– Fluid overload, which can cause pulmonary edema or heart strain
– Iatrogenic complications, particularly in vulnerable populations like children and the elderly
It’s crucial to monitor patients closely and adjust fluid rates as necessary to mitigate these risks and ensure safe and effective treatment.
Important Disclaimer
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information and reviews in this guide are for educational purposes only and are based on publicly available information. We are not affiliated with any of the tools mentioned. Features and pricing may change. Always conduct your own research before choosing a tool for your needs.