Best CRM Software: The Top 7 Platforms Reviewed
Introduction: Why Your Business Needs More Than a Spreadsheet
In the fast-paced world of business, effective customer relationship management is crucial for success. However, many organizations still rely on outdated methods, such as spreadsheets and scattered notes, to manage their customer data. This approach often leads to chaos, miscommunication, and lost opportunities. Business owners and managers may find themselves sifting through countless rows of data, struggling to track interactions, or worse, missing critical insights that could drive growth.
Spreadsheets may seem like a convenient solution for tracking customer information, but they fall short in several key areas. They lack real-time collaboration capabilities, making it difficult for teams to work together efficiently. Moreover, manual data entry increases the risk of errors, which can lead to misinformation and poor customer experiences. As your business grows, the limitations of spreadsheets become even more pronounced, leaving you and your team overwhelmed and unable to respond effectively to customer needs.
This is where Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems come into play. A CRM is a technology platform designed to help businesses manage their interactions with customers and potential customers. It serves as a central hub for storing customer information, tracking interactions, and analyzing data to enhance customer relationships. The core purpose of a CRM is to streamline processes, improve communication, and ultimately drive sales and customer satisfaction.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the multifaceted world of CRM systems. We will begin by defining what a CRM is and examining its core features, such as contact management, sales tracking, and reporting capabilities. Next, we will delve into the key benefits of implementing a CRM, including improved customer insights, enhanced team collaboration, and increased operational efficiency.
Additionally, we will provide a review of some of the top CRM platforms on the market, highlighting their strengths and unique features to help you make an informed decision. Finally, we will offer a step-by-step guide to choosing the right CRM for your business, ensuring that you find a solution that aligns with your specific needs and goals.
By the end of this guide, you will have a clear understanding of how a CRM can transform your business and why it is essential to move beyond spreadsheets for managing customer relationships. Let’s embark on this journey to discover the power of CRM and how it can drive your business forward.
The Top 7 CRM Platforms of 2025
What is Call Center CRM? Top 5 Call Center CRM Software
The article “What is Call Center CRM? Top 5 Call Center CRM Software” on Creatio provides an insightful overview of call center CRM solutions, highlighting their essential features tailored for B2B and B2C organizations. It emphasizes Zoho Desk as a key player, particularly suitable for businesses with straightforward customer service needs, showcasing how integrated CRM systems can enhance customer interactions and streamline support processes.
- Website: creatio.com
- Company Age: Approx. 11 years (domain registered in 2014)
What is a CRM System? A Deep Dive
Understanding CRM Systems
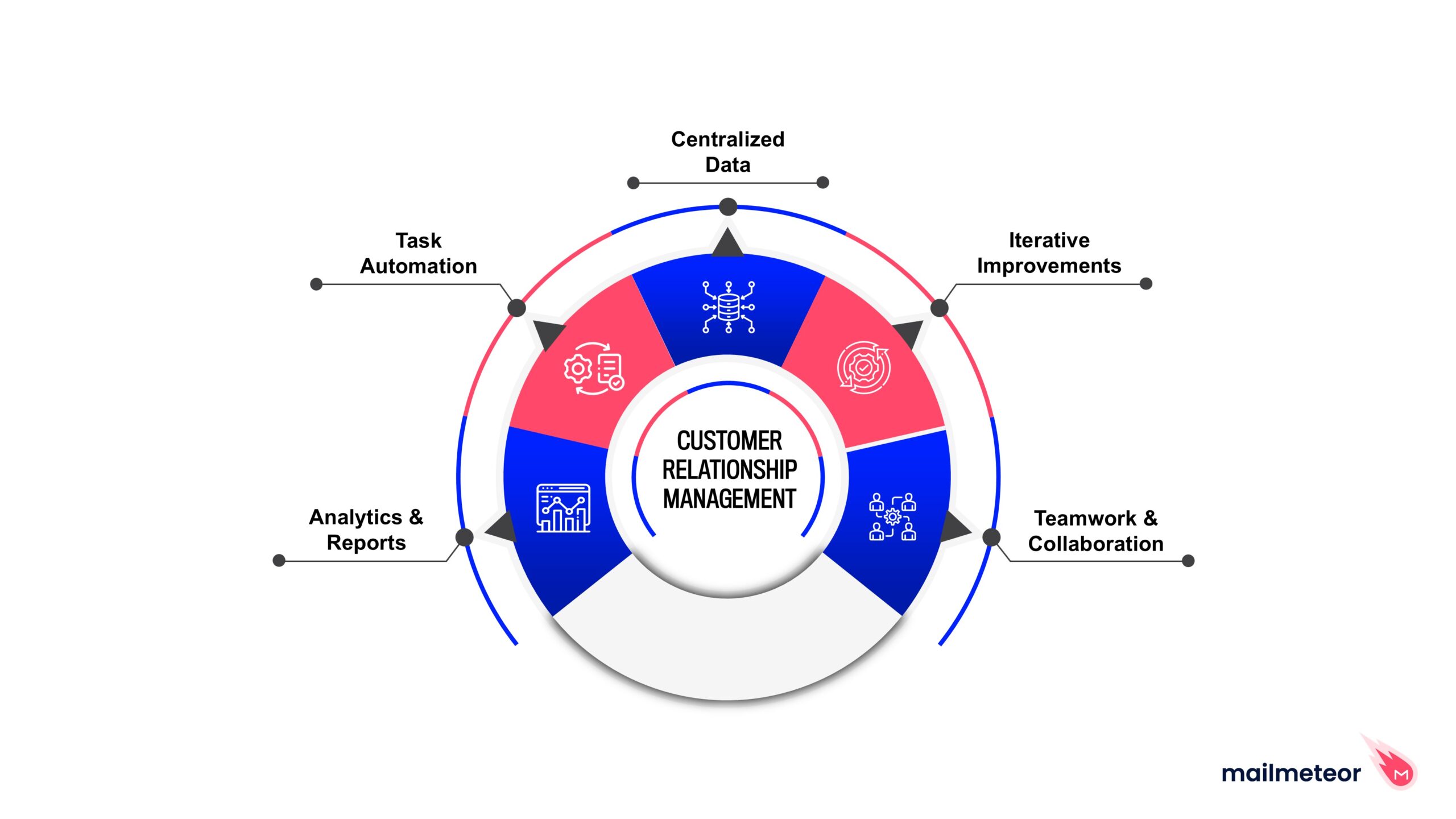
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are software solutions designed to help organizations manage their interactions with current and potential customers. At their core, CRM systems centralize customer data, streamline processes, and enhance communication across various departments. By providing a 360-degree view of customer interactions, CRM systems empower businesses to improve customer relationships, increase sales, and drive overall growth.
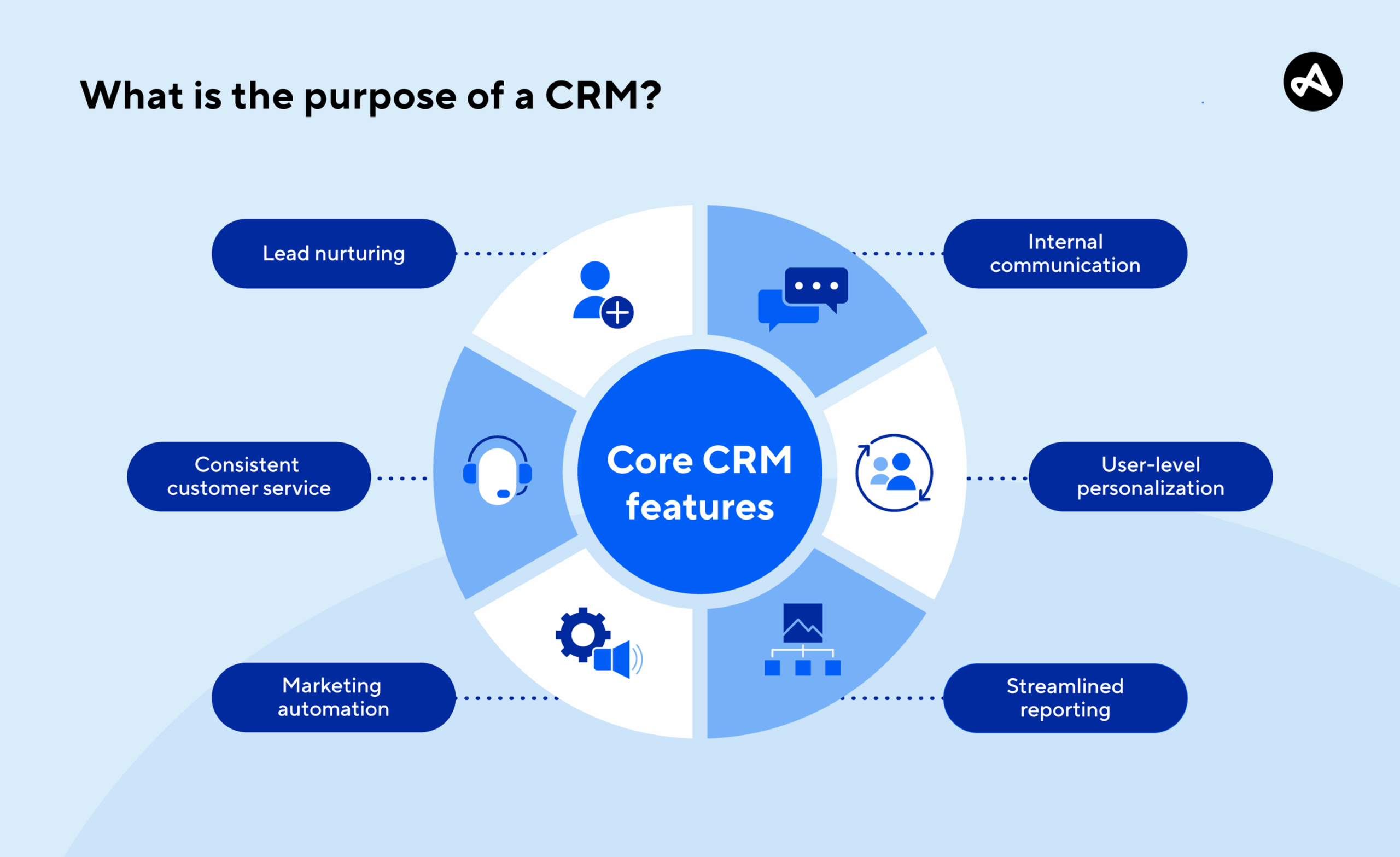
The Goals of a CRM System
The primary goal of a CRM system is to foster stronger relationships between a business and its customers. Here are several key objectives that CRM systems aim to achieve:
-
Centralized Customer Information: CRM systems aggregate customer data from various sources, including email, social media, and direct interactions. This centralization allows businesses to access and analyze customer information easily, ensuring that all team members have the most up-to-date insights.
-
Improved Customer Service: By providing customer service representatives with a complete view of customer history and preferences, CRM systems enable faster and more personalized responses to inquiries. This leads to enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty.
-
Increased Sales Efficiency: CRM systems streamline the sales process by automating repetitive tasks, tracking leads, and managing customer interactions. Sales teams can prioritize prospects based on their engagement level and track the progress of deals in real-time, ultimately improving conversion rates.
-
Enhanced Marketing Efforts: CRM systems help marketing teams segment customers based on behavior and preferences, allowing for targeted campaigns that resonate more effectively with specific audiences. By analyzing customer interactions, businesses can refine their marketing strategies and improve return on investment (ROI).
-
Data-Driven Decision Making: With robust analytics and reporting features, CRM systems provide valuable insights into customer behavior and sales performance. This data empowers businesses to make informed decisions, identify trends, and develop strategies for growth.
Who Uses a CRM?
CRM systems are versatile tools utilized across various departments within an organization, each benefiting from its unique functionalities:
-
Sales Teams: Sales professionals leverage CRM systems to track leads, manage customer relationships, and forecast sales. With access to a comprehensive view of customer interactions, sales teams can engage prospects more effectively and close deals faster.
-
Marketing Departments: Marketers use CRM systems to analyze customer data, segment audiences, and automate campaigns. By understanding customer preferences and behaviors, marketing teams can design personalized content and promotions that drive engagement.
-
Customer Service Representatives: Customer service teams rely on CRM systems to access customer histories, resolve issues efficiently, and provide tailored support. This not only enhances the customer experience but also helps build long-term loyalty.
-
Management and Executives: Leaders use CRM analytics to track performance metrics, assess the effectiveness of sales and marketing strategies, and make strategic decisions. By evaluating data trends, executives can identify opportunities for growth and improvement.
Why a Spreadsheet Isn’t Enough
While many businesses initially manage customer data using spreadsheets, this approach has significant limitations:
-
Lack of Centralization: Spreadsheets often lead to fragmented data across multiple files, making it difficult to gain a holistic view of customer interactions. CRM systems centralize this data, ensuring that all team members have access to consistent and up-to-date information.
-
Limited Collaboration: Spreadsheets are typically static and do not facilitate real-time collaboration among team members. CRM systems, on the other hand, enable multiple users to access and update customer information simultaneously, fostering collaboration and improving communication.
-
Inefficient Automation: Manual data entry and updates in spreadsheets are time-consuming and prone to errors. CRM systems automate many processes, such as lead tracking and reporting, saving time and reducing the risk of mistakes.
-
Poor Scalability: As businesses grow, managing customer relationships through spreadsheets becomes increasingly complex. CRM systems are designed to scale with the organization, accommodating growing data volumes and user numbers without compromising performance.
-
Limited Analytics: Spreadsheets offer basic data analysis capabilities, but they lack the advanced analytics and reporting features found in CRM systems. CRM tools provide insights into customer behavior, sales trends, and marketing effectiveness, enabling data-driven decision-making.
Benefits to Different Departments
-
Sales: CRM systems enhance sales productivity by automating lead management, providing actionable insights, and improving communication. Sales teams can track interactions, set reminders for follow-ups, and analyze performance metrics to refine their strategies.
-
Marketing: Marketing departments benefit from CRM systems through improved targeting and personalization. By analyzing customer data, marketers can develop campaigns that resonate with their audience, leading to higher engagement rates and improved ROI.
-
Customer Service: CRM systems empower customer service representatives with the tools needed to provide exceptional support. With access to customer histories and preferences, support teams can resolve issues quickly and create a positive customer experience.
-
Management: Executives gain valuable insights from CRM analytics, enabling them to assess the effectiveness of strategies, allocate resources effectively, and identify growth opportunities. This data-driven approach supports informed decision-making at all levels of the organization.
Conclusion
In summary, CRM systems are essential tools for businesses seeking to enhance customer relationships, streamline processes, and drive growth. By centralizing customer data, improving collaboration, and enabling data-driven decision-making, CRM systems provide significant advantages over traditional methods like spreadsheets. As organizations continue to prioritize customer experience, investing in a robust CRM system is a strategic move that can yield long-term benefits across all departments.
Core Features: What to Expect from a Modern CRM
Contact Management
What It Is
Contact Management is the foundational feature of any modern CRM system. It allows businesses to store, organize, and manage information about customers, leads, and prospects in a centralized database. This information typically includes names, contact details, company affiliations, communication history, and any relevant notes.
How It Works
Modern CRM systems provide intuitive interfaces for entering and retrieving contact information. They often include features such as contact segmentation, which allows users to categorize contacts based on specific criteria such as demographics, behavior, or sales stage. Advanced systems may also integrate with social media platforms to automatically pull in contact details and updates.
Direct Business Benefit
The primary benefit of effective contact management is the enhanced ability to nurture relationships. By having all relevant information at their fingertips, sales and marketing teams can tailor their communications and improve engagement. This leads to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty, ultimately driving revenue growth.
Lead and Opportunity Management
What It Is
Lead and Opportunity Management is a feature that helps organizations track potential customers (leads) and their progress through the sales funnel (opportunities). This functionality allows businesses to identify which leads are most likely to convert into paying customers.
How It Works
Leads can be captured through various channels such as web forms, social media, and email campaigns. Once captured, they are entered into the CRM system where they can be scored based on predefined criteria (e.g., demographic information, engagement level). As leads progress, they can be converted into opportunities, allowing sales teams to track their interactions, set follow-up tasks, and record outcomes.
Direct Business Benefit
Effective lead and opportunity management streamlines the sales process, enabling teams to prioritize high-quality leads and focus their efforts on the most promising opportunities. This results in shorter sales cycles and increased conversion rates, leading to higher revenue generation.
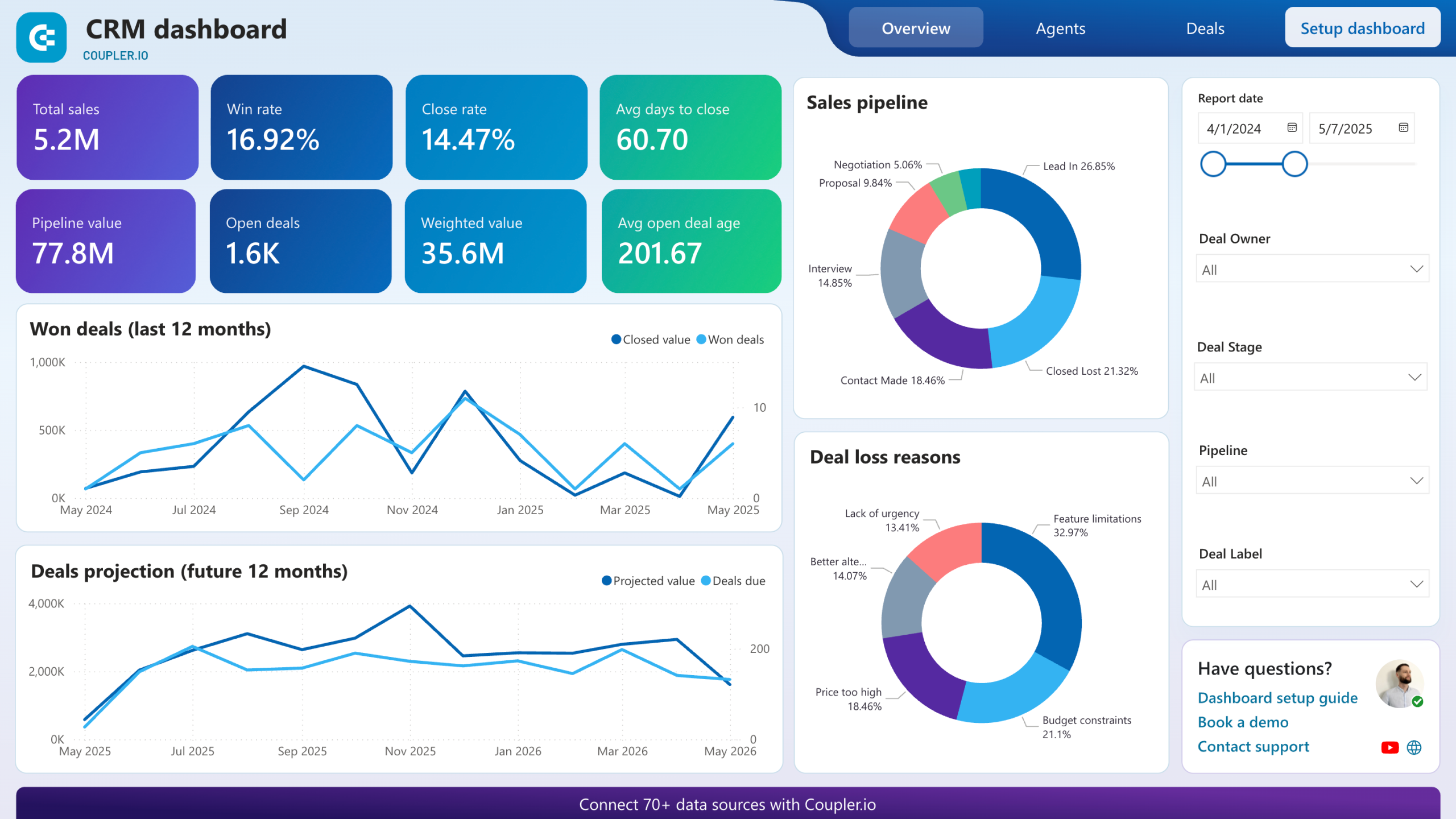
Sales Pipeline Visualization
What It Is
Sales Pipeline Visualization is a graphical representation of the sales process, showcasing the various stages that opportunities go through before closing. This feature allows users to see the overall health of their sales pipeline at a glance.
How It Works
Modern CRMs provide visual dashboards that display opportunities in different stages, such as “New Lead,” “Qualified,” “Proposal Sent,” and “Closed Won.” Users can often drag and drop opportunities between stages, making it easy to update their status. Additionally, these dashboards can provide insights into the average time spent in each stage and the expected revenue from opportunities.
Direct Business Benefit
By visualizing the sales pipeline, businesses can quickly identify bottlenecks and areas needing attention. This enables sales managers to allocate resources effectively, forecast revenue more accurately, and ultimately increase the efficiency of the sales team.
Task and Activity Tracking
What It Is
Task and Activity Tracking is a feature that enables users to monitor and manage tasks associated with contacts and opportunities. This includes scheduling follow-up calls, sending emails, and recording meetings.
How It Works
Modern CRMs allow users to create, assign, and prioritize tasks within the system. Users can set deadlines and reminders, ensuring that important follow-ups are not overlooked. Additionally, activity logs track all interactions with contacts, providing a comprehensive view of engagement history.
Direct Business Benefit
By effectively tracking tasks and activities, organizations can ensure timely follow-ups and maintain consistent communication with leads and customers. This leads to improved customer relationships and higher chances of closing deals, ultimately enhancing overall sales performance.
Marketing Automation
What It Is
Marketing Automation is a feature that streamlines marketing tasks and workflows, enabling businesses to create, execute, and analyze marketing campaigns efficiently. This includes email marketing, social media posting, and lead nurturing.
How It Works
Modern CRMs often integrate marketing automation tools that allow users to segment their audience and create targeted campaigns. Users can set up automated workflows that trigger actions based on user behavior (e.g., sending a follow-up email after a webinar). Performance analytics provide insights into campaign effectiveness.
Direct Business Benefit
With marketing automation, businesses can engage leads at the right time with personalized content, significantly improving conversion rates. This not only saves time but also maximizes marketing ROI by ensuring that resources are focused on high-impact initiatives.
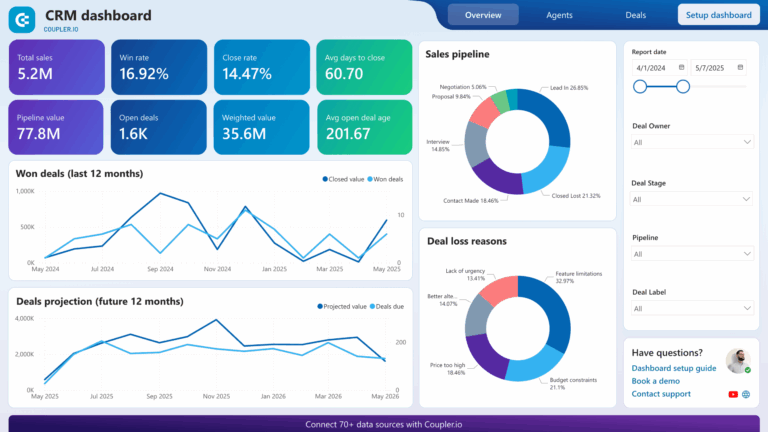
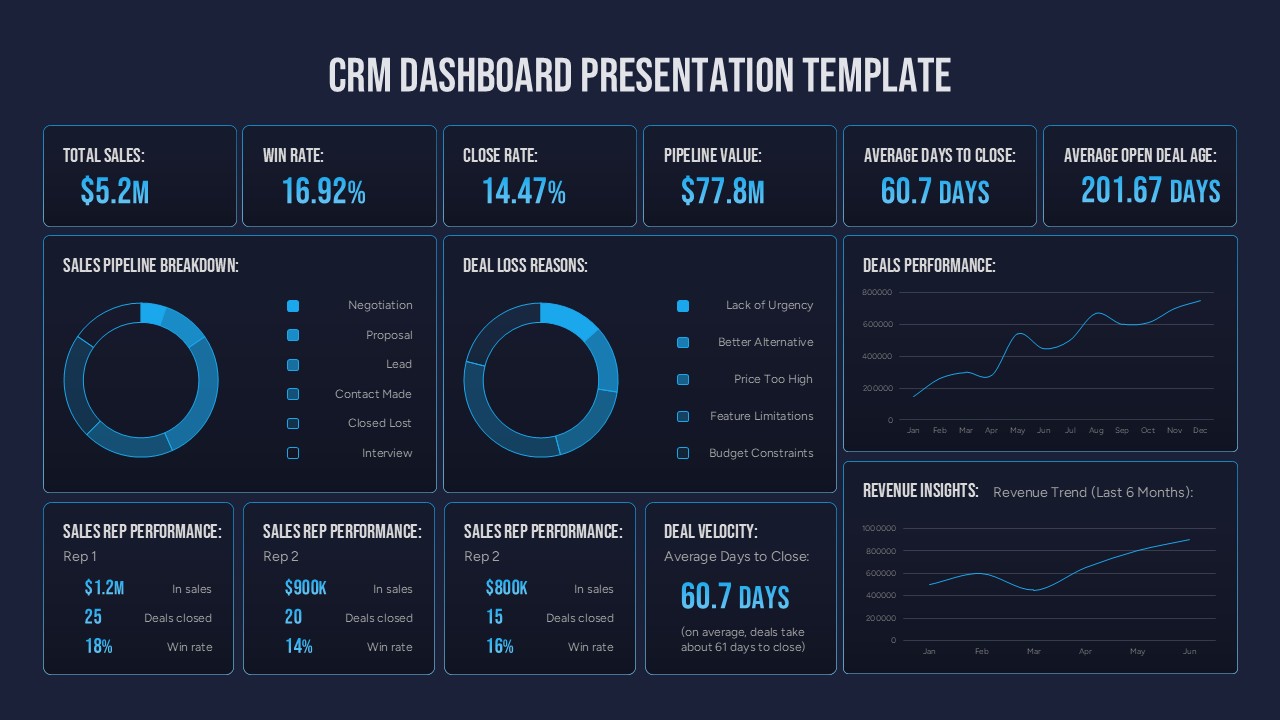
Reporting and Analytics
What It Is
Reporting and Analytics features in a CRM provide businesses with insights into sales performance, customer behavior, and overall business health. These tools enable data-driven decision-making.
How It Works
Modern CRMs come equipped with customizable reporting tools that allow users to generate reports based on various metrics, such as sales figures, lead conversion rates, and campaign performance. Dashboards can visualize this data, offering real-time insights into key performance indicators (KPIs).
Direct Business Benefit
By leveraging reporting and analytics, organizations can identify trends, measure the effectiveness of strategies, and make informed decisions. This leads to better resource allocation, improved forecasting, and ultimately enhanced business performance.
Integrations
What It Is
Integrations refer to the ability of a CRM to connect with other business tools and platforms, such as email services, accounting software, and customer support systems. This feature enables seamless data sharing and workflow automation across the organization.
How It Works
Modern CRMs often provide APIs and pre-built connectors to facilitate integrations with popular software applications. Users can synchronize data between systems, ensuring that information is consistent and up-to-date across platforms. For example, integration with email marketing tools allows for automatic updates to contact lists based on CRM data.
Direct Business Benefit
Integrations enhance operational efficiency by reducing manual data entry and ensuring that teams have access to accurate information. This leads to improved collaboration, streamlined processes, and a more cohesive customer experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a modern CRM system is an essential tool for business owners, sales managers, and marketing professionals looking to enhance customer relationships and drive growth. By understanding and leveraging core features such as Contact Management, Lead and Opportunity Management, Sales Pipeline Visualization, Task and Activity Tracking, Marketing Automation, Reporting and Analytics, and Integrations, organizations can optimize their processes, increase efficiency, and ultimately achieve better business outcomes. As you consider implementing a CRM solution, prioritize these features to ensure that you choose a system that meets your needs and supports your business goals.
The 3 Types of CRM Systems Explained
Comparison Table of CRM Types
| CRM Type | Primary Goal | Key Features | Best For (Department) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operational CRM | Streamline customer interactions | Contact management, sales automation, marketing automation, service automation | Sales, Marketing, Customer Service |
| Analytical CRM | Gain insights from customer data | Data mining, reporting, predictive analytics, customer segmentation | Marketing, Analytics |
| Collaborative CRM | Enhance communication and collaboration | Shared databases, integrated communication tools, project management features | All departments |
Operational CRM
Operational CRM systems are designed primarily to streamline and automate customer interactions across various channels, improving the efficiency of sales, marketing, and customer service processes. These systems focus on managing the day-to-day operations of customer engagement, ensuring that businesses can respond promptly and effectively to customer inquiries and needs.
Key features of operational CRM include contact management, sales force automation, marketing automation, and service automation. For instance, a sales team using operational CRM can automate lead tracking, follow-ups, and pipeline management, allowing them to focus more on closing deals rather than managing administrative tasks. Marketing automation tools integrated within the system can help in segmenting customers, designing targeted campaigns, and tracking their effectiveness.
Real-world examples include Salesforce, which offers a robust operational CRM solution that enables companies to manage customer relationships through a unified platform. Additionally, HubSpot provides marketing automation features that help businesses attract, engage, and delight customers throughout their journey. Companies like Zocdoc utilize operational CRM to manage appointments and customer interactions seamlessly, ensuring a smooth customer experience.
Analytical CRM
Analytical CRM systems focus on the analysis of customer data to provide insights that help businesses make informed decisions. These systems are equipped with data mining, reporting, predictive analytics, and customer segmentation capabilities, allowing organizations to understand customer behavior and preferences better.
By leveraging analytical CRM, businesses can analyze trends, identify customer segments, and predict future customer behaviors, which aids in crafting personalized marketing strategies. For example, a retail company could use analytical CRM to analyze purchasing patterns, enabling them to tailor promotions and inventory management to meet customer demands effectively.
A real-world example is SAS Customer Intelligence, which provides advanced analytics tools for businesses to derive actionable insights from customer data. Another example is Adobe Analytics, which helps companies track and analyze customer interactions across various digital platforms. Organizations like Netflix use analytical CRM to analyze viewer preferences and behavior, allowing them to create personalized recommendations that enhance user engagement and satisfaction.
Collaborative CRM
Collaborative CRM systems aim to improve communication and collaboration among different departments within an organization, as well as between the business and its customers. These systems facilitate sharing of customer information across departments, enabling a holistic view of customer interactions and enhancing customer service.
Key features of collaborative CRM include shared databases, integrated communication tools, and project management functionalities. By using collaborative CRM, sales, marketing, and customer service teams can work together more effectively, sharing insights and strategies to improve customer experiences. For instance, a customer service representative can access sales data to understand a customer’s history and preferences, which allows for more personalized service.
An example of a collaborative CRM is Zoho CRM, which offers features that promote team collaboration through shared customer data and integrated communication tools. Microsoft Dynamics 365 also provides collaborative features that enable different departments to work together seamlessly. Companies like Slack exemplify collaborative CRM by allowing teams to communicate and share customer information in real-time, enhancing responsiveness and customer satisfaction.
In conclusion, understanding the three types of CRM systems—Operational, Analytical, and Collaborative—is crucial for business owners, sales managers, and marketing professionals. Each type serves a distinct purpose and can significantly enhance different aspects of customer relationship management. Choosing the right CRM system depends on the specific needs of your organization and how you aim to interact with and understand your customers.
Key Business Benefits of Using a CRM
1. Centralized Customer Data
A CRM system provides a centralized repository for all customer-related data, enabling businesses to store, manage, and access vital information in one place. This consolidation ensures that all team members, from sales and marketing to customer support, have up-to-date insights into customer interactions, preferences, and history. As a result, organizations can deliver personalized experiences tailored to individual customer needs. Centralized data not only improves communication across departments but also enhances collaboration, allowing teams to work more efficiently and respond to customer inquiries swiftly. This holistic view of customer data ultimately leads to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
2. Improved Sales Productivity
With the implementation of a CRM, businesses can significantly enhance their sales productivity. CRMs automate routine tasks, such as data entry and follow-up reminders, freeing up sales teams to focus on building relationships and closing deals. The system streamlines the sales process by providing tools for tracking leads, managing pipelines, and forecasting sales performance. Additionally, CRMs often include analytics features that help identify high-performing strategies and areas needing improvement. By leveraging these insights, sales professionals can prioritize their efforts effectively, leading to increased conversion rates and higher revenue.
3. Enhanced Customer Retention
Retaining existing customers is often more cost-effective than acquiring new ones, and a CRM plays a critical role in enhancing customer retention rates. By analyzing customer interactions and feedback, businesses can identify trends and patterns that inform their customer service strategies. CRMs enable proactive engagement through automated reminders for follow-ups, personalized communications, and tailored offers. By understanding customer needs and addressing issues promptly, organizations can foster stronger relationships and ensure a positive customer experience. This focus on retention not only increases customer loyalty but also encourages repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
4. Data-Driven Decision Making
In today’s data-centric world, informed decision-making is crucial for business success. CRMs provide valuable insights through robust analytics and reporting features, empowering managers to make strategic decisions based on real-time data. By tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales trends, customer behavior, and campaign effectiveness, businesses can evaluate the success of their initiatives and adjust strategies accordingly. This data-driven approach minimizes guesswork and enhances the ability to respond to market changes swiftly. Organizations that leverage CRM analytics can capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks more effectively, leading to sustained growth and competitive advantage.
5. Scalable Growth
As businesses evolve, their systems must be able to scale accordingly. A CRM is designed to grow with your organization, accommodating increasing volumes of data, users, and functionalities without compromising performance. This scalability allows businesses to expand their operations, whether through entering new markets, launching new products, or increasing their customer base. CRMs offer various features and integrations that can be customized to meet the changing needs of the business, ensuring that as your organization grows, your customer management capabilities keep pace. This flexibility not only supports business expansion but also enhances overall operational efficiency, providing a solid foundation for future growth.
Conclusion
Implementing a CRM system offers numerous benefits that can significantly enhance a business’s operations and customer interactions. From centralized data management and improved sales productivity to enhanced customer retention and data-driven decision-making, a CRM serves as an invaluable tool for driving growth and achieving long-term success. By embracing the advantages of a CRM, organizations position themselves to thrive in a competitive marketplace, ensuring they meet customer expectations while optimizing their internal processes.
How to Choose the Right CRM: A 7-Step Buyer’s Guide
1. Define Your Business Goals and Needs
Before diving into the world of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of your business goals and needs. A CRM should not only support your current operations but also align with your long-term objectives.
Identify Key Objectives
- Sales Management: Are you looking to improve sales tracking and forecasting?
- Customer Service: Do you need to enhance customer support and interaction tracking?
- Marketing Automation: Is your focus on automating marketing campaigns and tracking leads?
Understand Your Target Users
Identify who will be using the CRM. Different departments may have different requirements. For instance:
- Sales Teams: May require tools for lead management, pipeline tracking, and reporting.
- Marketing Teams: Might need functionalities for campaign management and analytics.
- Customer Support Teams: Could benefit from ticketing systems and customer interaction history.
2. Establish Your Budget
With a clear understanding of your needs, the next step is to establish a budget. CRM systems can vary significantly in price, and it’s essential to determine what you can afford without compromising on essential features.
Cost Considerations
- Subscription vs. One-Time Purchase: Most modern CRMs operate on a subscription model, which can spread costs over time. However, some systems may offer a one-time purchase option.
- Hidden Costs: Be aware of potential hidden costs, such as implementation fees, training costs, and costs for additional users or features.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Consider how the CRM will impact your business’s bottom line. A CRM that enhances efficiency and customer satisfaction can yield significant ROI.
3. Consider Ease of Use and User Adoption
A CRM system is only as good as its adoption by your team. Therefore, ease of use is a critical factor in your selection process.
User Interface and Experience
- Intuitive Design: Look for a CRM with a user-friendly interface that minimizes the learning curve.
- Training Resources: Check if the vendor provides sufficient training materials, tutorials, and support.
User Adoption Strategies
- Involve Your Team: Include team members in the selection process to ensure the system meets their needs and preferences.
- Feedback Mechanism: Establish a way to gather user feedback during the trial phase to address any concerns before full implementation.
4. Check for Essential Integrations
To maximize the effectiveness of your CRM, it should seamlessly integrate with your existing tools and platforms.
Key Integrations to Consider
- Email: Ensure the CRM can integrate with your email platform (e.g., Outlook, Gmail) for streamlined communication.
- Marketing Tools: Check for compatibility with marketing automation tools, such as Mailchimp or HubSpot.
- Accounting Software: Integration with financial tools like QuickBooks can help maintain accurate financial records.
API and Custom Integrations
If your business relies on specific applications, ensure the CRM has robust API capabilities for custom integrations. This flexibility can significantly enhance operational efficiency.
5. Evaluate Scalability for Future Growth
As your business grows, your CRM needs may evolve. It’s crucial to choose a system that can scale with your organization.
Assess Scalability Features
- User Limits: Check if there are limits on the number of users or contacts you can manage.
- Advanced Features: Consider whether the CRM offers advanced features or modules that can be added as your needs grow.
Future-Proofing
- Vendor Longevity: Research the vendor’s history and stability to ensure they are likely to remain in business and continue to support their software.
- Regular Updates: A good CRM should receive regular updates and improvements, which can introduce new features to meet changing market demands.
6. Request Demos and Start Free Trials
Once you’ve narrowed down your options, it’s time to see the systems in action. Most CRM vendors offer demos or free trials.
Importance of Demos
- Live Interaction: A demo allows you to interact with the system and ask questions in real time.
- Feature Exploration: You can see if the features align with your business needs and how intuitive the system is for your team.
Utilizing Free Trials
- Hands-On Experience: Use free trials to test the CRM in your daily operations.
- Evaluate Performance: Monitor how well the CRM integrates with your existing systems and whether it enhances productivity.
7. Read Reviews and Case Studies
Finally, leverage existing user experiences to make an informed decision. Customer reviews and case studies can provide valuable insights into the CRM’s performance and reliability.
Where to Find Reviews
- Third-Party Review Sites: Websites like G2, Capterra, and Gartner provide user ratings and detailed reviews.
- Vendor Websites: Look for testimonials and case studies on the CRM vendor’s site.
Analyzing Case Studies
- Similar Industries: Focus on case studies from companies in your industry to understand how the CRM has benefited similar organizations.
- Quantifiable Results: Seek out case studies that provide metrics showing improvements in sales, customer satisfaction, or operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Choosing the right CRM is a significant decision that can influence your organization’s success. By following these seven steps—defining your goals, establishing a budget, considering ease of use, checking integrations, evaluating scalability, requesting demos, and reading reviews—you will be well-equipped to make an informed choice that aligns with your business needs. Take your time in this process; a well-chosen CRM can become an invaluable asset in your business strategy.
CRM vs. ERP: Understanding the Key Differences
Definitions of CRM and ERP
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) refers to systems and strategies that businesses use to manage interactions with current and potential customers. CRM systems help organizations streamline processes, build customer relationships, increase sales, improve customer service, and enhance profitability. The primary focus is on managing customer data, tracking interactions, and facilitating communication.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), on the other hand, is a type of software that organizations use to manage and integrate the important parts of their businesses. An ERP software system can integrate planning, purchasing inventory, sales, marketing, finance, human resources, and more. The primary goal of ERP is to streamline and automate business processes, provide real-time data, and improve overall efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | CRM (Customer-Facing) | ERP (Business Operations-Facing) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Enhancing customer relationships and experiences | Streamlining business operations and resource management |
| Core Users | Sales teams, marketing departments, customer service | Finance, HR, supply chain, manufacturing, and operations |
| Key Processes | Lead management, sales forecasting, customer support | Inventory management, order processing, financial reporting |
| Main Goal | Increase customer satisfaction and drive sales growth | Improve operational efficiency and reduce costs |
Detailed Comparison
Primary Focus
The primary focus of a CRM system is to improve customer interactions and relationships. This involves gathering customer information, tracking communications, and analyzing data to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. CRM systems are designed to provide a comprehensive view of customer interactions across various channels, allowing businesses to tailor their services and marketing efforts effectively.
In contrast, ERP systems concentrate on optimizing business processes and resource management. They provide a centralized platform for managing various functions across an organization, such as finance, HR, manufacturing, and supply chain management. The goal is to ensure that all parts of the business are working efficiently and cohesively, ultimately leading to improved productivity and cost savings.
Core Users
CRM systems are primarily used by customer-facing teams, including sales representatives, marketing professionals, and customer service agents. These users rely on CRM tools to access customer data, manage leads, track communications, and analyze customer behavior. The insights gained from CRM systems help these teams devise strategies to enhance customer engagement and drive sales.
On the other hand, ERP systems are utilized by internal departments such as finance, HR, operations, and supply chain management. These users depend on ERP tools for tasks like financial reporting, payroll processing, inventory management, and production planning. The integrated nature of ERP systems allows these departments to collaborate more effectively and make data-driven decisions.
Key Processes
Key processes in CRM systems typically include lead management, sales pipeline tracking, customer segmentation, marketing automation, and customer support management. These processes are geared towards nurturing customer relationships and maximizing sales opportunities.
In ERP systems, key processes encompass inventory management, order processing, financial management, supply chain coordination, and human resources management. These processes are designed to streamline operations, reduce redundancies, and ensure that resources are allocated efficiently.
Main Goal
The main goal of CRM systems is to increase customer satisfaction and drive sales growth. By providing insights into customer behavior and preferences, CRM systems help businesses create personalized experiences that foster loyalty and repeat business.
Conversely, ERP systems aim to improve operational efficiency and reduce costs. By integrating various business functions and providing real-time data, ERP systems enable organizations to optimize their operations, minimize waste, and enhance overall productivity.
Do You Need CRM, ERP, or Both?
Deciding whether your business needs a CRM system, an ERP system, or both depends on your specific operational needs and goals. If your primary focus is on enhancing customer relationships, improving sales processes, and delivering exceptional customer service, a CRM system may be sufficient.
However, if your organization requires comprehensive management of internal operations, including finance, supply chain, and human resources, an ERP system would be essential. For many businesses, a combination of both systems is ideal. Integrating CRM and ERP allows for a seamless flow of information across departments, enabling a holistic approach to managing both customer relationships and internal processes effectively.
In conclusion, understanding the distinct functions and benefits of CRM and ERP systems can help you make informed decisions tailored to your business’s specific needs, ultimately driving growth and efficiency.
Best Practices for Successful CRM Implementation
Getting Leadership Buy-In
One of the critical success factors for a successful CRM implementation is securing buy-in from leadership. Without strong support from the top, projects can struggle due to lack of resources, insufficient prioritization, or even outright resistance. Here are some strategies to garner that essential leadership support:
-
Present a Clear Business Case: Articulate how the CRM system will address specific business needs. Use data to demonstrate potential ROI, such as improved customer retention, increased sales, or enhanced operational efficiencies.
-
Involve Leadership Early: Engage leaders in the initial planning phases. Their insights can help shape the CRM selection process and ensure alignment with overall business objectives.
-
Highlight Competitive Advantage: Emphasize how a robust CRM can help the organization stay competitive. Discuss trends in customer relationship management and how leading firms are leveraging CRM systems for better customer engagement.
-
Establish a Change Management Strategy: Prepare leadership to champion a culture of change. This includes communicating the benefits of the CRM, addressing potential concerns, and outlining the support available to staff during the transition.
Planning Your Data Migration
Data migration is often a daunting task and can lead to significant issues if not managed properly. Here’s how to ensure a smooth data migration process:
-
Conduct a Data Audit: Before migrating, assess your existing data. Identify what data is relevant, what needs to be cleaned, and what can be archived. This will help in eliminating unnecessary clutter and ensuring only high-quality data is transferred.
-
Choose the Right Migration Tools: Depending on the size and complexity of your data, select appropriate tools that facilitate smooth migration. These tools should also ensure data integrity and security during the transfer process.
-
Map Data Fields: Create a detailed mapping of data fields from the old system to the new CRM. This ensures that data is transferred accurately and that no important information is lost during migration.
-
Test Migration Processes: Conduct a trial run of the migration process with a small subset of data. This allows you to identify issues before the full-scale migration and adjust as necessary.
-
Implement Post-Migration Review: After the data has been migrated, perform a thorough review to verify data integrity and completeness. This step is crucial in ensuring that the CRM is functioning with accurate data from the outset.
Customizing the CRM to Your Process (Not the Other Way Around)
A common pitfall in CRM implementation is the tendency to adapt business processes to fit the CRM system rather than the other way around. Here’s how to ensure your CRM supports your unique processes:
-
Define Core Business Processes: Clearly document your existing processes before customizing the CRM. Understand what works and what doesn’t to inform how the CRM can enhance your operations.
-
Involve Users in Customization: Engage end-users in the customization process. Their hands-on experience will provide valuable insights into necessary features and adjustments that can improve usability and efficiency.
-
Avoid Over-Customization: While it may be tempting to customize extensively, focus on essential changes that will enhance user experience and meet business needs. Over-customization can lead to complexity and hinder future upgrades.
-
Leverage Built-In Functionality: Before customizing, explore the built-in features of the CRM. Many systems offer extensive capabilities that may already meet your requirements without the need for customization.
-
Establish Change Control Procedures: As your business evolves, so will your processes. Implement a change control process to manage ongoing adjustments to the CRM, ensuring that modifications are necessary, documented, and tested before implementation.
Effective User Training and Onboarding
Training and onboarding are often overlooked but are vital for maximizing CRM adoption and effectiveness. Here are best practices for effective user training:
-
Develop a Comprehensive Training Plan: Tailor training sessions to different user roles and their specific CRM needs. This ensures that each user receives relevant information and skills that pertain to their job functions.
-
Utilize Multiple Training Formats: Offer training through various formats such as live sessions, recorded webinars, written manuals, and hands-on workshops. This caters to different learning styles and preferences.
-
Incorporate Real-Life Scenarios: Use real-life scenarios and case studies during training to illustrate how the CRM can be applied to everyday tasks. This practical approach helps users understand the relevance of the system.
-
Encourage Ongoing Support: Create a support structure post-training where users can ask questions and seek assistance. This could include dedicated help desks, user forums, or regular check-ins.
-
Gather Feedback and Iterate: After the training, collect feedback from users to assess the effectiveness of the program. Use this information to refine future training sessions and address any gaps in knowledge.
Setting Clear KPIs to Measure Success
To gauge the effectiveness of your CRM implementation, it is essential to establish clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Here’s how to set and utilize KPIs effectively:
-
Align KPIs with Business Goals: Ensure that the KPIs you choose directly relate to your organization’s objectives. This alignment will help demonstrate the CRM’s impact on overall business performance.
-
Select a Mix of Quantitative and Qualitative Metrics: Use a combination of metrics, such as sales growth, customer satisfaction scores, and user adoption rates. This holistic view will provide a better understanding of the CRM’s effectiveness.
-
Set Benchmarks and Targets: Establish benchmarks based on historical data or industry standards. Setting targets will help motivate teams and provide a clear goal for assessing success.
-
Regularly Review and Adjust KPIs: Continuously monitor the KPIs to assess the CRM’s performance. Be prepared to adjust them as business needs evolve or as you identify new areas for improvement.
-
Communicate Results Across the Organization: Share KPI results with all stakeholders, highlighting successes and areas for improvement. This transparency fosters a culture of accountability and encourages ongoing engagement with the CRM.
By following these best practices, organizations can enhance their chances of a successful CRM implementation, ultimately leading to improved customer relationships and business growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a contact center CRM?
A contact center CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system is a specialized software solution that integrates customer interactions across various communication channels, such as voice, email, chat, and social media. It helps businesses manage customer relationships more effectively by providing a unified view of customer data, tracking interactions, and facilitating better communication between customer service representatives and clients. This system enhances customer experience and boosts operational efficiency by streamlining workflows and automating routine tasks.
2. How much does a contact center CRM cost?
The cost of a contact center CRM varies significantly based on several factors, including the size of your business, the number of users, the features you require, and whether you choose a cloud-based or on-premise solution. Generally, subscription-based cloud CRMs can range from $12 to $300 per user per month, while on-premise solutions often entail higher upfront costs, including licensing fees, hardware, and maintenance. Additionally, some providers offer tiered pricing plans based on the features included, so it’s essential to evaluate your specific needs to determine the most cost-effective option.
3. Can a contact center CRM be used for B2C (Business to Consumer) interactions?
Yes, a contact center CRM is highly suitable for B2C interactions. It enables businesses to manage customer relationships effectively by tracking customer inquiries, preferences, and purchase history. With features like automated follow-ups, personalized communication, and multi-channel support, a contact center CRM can enhance the customer experience, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty. Many businesses in retail, hospitality, and services sectors leverage contact center CRMs to facilitate seamless B2C interactions.
4. How long does it take to implement a contact center CRM?
The implementation timeline for a contact center CRM can vary based on the complexity of the system, the size of your organization, and the level of customization required. On average, implementation can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months. Factors influencing the timeline include data migration, user training, integration with existing systems, and testing. It is crucial to work closely with your CRM provider to establish a realistic timeline and ensure a smooth transition.
5. What features should I look for in a contact center CRM?
When selecting a contact center CRM, consider the following essential features:
- Multi-channel support: The ability to manage customer interactions across various channels, including voice, email, chat, and social media.
- Automation: Automated workflows for routine tasks, such as ticketing, follow-ups, and reporting.
- Reporting and analytics: Comprehensive reporting tools to analyze customer interactions and agent performance.
- Integration capabilities: The ability to integrate with other business systems (e.g., marketing automation, e-commerce platforms) for a seamless workflow.
- User-friendly interface: An intuitive interface that makes it easy for agents to navigate and access customer information.
6. How does a contact center CRM improve customer service?
A contact center CRM improves customer service by providing agents with a complete view of customer interactions and history, enabling them to deliver personalized and efficient support. It centralizes customer data, allowing for quick access to information, which reduces response times and enhances resolution rates. Additionally, CRM systems often include automation features that streamline processes, such as ticket management and follow-ups, further improving the overall customer experience.
7. Is training required for using a contact center CRM?
Yes, training is typically required for using a contact center CRM effectively. While many systems are designed to be user-friendly, comprehensive training ensures that employees can leverage the software’s features to their fullest potential. Training may include hands-on sessions, tutorials, and resources provided by the CRM vendor. Investing in training can significantly enhance user adoption and maximize the benefits of the CRM system.
8. Can a contact center CRM be customized to fit my business needs?
Most contact center CRMs offer customization options to tailor the system to your specific business needs. Customization can range from modifying user interfaces and workflows to integrating third-party applications and developing unique reporting metrics. When evaluating potential CRM solutions, inquire about the extent of customization available and whether it aligns with your operational requirements. This flexibility allows businesses to create a system that truly supports their customer engagement strategies.
Conclusion: Taking the Next Step in Customer Management
The Role of CRM in Business Growth
In today’s competitive landscape, a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is not merely a technological investment; it is a foundational tool that drives modern business growth. A robust CRM empowers organizations to streamline their customer interactions, enhance sales processes, and improve marketing effectiveness. By centralizing customer data and automating routine tasks, CRMs enable businesses to build stronger relationships with their clients and make informed decisions that foster loyalty and profitability.
Aligning CRM with Business Needs
Choosing the right CRM system is critical. It is essential to select a platform that aligns with your specific business needs, whether that involves managing a large volume of customer interactions, improving team collaboration, or utilizing advanced analytics for strategic insights. Different organizations may require different functionalities, such as multi-channel support, integration capabilities, or workforce engagement management. Therefore, understanding your business objectives and existing workflows is paramount in making an informed choice.
Take Action Today
As you contemplate the integration of a CRM system into your business strategy, consider this an opportunity for transformation. Start by evaluating your current sales and marketing workflows—identify the bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas where customer engagement could be enhanced. By gaining clarity on your existing processes, you can better articulate your needs and expectations for a CRM solution.
Embrace this journey towards optimized customer management. Take the first step by assessing your current practices and envisioning how a tailored CRM solution can elevate your business to new heights. The future of your customer relationships—and your business success—begins with the right CRM. Start today!
Important Disclaimer
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information and reviews in this guide are for educational purposes, based on publicly available data. We are not affiliated with any software providers mentioned. Features and pricing change frequently. Always conduct your own due diligence and request a demo before committing to a CRM platform.