Best CRM Software: The Top 7 Platforms Reviewed
Introduction: Why Your Business Needs More Than a Spreadsheet
In today’s fast-paced business environment, managing customer relationships effectively is crucial for sustained success. Many businesses, especially small to medium-sized enterprises, often rely on spreadsheets and scattered notes to track customer interactions and manage their sales pipelines. While spreadsheets can serve as a temporary solution, they present a myriad of challenges. Data can easily become outdated or inconsistent, collaboration becomes cumbersome, and critical customer insights may be overlooked. As a result, businesses risk losing potential leads, compromising customer satisfaction, and ultimately, diminishing their bottom line.
This chaotic approach to customer management can lead to missed opportunities and hindered growth. To address these issues, businesses need a more robust solution that can centralize customer data, streamline processes, and enhance communication. Enter Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems. A CRM is a powerful tool designed to help businesses manage and analyze customer interactions throughout the entire customer lifecycle. By consolidating all customer-related information into one platform, CRMs empower businesses to foster stronger relationships, increase customer loyalty, and drive sales growth.
At its core, CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management. The primary purpose of a CRM is to provide a comprehensive view of each customer, enabling businesses to tailor their interactions and improve overall customer experience. By utilizing a CRM, companies can gather valuable data from various touchpoints, automate repetitive tasks, and gain insights that inform strategic decision-making.
This comprehensive guide aims to illuminate the world of CRM systems and assist you in navigating the selection process. We will begin by defining what a CRM is and exploring its core features, such as contact management, sales tracking, and reporting capabilities. Next, we will delve into the key benefits of implementing a CRM, including improved customer experiences, increased productivity, and enhanced data-driven insights.
Furthermore, we will review some of the top CRM platforms available in the market, highlighting their unique features and ideal use cases. Finally, we will provide a step-by-step guide to choosing the right CRM for your business, ensuring you make an informed decision that aligns with your specific needs and goals.
By transitioning from spreadsheets to a dedicated CRM system, you can transform the way your business interacts with customers, paving the way for long-term success.
The Top 7 CRM Platforms of 2025
8 款最佳销售 CRM 软件 + 功能对比 [2025]
In the Salesflare Blog’s review of the “8 Best Sales CRM Software for 2025,” various CRM solutions are evaluated for their features and usability, particularly for small businesses and sales teams. The article highlights HubSpot CRM and Sales Hub for their extensive range of integrated tools designed to enhance sales management and streamline processes, making it easier for users to optimize their sales strategies and improve customer relationships.
- Website: blog.salesflare.com
- Company Age: Approx. 11 years (domain registered in 2014)
What is CRM software? 8 best CRM tools of 2025
The article from Zendesk explores the top eight CRM software options for 2025, highlighting their key features and suitability for various target audiences, including small businesses and sales teams. Among the featured tools are HubSpot Sales Hub and Salesforce Sales Cloud, known for their robust capabilities in managing customer relationships, enhancing sales processes, and improving overall team collaboration. This guide serves as a valuable resource for businesses seeking to optimize their CRM strategies.
- Website: zendesk.com
- Company Age: Approx. 20 years (domain registered in 2005)
Top 10: CRM Platforms
In the review article “Top 10: CRM Platforms” by Technology Magazine, a curated list of the most effective CRM solutions is presented, catering to diverse business needs. From Monday.com and Nimble for small businesses to robust options like Zoho CRM and Pipedrive for sales teams, the article highlights key features, user-friendliness, and scalability, making it a valuable resource for organizations seeking to enhance customer relationship management and streamline sales processes.
- Website: technologymagazine.com
- Company Age: Approx. 22 years (domain registered in 2003)
27 of the Best CRM Software Companies to Know About for 2025
In “27 of the Best CRM Software Companies to Know About for 2025,” Solutions Review highlights a diverse array of CRM solutions tailored to various business needs, from small startups to established enterprises. Featuring notable platforms like Act!, ActiveCampaign, and Bitrix24, the article provides insights into each company’s unique features, making it an invaluable resource for sales teams and marketing professionals seeking to enhance customer relationship management and streamline operations in the coming year.
- Website: solutionsreview.com
- Company Age: Approx. 13 years (domain registered in 2012)
Best CRM Software in 2025: Top 10 Platforms
The article “Best CRM Software in 2025: Top 10 Platforms” by O8 Agency provides a comprehensive review of leading CRM solutions tailored for various business needs. It highlights top contenders such as Salesforce, known for its robust organizational capabilities, and HubSpot CRM, favored for its user-friendly interface. Targeting sales teams and small to medium-sized businesses, the guide emphasizes essential features like automation, analytics, and integration to enhance customer relationship management.
- Website: o8.agency
CRM software: the ultimate guide and 10 top AI
The article “CRM Software: The Ultimate Guide and 10 Top AI-Powered Solutions” on monday.com explores SugarCRM, a versatile platform designed for businesses seeking to enhance customer interactions, streamline sales processes, and optimize marketing strategies. Ideal for small to medium-sized enterprises, SugarCRM integrates advanced AI features to improve efficiency, making it a valuable tool for sales teams aiming to boost productivity and drive growth.
- Website: monday.com
- Company Age: Approx. 30 years (domain registered in 1995)
What is a CRM System? A Deep Dive
Understanding CRM Systems
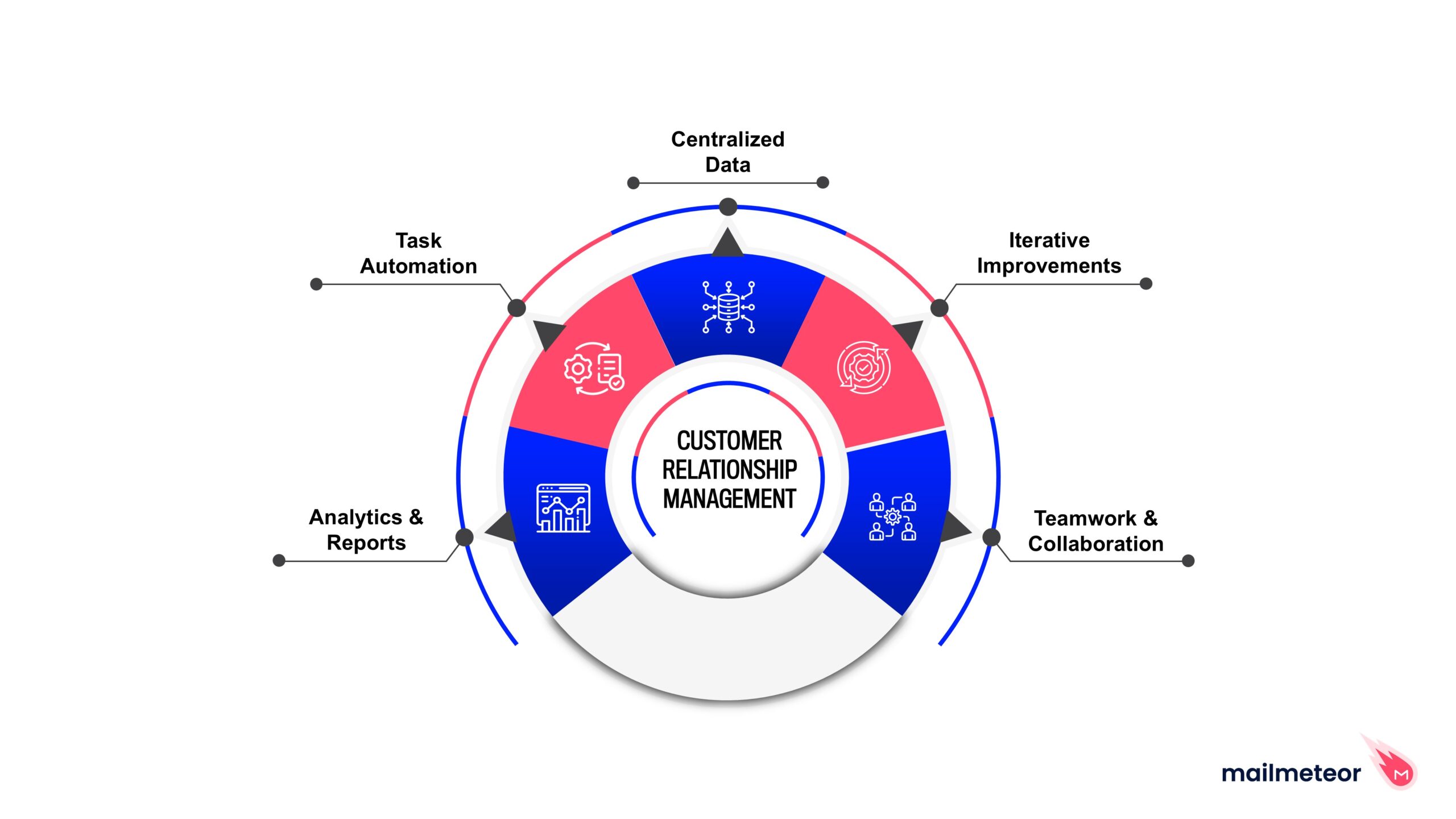
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are essential tools for businesses aiming to enhance their relationships with customers, streamline operations, and drive growth. At their core, CRMs collect and organize customer information, interactions, and history, providing a holistic view of the customer journey. However, the advantages of a CRM system extend far beyond mere data collection.
The Goals of a CRM System
The primary goal of a CRM system is to improve business relationships. This encompasses various objectives, including:
-
Enhancing Customer Satisfaction: By centralizing customer data, businesses can gain insights into customer preferences and behaviors. This information enables personalized communication and services, ultimately leading to higher customer satisfaction.
-
Streamlining Processes: CRMs automate routine tasks, such as data entry and follow-up reminders. This automation frees up valuable time for employees, allowing them to focus on higher-value activities that drive revenue.
-
Increasing Sales and Revenue: With tools for tracking leads and managing sales pipelines, CRMs empower sales teams to close deals more effectively. By analyzing customer interactions, businesses can identify opportunities for upselling and cross-selling.
-
Improving Collaboration: CRMs facilitate better communication and collaboration among different departments. Whether it’s marketing, sales, or customer service, all teams can access the same customer information, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
-
Data-Driven Decision Making: By providing analytics and reporting features, CRMs enable businesses to make informed decisions based on real-time data. This insight allows for the identification of trends, forecasting future sales, and measuring the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
Who Uses a CRM?
CRM systems are not limited to sales teams; they benefit various departments across an organization. Here’s how different teams utilize CRMs:
-
Sales Teams: Sales professionals rely heavily on CRMs to track leads, manage their sales pipeline, and automate follow-ups. With a CRM, sales reps can access comprehensive customer profiles that include interaction history, preferences, and purchase behavior, allowing them to tailor their sales approach effectively.
-
Marketing Teams: Marketers use CRMs to segment audiences, track campaign performance, and nurture leads through automated marketing workflows. By integrating customer data from various touchpoints, marketing teams can create targeted campaigns that resonate with potential customers, enhancing the likelihood of conversion.
-
Customer Service Teams: Customer service representatives leverage CRMs to manage customer inquiries, track service requests, and analyze support interactions. A CRM helps ensure that customers receive timely responses and personalized support, leading to improved customer loyalty and retention.
-
Management: Executives and managers utilize CRM analytics to gain insights into overall business performance. By reviewing key performance indicators (KPIs) such as customer lifetime value (CLV) and sales conversion rates, they can make strategic decisions that align with organizational goals.
Why a Spreadsheet Isn’t Enough
While spreadsheets may seem like a convenient way to manage customer data, they fall short in several critical areas compared to a dedicated CRM system:
-
Limited Scalability: As businesses grow, the volume of customer data increases significantly. Spreadsheets can become cumbersome and error-prone, making it difficult to manage large datasets effectively. CRMs are designed to handle vast amounts of information, ensuring that data remains organized and accessible.
-
Inefficient Collaboration: Spreadsheets often lead to version control issues, especially when multiple team members are involved. A CRM provides a centralized platform where all users can access the most up-to-date information, facilitating better collaboration among teams.
-
Lack of Automation: Manual data entry and tracking in spreadsheets can be time-consuming and prone to errors. CRMs automate many of these processes, reducing the risk of human error and freeing up time for employees to focus on strategic initiatives.
-
Inadequate Insights: While spreadsheets can perform basic calculations and data analysis, they do not offer the advanced analytics capabilities of a CRM. CRMs provide real-time reporting and visualization tools that allow businesses to track performance metrics, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
-
Customer Interaction Tracking: Spreadsheets lack the ability to track customer interactions comprehensively. A CRM records every interaction across various channels—email, phone, social media—creating a complete history that can inform future communications and strategies.
Conclusion
In summary, a CRM system is a multifaceted tool that enhances the way businesses interact with their customers. By centralizing customer data and automating processes, CRMs empower sales, marketing, and customer service teams to work more efficiently and effectively. As the business landscape continues to evolve, investing in a robust CRM system is essential for companies looking to foster strong customer relationships and drive sustainable growth.
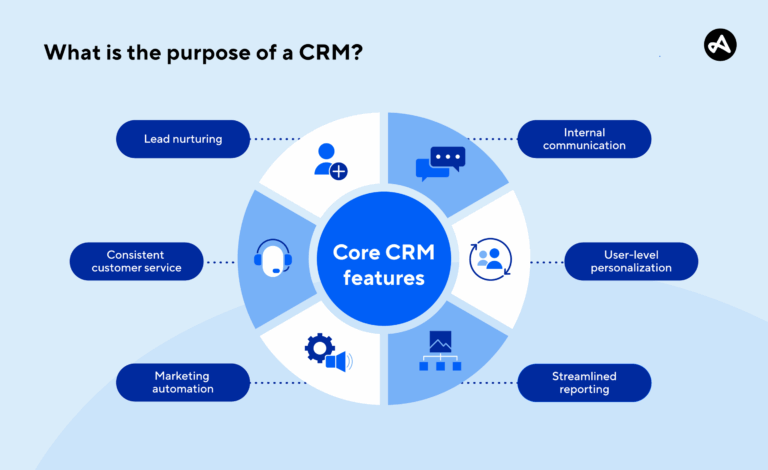
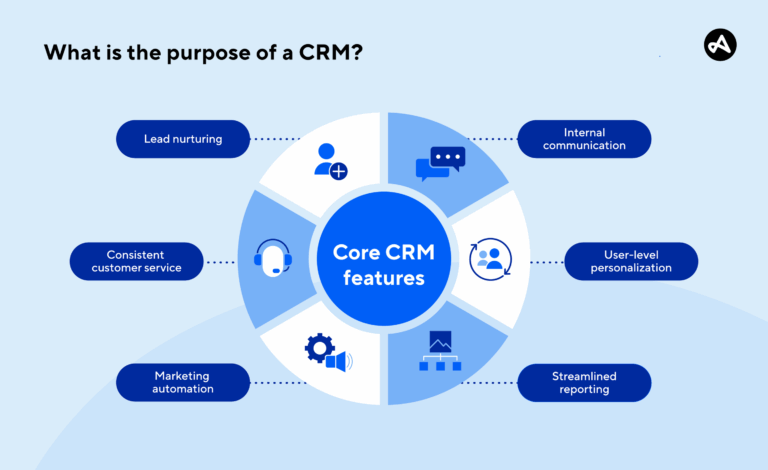
Core Features: What to Expect from a Modern CRM
Contact Management
Contact management is the cornerstone of any modern CRM system. It involves the organization and maintenance of detailed information about customers, prospects, and leads. A robust CRM allows businesses to store vital data such as contact details, communication history, preferences, and even notes from previous interactions.
How It Works
Modern CRM systems utilize a centralized database that captures all customer interactions across multiple channels, including emails, phone calls, and social media. This information is easily accessible to sales and support teams, enabling them to provide personalized service based on the context of past interactions.
Business Benefits
The primary benefit of effective contact management is the ability to foster stronger relationships with customers. By having a comprehensive view of each contact, teams can tailor their communications and offerings, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty. Furthermore, this organized approach reduces the risk of miscommunication and enhances collaboration among team members.
Lead and Opportunity Management
Lead and opportunity management functionalities are designed to help businesses identify, track, and nurture potential customers throughout the sales funnel. These features allow sales teams to categorize leads based on their readiness to purchase and prioritize follow-ups accordingly.
How It Works
Within a CRM, leads can be assigned statuses such as “new,” “in progress,” or “converted.” The system often incorporates scoring mechanisms to evaluate lead quality based on predefined criteria, such as engagement level or demographic information. Opportunity management tools help sales teams visualize potential sales and forecast revenue by tracking the progress of deals in the pipeline.
Business Benefits
The ability to effectively manage leads and opportunities directly impacts sales efficiency and conversion rates. By focusing efforts on high-potential leads, businesses can optimize their sales strategies, allocate resources more effectively, and ultimately drive higher revenue growth. Furthermore, nurturing leads through targeted communication helps build trust and encourages prospects to make purchasing decisions.
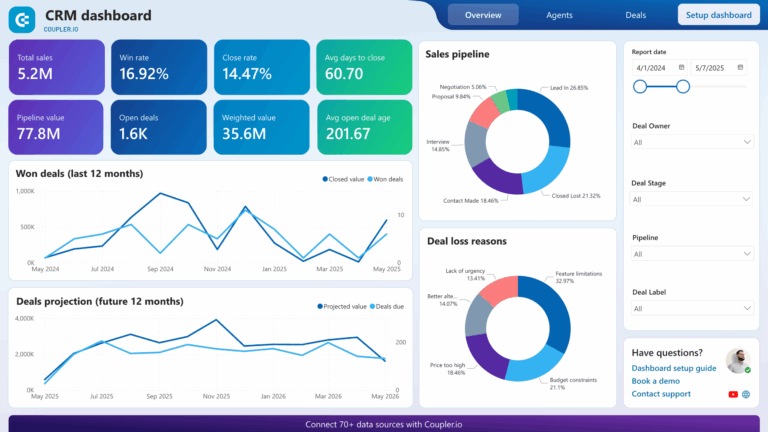
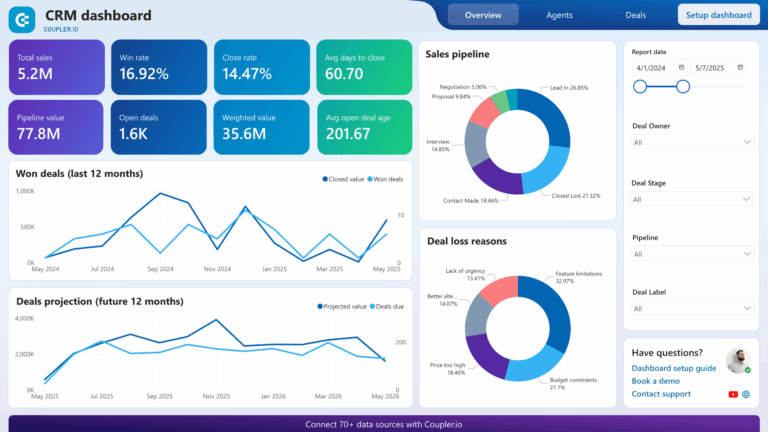
Sales Pipeline Visualization
Sales pipeline visualization provides a graphical representation of the sales process, illustrating where each deal stands within the sales funnel. This feature enables sales teams to monitor progress and identify bottlenecks in the sales cycle.
How It Works
Modern CRMs often include customizable pipeline views that display stages of the sales process, such as “prospecting,” “qualification,” “proposal,” and “closed.” Sales representatives can drag and drop opportunities between stages, making it easy to update statuses in real time. This visual representation aids in understanding the overall health of the sales pipeline.
Business Benefits
A well-defined sales pipeline allows businesses to gain insights into their sales performance and identify trends over time. By visualizing the pipeline, teams can quickly spot areas needing improvement and make data-driven decisions to enhance their sales strategies. This transparency leads to better forecasting accuracy and improved resource allocation, ultimately driving more successful outcomes.
Task and Activity Tracking
Task and activity tracking features in a CRM help sales and marketing teams manage their daily responsibilities and ensure timely follow-ups with leads and customers. This functionality allows users to create, assign, and monitor tasks related to specific contacts or opportunities.
How It Works
Users can set reminders for follow-up calls, meetings, and other important activities within the CRM. Automated alerts notify team members of upcoming tasks, ensuring that no opportunities are missed. Additionally, the system can log completed activities, providing a comprehensive history of interactions with each contact.
Business Benefits
Effective task and activity tracking enhances accountability and productivity among team members. By streamlining task management, businesses can minimize the risk of missed follow-ups and improve response times to customer inquiries. This proactive approach not only boosts sales performance but also enhances the overall customer experience by demonstrating attentiveness and care.
Marketing Automation
Marketing automation features within a modern CRM enable businesses to streamline their marketing efforts by automating repetitive tasks and orchestrating multi-channel campaigns. This functionality helps bridge the gap between sales and marketing teams, ensuring a cohesive approach to customer engagement.
How It Works
A CRM with marketing automation capabilities allows users to create targeted email campaigns, schedule social media posts, and segment audiences based on behavior or demographics. Automation rules can trigger personalized communications based on customer interactions, such as sending follow-up emails after a lead downloads a resource or visits a website.
Business Benefits
By automating marketing tasks, businesses can save time and reduce manual effort, allowing teams to focus on strategy and creativity. This efficiency leads to increased engagement rates, as personalized and timely communications resonate more with customers. Moreover, the integration of marketing and sales data within a CRM provides valuable insights that can inform future campaigns and improve lead nurturing processes.
Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics features in a CRM provide businesses with the tools to analyze sales performance, customer behavior, and marketing effectiveness. These capabilities enable data-driven decision-making and strategic planning.
How It Works
Modern CRMs come equipped with customizable dashboards and reporting tools that visualize key performance indicators (KPIs), such as sales revenue, conversion rates, and customer lifetime value. Users can generate reports to track progress against goals, identify trends, and assess the effectiveness of different strategies.
Business Benefits
The insights gained from CRM analytics empower businesses to make informed decisions that enhance performance. By identifying successful tactics and areas for improvement, teams can refine their approaches and optimize their sales and marketing strategies. Furthermore, robust analytics foster accountability and transparency, as team members can track their contributions to overall business objectives.
Integrations
Integrations are a critical feature of modern CRM systems, enabling businesses to connect their CRM with other software tools and platforms. This functionality ensures that all customer data is centralized and accessible, allowing for a seamless flow of information across departments.
How It Works
Most modern CRMs offer a wide range of integrations with popular tools, such as email marketing platforms, customer support systems, e-commerce platforms, and social media channels. These integrations allow data to sync automatically, reducing the need for manual data entry and minimizing errors.
Business Benefits
Integrating a CRM with other business tools enhances operational efficiency and provides a holistic view of customer interactions. By having access to comprehensive data across systems, teams can make better-informed decisions and deliver a more personalized customer experience. Additionally, seamless integrations reduce the time spent on administrative tasks, allowing employees to focus on higher-value activities that drive business growth.
In summary, modern CRM systems are equipped with a range of core features designed to enhance customer relationship management and streamline business processes. By understanding and leveraging these features, business owners, sales managers, and marketing professionals can make informed decisions when choosing a CRM that aligns with their organizational goals and enhances customer engagement.
The 3 Types of CRM Systems Explained
Comparison of the 3 Types of CRM Systems
| CRM Type | Primary Goal | Key Features | Best For (Department) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operational CRM | Streamline and automate customer-facing processes | Contact management, sales automation, marketing automation, customer service | Sales, Marketing, Customer Service |
| Analytical CRM | Analyze customer data for insights and forecasting | Data mining, predictive analytics, reporting, performance tracking | Marketing, Sales, Management |
| Collaborative CRM | Enhance communication and collaboration among stakeholders | Shared databases, communication tools, project management | Sales, Marketing, Customer Service, R&D |
Operational CRM
Operational CRM focuses on automating and streamlining customer-facing processes, effectively managing interactions with customers across various channels. The primary goal is to enhance the efficiency of sales, marketing, and customer service departments by providing a cohesive platform where customer data can be accessed and utilized seamlessly.
Key features of operational CRM include contact management, sales automation, marketing automation, and customer service tools. For instance, a sales team can utilize operational CRM to track leads, manage customer interactions, and automate follow-ups. Marketing teams can create targeted campaigns based on customer profiles and track their effectiveness through the CRM’s reporting features. Customer service departments can manage inquiries and track resolutions, ensuring a consistent and efficient experience for customers.
A real-world example of operational CRM in action is Salesforce Sales Cloud, which integrates various functionalities to provide a comprehensive view of customer interactions. Sales representatives can track their pipelines, manage leads, and automate communication, all while accessing a centralized customer database. This not only enhances productivity but also ensures that every customer interaction is informed and personalized, ultimately leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Analytical CRM
Analytical CRM is designed to analyze customer data to gain insights that drive strategic decision-making and improve customer relationships. Its primary goal is to provide businesses with a deeper understanding of their customers through data analysis, which can lead to enhanced customer experiences and increased profitability.
Key features of analytical CRM include data mining, predictive analytics, and comprehensive reporting capabilities. This type of CRM allows businesses to segment their customer base, analyze purchasing behaviors, and forecast future trends based on historical data. For example, a retail company might use analytical CRM to identify its most profitable customer segments and tailor marketing efforts accordingly, optimizing return on investment (ROI).
A practical example of analytical CRM is Zoho CRM, which offers robust analytics tools to monitor various aspects of the sales cycle, such as lead analytics and email performance. Users can create customizable dashboards that visualize data, helping businesses identify trends and make data-driven decisions. This insight can significantly enhance targeted marketing strategies and improve sales forecasting, ultimately leading to more effective resource allocation.
Collaborative CRM
Collaborative CRM emphasizes the importance of communication and collaboration among different departments within an organization as well as with external stakeholders. The primary goal is to facilitate sharing of customer information across departments to create a unified approach to customer relationship management.
Key features of collaborative CRM include shared databases, communication tools, and project management capabilities. By centralizing customer data, teams can access the same information, ensuring that everyone is on the same page regarding customer interactions and strategies. This type of CRM is particularly beneficial for organizations with complex customer interactions that involve multiple departments, such as sales, marketing, customer service, and product development.
A real-world example of collaborative CRM is HubSpot, which integrates marketing, sales, and customer service functionalities. Teams can collaborate on customer accounts, share insights, and streamline communication, leading to a more cohesive customer experience. For instance, if a customer service representative identifies a recurring issue with a product, they can easily share that information with the product development team, fostering a collaborative approach to problem-solving and innovation.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of CRM systems—operational, analytical, and collaborative—can help business owners, sales managers, and marketing professionals make informed decisions when selecting a CRM that aligns with their organizational needs and goals. By leveraging the appropriate CRM type, businesses can enhance their customer relationships, improve efficiency, and ultimately drive growth.
Key Business Benefits of Using a CRM
1. Centralized Customer Data
One of the most significant advantages of implementing a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is the centralization of customer data. A CRM consolidates all customer interactions, preferences, and history into a single database, accessible to all relevant team members. This unified repository eliminates the silos often present in organizations, where different departments maintain separate records. With a comprehensive view of each customer, sales and support teams can deliver more informed and personalized interactions, enhancing customer satisfaction. Additionally, centralized data facilitates better communication among team members, ensuring everyone is on the same page regarding customer needs and engagement history.
2. Improved Sales Productivity
A CRM system can dramatically boost sales productivity by automating repetitive tasks and providing tools that streamline the sales process. Features such as automated reminders for follow-ups, email templates, and lead scoring help sales teams focus on high-priority tasks rather than getting bogged down in administrative work. By automating routine tasks, sales representatives can dedicate more time to engaging with prospects and nurturing relationships. Furthermore, CRMs often include pipeline management tools that visualize the sales process, making it easier for teams to track progress and identify bottlenecks. This level of efficiency not only accelerates the sales cycle but also enhances overall team performance.
3. Enhanced Customer Retention
Customer retention is essential for long-term business success, and a CRM system plays a crucial role in fostering loyalty. By tracking customer interactions and feedback, CRMs enable businesses to identify potential issues before they escalate. This proactive approach allows for timely follow-ups and personalized communication that resonates with customers. Moreover, CRMs can help implement loyalty programs or targeted marketing campaigns based on customer behavior and preferences, further encouraging repeat business. By nurturing existing relationships and addressing concerns effectively, businesses can significantly enhance customer satisfaction, leading to improved retention rates.
4. Data-Driven Decision Making
In today’s data-driven world, having access to accurate and comprehensive analytics is vital for making informed business decisions. A CRM system provides robust reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing businesses to track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales trends, customer acquisition costs, and conversion rates. With this data at their fingertips, managers can identify patterns and insights that inform strategic planning and resource allocation. For instance, understanding which marketing channels yield the highest ROI enables businesses to invest more wisely in their campaigns. By leveraging data-driven insights, organizations can make proactive adjustments to their strategies, ultimately driving growth and profitability.
5. Scalable Growth
As businesses expand, their customer management needs become increasingly complex. A CRM system is designed to scale alongside your business, providing the flexibility and functionality required to manage growing customer relationships effectively. Whether you’re adding new users, integrating additional features, or expanding into new markets, a robust CRM can adapt to your evolving requirements. This scalability ensures that as your organization grows, you can maintain a high level of customer service and engagement without sacrificing efficiency. Furthermore, many CRM solutions offer integration with other business systems, allowing for seamless expansion and the ability to harness synergies across different departments, all while maintaining a focus on customer satisfaction.
In summary, the implementation of a CRM system offers numerous key benefits that can significantly enhance business performance. From centralized customer data to improved sales productivity, enhanced retention strategies, data-driven decision-making, and scalable growth, a CRM is an invaluable tool for any organization looking to thrive in a competitive marketplace. By investing in a CRM, businesses can position themselves for long-term success and build stronger, more meaningful relationships with their customers.
How to Choose the Right CRM: A 7-Step Buyer’s Guide
1. Define Your Business Goals and Needs
Before diving into the CRM selection process, it’s crucial to clearly define your business goals and specific needs. A well-defined set of objectives will guide your decision-making and help you identify the features that are most important for your organization.
Identify Key Functions
Consider what you want the CRM to achieve. Are you primarily focused on enhancing customer relationships, improving sales processes, or streamlining marketing efforts? Common functionalities include:
- Contact Management: Organizing and tracking customer interactions.
- Sales Pipeline Management: Monitoring leads and opportunities through various stages.
- Reporting and Analytics: Gaining insights into sales performance and customer behaviors.
- Customer Support Features: Managing service requests and customer feedback.
Engage Stakeholders
Engage team members from sales, marketing, and customer service to gather input on what they need from a CRM. Their insights will help you form a comprehensive list of requirements, ensuring that the selected CRM supports the entire organization.
2. Establish Your Budget
Setting a budget for your CRM is a critical step that will shape your options. The price of CRM systems can vary significantly based on features, scalability, and vendor reputation.
Consider Total Cost of Ownership
When establishing your budget, consider the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes:
- Subscription Fees: Monthly or annual costs per user or team.
- Implementation Costs: Expenses related to setup, data migration, and training.
- Maintenance Fees: Ongoing costs for support, upgrades, and additional features.
- Add-Ons and Integrations: Costs for extra functionalities or third-party integrations.
Plan for Future Expenses
Account for potential future expenses as your business grows. Opting for a CRM with scalable pricing models can help you avoid financial strain as you add users or require more advanced features.
3. Consider Ease of Use and User Adoption
A CRM’s usability can significantly impact user adoption. If the system is too complex or unintuitive, your team may resist using it, leading to wasted resources and missed opportunities.
User-Friendly Interface
Look for a CRM with a clean, intuitive interface that allows users to navigate easily. A user-friendly design can facilitate faster onboarding and reduce the time spent on training.
Training and Support Resources
Evaluate the availability of training resources and customer support. A vendor that offers comprehensive training materials, webinars, and responsive support can help ensure a smooth transition and ongoing user satisfaction.
4. Check for Essential Integrations
Your CRM should seamlessly integrate with other tools and systems already in use within your organization. This connectivity allows for a unified view of customer data and enhances overall productivity.
Identify Critical Integrations
Determine which tools are essential for your business operations. Common integrations include:
- Email Marketing Platforms: To synchronize contact lists and track engagement.
- Customer Support Software: For a complete view of customer interactions across channels.
- Accounting Software: To streamline invoicing and financial reporting.
API Availability
Check if the CRM offers robust APIs for custom integrations. This flexibility allows your IT team to create tailored solutions that meet specific business needs.
5. Evaluate Scalability for Future Growth
Selecting a CRM that can grow with your business is essential. As your organization expands, your CRM should accommodate increasing user numbers and evolving feature requirements.
Assess Upgrade Paths
Investigate the vendor’s upgrade options. Can you easily transition to more advanced plans without significant disruption? Look for a CRM that offers tiered pricing and features that align with your growth trajectory.
Performance Under Load
Consider how the CRM performs under increased usage. A reliable vendor should provide insights into system performance, ensuring that the platform can handle higher volumes of data and user activity without lag or downtime.
6. Request Demos and Start Free Trials
Before committing to a CRM, take advantage of demos and free trials to test the software in real-world scenarios. This hands-on experience is invaluable in assessing whether the CRM meets your business needs.
Schedule Vendor Demos
Request demos from multiple vendors to get a feel for their offerings. During the demo, pay attention to:
- Feature Demonstration: Ensure the CRM can handle your specific requirements.
- User Experience: Evaluate how intuitive and user-friendly the interface is.
Utilize Free Trials
Take advantage of free trials to explore the CRM’s functionalities. Encourage team members to use the trial period to identify any potential challenges or limitations.
7. Read Reviews and Case Studies
Finally, gather insights from existing users by reading reviews and case studies. This research can provide valuable perspectives on the CRM’s performance, user satisfaction, and potential pitfalls.
Utilize Review Platforms
Explore platforms like G2, Capterra, and Trustpilot to read user reviews. Pay attention to comments regarding:
- Customer Support: The quality and responsiveness of the vendor’s support team.
- Feature Satisfaction: How well the CRM’s features align with user expectations.
Case Studies
Look for case studies that highlight how similar businesses have successfully implemented the CRM. These real-life examples can shed light on the CRM’s effectiveness in achieving specific business goals and provide inspiration for your own implementation strategy.
Conclusion
Choosing the right CRM is a significant decision that can profoundly impact your business’s success. By following these seven steps—defining your goals, establishing a budget, considering ease of use, checking for integrations, evaluating scalability, requesting demos, and reading reviews—you will be well-equipped to select a CRM that not only meets your current needs but also supports your future growth. Remember, investing time in research and planning now can lead to substantial benefits down the line, enhancing customer relationships and driving revenue growth.
CRM vs. ERP: Understanding the Key Differences
Definitions
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) refers to software systems designed to help businesses manage their interactions with current and potential customers. CRMs centralize customer information, streamline processes, and enhance relationships, ultimately aiming to improve customer satisfaction and drive sales growth.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), on the other hand, encompasses a broader scope of business management. ERP systems integrate various business processes across departments—such as finance, HR, supply chain, and manufacturing—into a unified system. The goal of ERP is to facilitate the flow of information between all business functions and manage connections to external stakeholders.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | CRM (Customer-Facing) | ERP (Business Operations-Facing) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Managing customer interactions and relationships | Managing internal business processes and resources |
| Core Users | Sales teams, marketing professionals, customer service agents | Finance teams, HR, supply chain managers, and executives |
| Key Processes | Sales tracking, lead management, customer support, and marketing automation | Financial management, inventory control, order processing, and reporting |
| Main Goal | Enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty, increase sales and marketing effectiveness | Improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and provide real-time data for decision-making |
Detailed Comparison
Primary Focus
The primary focus of CRM systems is on customer interactions. They provide tools for managing customer data, tracking sales activities, and automating marketing tasks. This focus allows businesses to tailor their services and communications to individual customer needs, fostering stronger relationships and driving customer loyalty.
In contrast, ERP systems are designed to optimize internal business processes. They provide comprehensive tools that integrate various departments, ensuring that all parts of the organization work in harmony. This integration leads to improved efficiency and better resource management, which is critical for large and complex organizations.
Core Users
CRM systems are typically used by customer-facing roles, such as sales representatives, marketing teams, and customer support agents. These users rely on CRMs to access customer data, track interactions, and analyze customer behavior to inform their strategies.
ERP systems, on the other hand, are used by a broader range of employees across different departments. Finance teams utilize ERP for budgeting and forecasting, HR for managing employee data, and supply chain managers for inventory control. This wide-ranging user base highlights the ERP’s role as a backbone of business operations.
Key Processes
Key processes in CRM systems include sales tracking, lead management, customer support, and marketing automation. These processes are designed to enhance the customer experience and drive revenue growth by ensuring that sales and marketing efforts are well-coordinated and data-driven.
ERP systems encompass a wider array of processes, including financial management, inventory control, order processing, and reporting. By integrating these processes, ERP systems provide organizations with a holistic view of their operations, allowing for informed decision-making and improved operational efficiency.
Main Goal
The main goal of CRM systems is to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. By providing tools to manage and analyze customer interactions, CRMs help businesses deliver personalized experiences that lead to increased sales and improved customer retention.
Conversely, ERP systems aim to improve operational efficiency and reduce costs. By streamlining processes and providing real-time data across departments, ERPs enable organizations to make informed decisions that enhance productivity and profitability.
Conclusion: Do You Need a CRM, ERP, or Both?
Choosing between a CRM and an ERP system—or deciding to implement both—depends on your business needs. If your primary goal is to improve customer relationships and drive sales, a CRM system is essential. It provides the tools necessary to understand and engage with customers effectively.
However, if your focus is on enhancing operational efficiency and integrating various business functions, an ERP system is more suitable. ERP can help you manage internal processes seamlessly, ultimately supporting better resource allocation and decision-making.
Many businesses find that using both systems in tandem provides the most comprehensive solution. Integrating a CRM with an ERP system allows for a complete view of customer interactions alongside efficient management of business operations. This synergy can lead to improved customer experiences and enhanced operational effectiveness, driving overall business success.
Best Practices for Successful CRM Implementation
Getting Leadership Buy-In
Successful CRM implementation starts at the top. Gaining leadership buy-in is crucial for several reasons. First, it ensures that the necessary resources—both financial and human—are allocated for the project. Second, it fosters a culture of accountability and commitment throughout the organization.
To achieve this, present a clear business case that outlines the expected benefits of the CRM, such as improved customer relationships, enhanced sales productivity, and better data analytics. Use data and case studies from similar organizations to demonstrate potential ROI. Involve key stakeholders early in the process to gather input and address any concerns. This collaborative approach helps create champions for the CRM across various departments, making it easier to drive adoption later.
Planning Your Data Migration
Data migration is often one of the most challenging aspects of CRM implementation. Poorly managed data migration can lead to data loss, inaccuracies, and ultimately, a failed CRM initiative.
Begin by conducting a thorough audit of your existing data. Identify what data is valuable, what needs to be cleansed, and what can be discarded. Create a data mapping plan that specifies how existing data will be transferred to the new system. This plan should detail the format and structure of the data in the new CRM, ensuring it aligns with your business processes.
Consider running a pilot migration with a smaller dataset to identify potential issues before the full migration. This allows your team to troubleshoot and refine the process, ensuring a smoother transition when moving all data. It’s also essential to establish a rollback plan in case something goes wrong during the migration process.
Customizing the CRM to Your Process (Not the Other Way Around)
One of the biggest mistakes organizations make during CRM implementation is forcing their processes to fit the software rather than customizing the software to fit their processes. A CRM should enhance your business operations, not dictate them.
Start by clearly defining your existing sales and marketing processes. Document workflows, customer interactions, and data flows. Once you have a clear understanding of your processes, work with your CRM vendor to customize the system accordingly. This could involve setting up specific fields, automating workflows, or integrating with other tools that your team uses regularly.
Remember, customization should be done thoughtfully. Over-customization can lead to complexity, making the system harder to use. Aim for a balance where the CRM supports your processes without becoming overly complicated.
Effective User Training and Onboarding
User adoption is critical to the success of any CRM implementation. Without proper training and onboarding, even the best CRM system can fail to deliver its promised benefits.
Develop a comprehensive training program that caters to different user roles within your organization. Sales teams may need different training than marketing or customer service teams. Include a mix of training formats such as live workshops, recorded tutorials, and hands-on practice sessions.
Encourage a culture of ongoing learning by providing resources like FAQs, user manuals, and a dedicated support team. Consider implementing a buddy system where more experienced users assist newcomers, fostering a supportive environment.
Additionally, gather feedback from users during and after the training process. This will help you identify areas that may require additional focus and allow you to adjust your training approach as needed.
Setting Clear KPIs to Measure Success
Establishing clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential for evaluating the success of your CRM implementation. These metrics will help you measure the impact of the CRM on your business processes and customer relationships.
Start by defining what success looks like for your organization. Common KPIs include:
- User Adoption Rate: Measure how many employees actively use the CRM compared to those who should be using it.
- Sales Productivity: Track metrics such as the number of leads generated, conversion rates, and average deal size.
- Customer Satisfaction: Use surveys or Net Promoter Scores (NPS) to gauge customer satisfaction levels pre- and post-implementation.
- Data Quality: Monitor the accuracy and completeness of data entered into the CRM to ensure high-quality information for decision-making.
Regularly review these KPIs with your team. This will not only help you identify areas for improvement but also reinforce the importance of the CRM in achieving business objectives. Adjust your strategies based on the insights gathered from these metrics to continuously optimize your CRM usage.
Conclusion
Implementing a CRM system is a significant investment that can yield substantial returns when done correctly. By focusing on leadership buy-in, careful data migration, thoughtful customization, effective user training, and clear KPIs, you can set your organization up for success. Remember, the goal of a CRM is to enhance customer relationships and streamline operations. With the right approach, your CRM can become a vital tool in achieving these objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. CRM 是什麼?
CRM(客户关系管理)软件是一种帮助企业管理与客户的关系和互动的工具。它可以收集和整理客户信息,提供对客户需求和偏好的全面了解,从而帮助销售团队和市场营销人员制定更具针对性的策略,提升客户满意度和忠诚度。
2. CRM 的工作原理是什么?
CRM 软件通过自动化和数据分析,改变了销售团队管理客户关系的方式。它实时跟踪和分析与客户的互动,确保销售团队能够获取最新的客户信息和销售管道视图。这种全面的客户记录使销售人员能够提供个性化的服务,从而提升客户体验。
3. 实施 CRM 需要多长时间?
实施 CRM 的时间因软件的复杂性和企业的需求而异。一般来说,简单的 CRM 解决方案可以在几天内完成设置,而更复杂的系统可能需要几周或几个月的时间。确保选择一个用户友好的平台,可以加快实施过程。
4. CRM 的成本是多少?
CRM 的成本取决于所选择的供应商和功能。一些基本的 CRM 解决方案可能每用户每月只需 15 美元,而功能更强大的系统(如 Salesforce)可能高达每用户每月 165 美元。许多 CRM 还提供免费试用,帮助企业在购买前评估其适用性。
5. CRM 可以用于 B2C 吗?
是的,CRM 不仅适用于 B2B(企业对企业)环境,也非常适合 B2C(企业对消费者)业务。通过 CRM,企业可以更好地了解消费者行为,提供个性化的营销和客户服务,从而增强客户体验和忠诚度。
6. CRM 软件是否支持移动设备?
许多现代 CRM 软件提供移动应用,使销售团队可以在外出时仍能访问客户数据和管理任务。这对于需要在不同地点与客户互动的外勤销售人员尤为重要,确保他们在路上也能保持高效。
7. CRM 能与其他工具集成吗?
大多数 CRM 软件都设计为与其他业务工具(如电子邮件、社交媒体和客户体验(CX)工具)集成。这种集成能够提供全面的客户视图,帮助企业更好地理解客户需求和行为,提高销售和市场营销的效率。
8. 如何选择合适的 CRM 软件?
选择合适的 CRM 软件需要考虑多种因素,包括用户友好性、定制能力、集成选项和总拥有成本。企业应该评估自身的需求,寻找能够快速提供价值的解决方案,并确保其可以与现有的技术堆栈无缝对接。
Conclusion: Taking the Next Step in Customer Management
The Foundation for Modern Business Growth
In today’s competitive landscape, a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system has become a foundational tool for driving business growth and enhancing customer loyalty. By centralizing customer data, streamlining processes, and providing actionable insights, CRMs empower businesses to foster deeper relationships with their customers. This capability is crucial not only for sales teams but also for marketing professionals and business owners who strive to deliver exceptional customer experiences.
Aligning CRM with Business Needs
Choosing the right CRM system is vital for maximizing its benefits. Businesses must evaluate their unique needs, whether that involves prioritizing user-friendliness, integration capabilities, or advanced analytics features. By aligning the CRM’s functionalities with specific business goals and workflows, organizations can ensure that they are not only adopting a tool but are also investing in a solution that will enhance productivity and drive results.
Take Action Today
As you consider the impact of a CRM on your organization, take the next step by thoroughly evaluating your current sales and marketing workflows. Identify pain points, opportunities for improvement, and the specific features that would best support your objectives. Whether you are a small startup or a large enterprise, investing time in this evaluation process will empower you to make informed decisions that can transform your customer management strategy.
Begin your journey towards effective customer management today. Explore available CRM options, engage with your teams, and envision how a tailored CRM solution can elevate your business to new heights. Your path to improved customer relationships and increased growth starts with a single step—take it now.
Important Disclaimer
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information and reviews in this guide are for educational purposes, based on publicly available data. We are not affiliated with any software providers mentioned. Features and pricing change frequently. Always conduct your own due diligence and request a demo before committing to a CRM platform.
![Screenshot of 8 款最佳销售 CRM 软件 + 功能对比 [2025] - Salesflare Blog](https://www.cify.info/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/blog-salesflare-com-screenshot-6398.jpg)