Discover Cost-Saving Strategies for Label China (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for label china
In today’s interconnected world, navigating the global market for label China can present unique challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The complexities of sourcing high-quality labels that meet diverse regulatory standards and consumer preferences can be daunting. This guide addresses these challenges by providing a comprehensive overview of the label industry in China, covering various types of labels, their applications across different sectors, and essential supplier vetting processes.
Understanding the nuances of label production, from materials to printing techniques, is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide also delves into cost factors, helping buyers gauge pricing structures to secure the best value for their investments. By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and strategies, this resource empowers them to confidently engage with suppliers, ensuring that their label needs are met with precision and reliability.
Whether you are a manufacturer looking to enhance your product packaging or a retailer aiming to improve brand visibility, this guide serves as a vital tool in your sourcing journey. With practical tips and expert analysis, international buyers will find the necessary information to successfully navigate the global market for labels sourced from China, ultimately facilitating better business outcomes and fostering sustainable partnerships.
Understanding label china Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porcelain Label China | High durability, elegant design, often hand-painted | Tableware, decorative items | Pros: Aesthetic appeal, high quality Cons: Higher cost, fragile if mishandled |
| Bone China | Made with bone ash, translucent, and lightweight | Fine dining, luxury gifts | Pros: Superior strength, elegant finish Cons: Expensive, requires careful handling |
| Stoneware | Heavier, more durable, and less expensive than porcelain | Everyday dinnerware, cookware | Pros: Affordable, chip-resistant Cons: Heavier, less refined appearance |
| Vitreous China | Non-porous, smooth surface, highly resistant to staining | Bathroom fixtures, sanitary ware | Pros: Easy to clean, hygienic Cons: Limited design options, heavy |
| Earthenware | Made from clay, often colorful and rustic | Casual dining, pottery crafts | Pros: Affordable, versatile designs Cons: Less durable, can absorb moisture |
What are the Key Characteristics of Porcelain Label China?
Porcelain label china is renowned for its durability and aesthetic appeal, often featuring intricate hand-painted designs. This type of china is ideal for high-end tableware and decorative items, making it a popular choice among luxury restaurants and gift retailers. When purchasing, buyers should consider the fragility and higher cost associated with porcelain, ensuring they have the proper logistics for safe handling and transport.
Why Choose Bone China for B2B Purchases?
Bone china stands out due to its lightweight nature and translucent quality, achieved through the inclusion of bone ash in its composition. It is frequently used in fine dining establishments and luxury gift markets. While its elegant finish appeals to buyers seeking premium products, the higher price point and need for careful handling can be a drawback, necessitating a well-planned supply chain.
What Makes Stoneware a Practical Choice?
Stoneware is characterized by its robust construction and affordability, making it an excellent option for everyday dinnerware and cookware. Its chip-resistant quality makes it suitable for high-traffic environments, such as restaurants and cafes. However, buyers should be aware that stoneware is generally heavier and may lack the refined aesthetic of porcelain or bone china, which could affect branding perceptions.
How Does Vitreous China Stand Out in the Market?
Vitreous china is known for its non-porous surface, making it highly resistant to staining and easy to clean, which is particularly beneficial in bathroom fixtures and sanitary ware. Its hygienic properties are a significant selling point for B2B buyers in the construction and renovation sectors. However, buyers may find a limited range of designs available, and the weight of vitreous china can impact shipping costs.
What are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Earthenware?
Earthenware is made from clay and often features colorful, rustic designs, making it popular for casual dining and pottery crafts. Its affordability and versatility in design are appealing to businesses looking to offer unique products. However, earthenware is less durable and can absorb moisture, which may lead to quality concerns in certain applications. Buyers should consider the intended use and environment when choosing earthenware products.
Related Video: Paiste 18″, 20″, and 22″ Formula 602 Blue Label China Types
Key Industrial Applications of label china
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of label china | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Product labeling for compliance and branding | Ensures regulatory compliance and enhances brand visibility | Quality of materials, durability, and design customization |
| Pharmaceuticals | Medication packaging and labeling | Improves patient safety through clear dosage information | Compliance with international regulations and safety standards |
| Retail | Price tags and promotional labels | Increases sales through effective marketing and pricing clarity | Readability, adhesive quality, and weather resistance |
| Electronics | Barcode labels for inventory management | Streamlines inventory tracking and reduces errors | Adhesion properties, compatibility with surfaces, and durability |
| Logistics & Shipping | Shipping labels for tracking and identification | Enhances logistics efficiency and reduces shipment errors | Customization options, barcode printing, and international shipping compliance |
How is ‘label china’ used in the Food & Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, ‘label china’ is primarily utilized for product labeling that complies with local and international food safety regulations. Labels must include essential information such as ingredient lists, nutritional facts, and expiration dates. For international buyers, it is crucial that these labels are printed on durable materials that can withstand temperature variations and moisture, ensuring they remain intact throughout the product’s shelf life. Additionally, the aesthetic design of labels can significantly influence consumer purchasing decisions, necessitating high-quality printing capabilities.
What are the applications of ‘label china’ in Pharmaceuticals?
In the pharmaceutical industry, ‘label china’ plays a vital role in medication packaging and labeling. Clear and accurate labels are essential for providing dosage instructions, safety warnings, and expiration dates, thereby improving patient safety and compliance. International B2B buyers need to ensure that labels meet stringent regulatory requirements, which may vary by country. This includes using materials that are resistant to tampering and can endure various environmental conditions. As such, sourcing partners should provide comprehensive documentation to validate compliance with health regulations.
How do Retailers benefit from ‘label china’?
Retailers utilize ‘label china’ for price tags and promotional labels that are pivotal in driving sales. Effective labeling not only clarifies pricing but also communicates special offers, enhancing customer engagement. For B2B buyers, considerations include the labels’ readability and adhesive quality, which should ensure they adhere well to different surfaces and withstand handling. Furthermore, labels should be designed to be visually appealing, aligning with branding strategies while also being cost-effective to produce in bulk.
What is the significance of ‘label china’ in Electronics?
In the electronics sector, ‘label china’ is essential for barcode labels that facilitate inventory management. These labels allow for efficient tracking of products throughout the supply chain, minimizing errors in stock management. Buyers in this industry should prioritize sourcing labels that have strong adhesion properties and can withstand environmental factors such as humidity and temperature fluctuations. Additionally, compatibility with various surfaces, including plastics and metals, is crucial for ensuring that labels remain intact during handling and usage.
How does ‘label china’ enhance Logistics & Shipping?
In logistics and shipping, ‘label china’ is used for shipping labels that provide crucial information for tracking and identification. These labels help streamline logistics operations, reducing the likelihood of shipment errors and enhancing overall efficiency. When sourcing these labels, international B2B buyers should consider customization options, including the ability to print barcodes and QR codes for easy scanning. Compliance with international shipping regulations is also essential, ensuring that labels are durable enough to endure the rigors of transportation.
Related Video: Uses Of Polymers | Organic Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘label china’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Complicated Compliance and Regulations for Labeling in Different Markets
The Problem: International B2B buyers often struggle with the complex web of compliance and regulatory requirements related to labeling, especially when sourcing labels from China. Different regions, such as Europe, Africa, and the Middle East, have distinct labeling laws regarding language, material, and content that must be adhered to. Failure to comply can lead to product recalls, fines, and reputational damage, making it a significant concern for businesses.
The Solution: To navigate these challenges effectively, B2B buyers should establish a comprehensive understanding of the labeling regulations specific to each target market. This involves conducting thorough research on the required standards and materials for labels in each region. Collaborating with local legal experts or compliance consultants can provide insights into the nuances of each market. Additionally, buyers should work closely with their suppliers in China to ensure that all labels are designed and produced in accordance with these regulations from the outset. Utilizing a checklist of compliance requirements during the sourcing process can also help to prevent issues before they arise.
Scenario 2: Quality Control Issues with Imported Labels
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers sourcing labels from China is the inconsistency in quality. Variations in materials, printing quality, and adherence to specifications can lead to labels that do not meet the buyer’s standards, resulting in wasted resources and dissatisfaction from end customers. This inconsistency can severely affect branding and product perception in the market.
The Solution: To mitigate quality control issues, buyers should implement a rigorous quality assurance process. This can include setting clear specifications and expectations for the labels before production begins. It is advisable to conduct factory audits and request samples before placing large orders. Additionally, establishing a quality control team that can inspect the labels during production and before shipment can help ensure that the final products meet the required standards. Utilizing third-party inspection services in China can also provide an unbiased assessment of the label quality and compliance with specifications.
Scenario 3: Language and Cultural Barriers in Label Design
The Problem: Language barriers and cultural differences can create significant challenges for B2B buyers when it comes to designing labels that resonate with local consumers. Misinterpretations in language can lead to incorrect messaging, which can confuse or alienate the target audience. This is particularly relevant for companies looking to expand their market reach in diverse regions such as Africa and South America.
The Solution: To overcome these barriers, buyers should invest in working with local experts who understand the cultural nuances and language requirements of the target market. This may involve hiring translators and cultural consultants who can provide insights into effective messaging and design. Additionally, conducting focus groups or surveys with local consumers can help gauge the effectiveness of label designs before launching products. Leveraging technology, such as AI-driven translation services, can also assist in ensuring that label content is culturally appropriate and linguistically accurate. By prioritizing these steps, B2B buyers can create labels that not only comply with regulations but also connect with consumers on a deeper level.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for label china
When selecting materials for label production in China, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence product performance, cost, and compliance with regional standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in label manufacturing, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Polypropylene (PP) in Label Production?
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used in label manufacturing due to its favorable properties. It boasts a high-temperature resistance (up to 100°C), making it suitable for applications requiring durability under heat. Additionally, PP exhibits excellent chemical resistance, which is crucial for labels exposed to solvents and oils.
Pros and Cons:
PP labels are lightweight and cost-effective, making them a popular choice for high-volume production. However, they can be less durable than other materials when exposed to UV light, leading to fading and brittleness over time.
Impact on Application:
PP is compatible with various printing technologies, including flexographic and digital printing. It is ideal for labels used in food packaging and consumer goods due to its safety and recyclability.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that the PP labels comply with regional food safety standards, such as those set by the FDA in the U.S. or EFSA in Europe. Understanding local regulations is essential for successful market entry.
How Does Vinyl (PVC) Compare as a Material for Labels?
Vinyl (PVC) is another commonly used material for labels, known for its flexibility and durability. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -10°C to 70°C, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. PVC is also resistant to moisture and chemicals, which enhances its longevity.
Pros and Cons:
The primary advantage of PVC labels is their robust nature, which makes them ideal for products that require a long lifespan. However, PVC is generally more expensive than PP and can be less environmentally friendly due to its production process and disposal issues.
Impact on Application:
PVC labels are highly effective for applications requiring high visibility, such as promotional labels or outdoor signage. Their ability to maintain vibrant colors and resist fading makes them a preferred choice for branding.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the environmental regulations regarding PVC in their respective countries, particularly in Europe, where there is a strong push towards sustainable materials. Compliance with standards like REACH is crucial for market acceptance.
What Are the Advantages of Paper Labels?
Paper labels are a traditional choice in the label industry, favored for their versatility and cost-effectiveness. They can be produced with various coatings to enhance water and oil resistance, withstanding moderate exposure to moisture.
Pros and Cons:
While paper labels are generally cheaper and can be easily printed on, they are less durable than synthetic materials. They may not hold up well in extreme conditions, such as high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
Impact on Application:
Paper labels are widely used in retail and logistics, where they are often required for short-term applications. Their biodegradability makes them suitable for eco-conscious brands.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the lifecycle of paper labels and their environmental impact. Adhering to standards like FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) certification can enhance brand reputation in markets that prioritize sustainability.
How Does Polyester (PET) Stand Out in Label Manufacturing?
Polyester (PET) is a synthetic material known for its exceptional durability and resistance to tearing, moisture, and chemicals. It can withstand temperatures up to 150°C, making it suitable for high-performance applications.
Pros and Cons:
The key advantage of PET labels is their strength and longevity, which makes them ideal for products that require labels to endure harsh conditions. However, PET is typically more expensive than other materials, which can impact overall production costs.
Impact on Application:
PET labels are often used in industrial applications, such as chemical labeling and automotive parts, where durability is paramount. Their compatibility with various printing methods allows for high-quality graphics.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers must ensure that PET labels meet international standards such as ISO for labeling and safety. Understanding the market demand for durable labels can guide purchasing decisions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Label China
| Material | Typical Use Case for label china | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | Food packaging, consumer goods | Cost-effective, lightweight | UV sensitivity, less durable | Low |
| Vinyl (PVC) | Outdoor signage, promotional labels | High durability, vibrant colors | Higher cost, environmental concerns | Medium |
| Paper | Retail, logistics | Biodegradable, cost-effective | Less durable, moisture-sensitive | Low |
| Polyester (PET) | Industrial, chemical labeling | Exceptional durability | Higher cost, limited eco-friendliness | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for label production in China, equipping international B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions tailored to their specific market requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for label china
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Labels in China?
The manufacturing process for labels in China typically involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards. Understanding these stages will help international B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing labels.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Commonly Used?
The first step in the label manufacturing process is the selection and preparation of materials. Common materials include:
- Paper: Widely used for labels, it can be coated or uncoated, depending on the application.
- Vinyl: Known for its durability, it is often used for outdoor labels or products requiring moisture resistance.
- Polyester: This synthetic material is used for high-performance labels due to its strength and resistance to chemicals.
Once materials are chosen, they undergo cutting and converting to prepare for the next stage.
2. Forming: How Are Labels Created?
During the forming stage, the prepared materials are shaped into labels using various techniques:
- Flexographic Printing: This is the most common method for label printing, utilizing flexible relief plates. It’s efficient for large runs and provides vibrant colors.
- Digital Printing: Ideal for short runs, digital printing allows for quick turnaround times with high-quality results. It’s particularly useful for custom labels.
- Screen Printing: Often used for specialty labels, this technique provides thick ink layers, making it ideal for opaque or metallic finishes.
These techniques ensure that labels are not only visually appealing but also functional.
3. Assembly: What Happens During This Stage?
In the assembly stage, labels may undergo several additional processes:
- Die-Cutting: Labels are cut into specific shapes using a die, ensuring uniformity and precision.
- Lamination: A protective layer is added to enhance durability and resistance to elements, which is especially important for labels intended for outdoor use.
- Slitting: The large rolls of labels are cut down to smaller sizes for easier handling and application.
This stage ensures that the labels are ready for packaging and shipment.
4. Finishing: How Are Labels Prepared for Delivery?
The finishing stage is crucial for preparing the labels for market delivery. It includes:
- Quality Control Checks: Every batch undergoes thorough inspections to ensure that the labels meet design specifications and quality standards.
- Packaging: Labels are packaged securely to prevent damage during transportation, often in rolls or sheets, depending on customer requirements.
By this stage, the labels are ready for distribution to various markets.
What International Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Label Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a critical component of the manufacturing process. International standards help ensure that products are safe, reliable, and of good quality.
ISO 9001: What Does This Standard Entail?
ISO 9001 is an internationally recognized standard for quality management systems. It provides a framework for organizations to ensure that they meet customer and regulatory requirements consistently. Companies engaged in label manufacturing in China often seek ISO 9001 certification to demonstrate their commitment to quality.
Industry-Specific Standards: Which Ones Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
In addition to ISO 9001, there are industry-specific standards that may apply, such as:
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, it indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For labels used in pharmaceuticals, adherence to API standards is critical to ensure safety and efficacy.
These certifications provide buyers with assurance regarding the quality and safety of the labels.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Label Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integral to the label manufacturing process, with several checkpoints established to maintain high standards.
1. Incoming Quality Control (IQC): What Does It Involve?
IQC involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production process. This ensures that only materials meeting specified quality standards are used, reducing the risk of defects in the final product.

A stock image related to label china.
2. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): How Is It Conducted?
IPQC is conducted during the manufacturing process. It includes regular checks to monitor printing quality, color consistency, and adherence to design specifications. This stage is crucial for identifying issues early and preventing defects from reaching the final inspection stage.
3. Final Quality Control (FQC): What Is Its Role?
FQC is the last checkpoint before products are packaged and shipped. It involves a comprehensive inspection of the finished labels, ensuring they meet all quality and regulatory standards. Common testing methods include:
- Adhesion Tests: To ensure that the labels adhere properly to surfaces.
- Durability Tests: Assessing how labels withstand exposure to moisture, UV light, and chemicals.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
International B2B buyers must be proactive in verifying the quality control processes of their suppliers to ensure they receive high-quality products.
1. Audits: What Should Buyers Look For?
Conducting on-site audits can provide valuable insights into a supplier’s manufacturing and quality control processes. Buyers should look for:
- Evidence of compliance with ISO standards.
- Documentation of quality control procedures and results.
2. Quality Control Reports: How Useful Are They?
Requesting quality control reports can help buyers understand a supplier’s performance over time. These reports should detail:
- Defect rates.
- Results of quality tests conducted during manufacturing.
3. Third-Party Inspections: When Should They Be Considered?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. This is particularly useful for buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where logistics and communication can be challenging.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control Certifications for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers must also be aware of the nuances associated with quality control certifications, as these can vary significantly by region.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding the local manufacturing culture can help buyers interpret quality control practices and expectations more effectively.
- Regulatory Requirements: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements for product labeling, which can impact the quality assurance processes.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of these aspects, buyers can ensure they partner with reliable suppliers who meet their quality standards.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for labels in China are robust and designed to meet international standards. By focusing on the key stages of manufacturing and implementing rigorous quality control practices, suppliers can deliver high-quality labels that meet the diverse needs of B2B buyers globally.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘label china’
When sourcing labels from China, it’s essential to have a structured approach to ensure you procure quality products that meet your specific needs. This checklist is designed to guide international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, through the critical steps of sourcing labels effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specifications for the labels you need, including size, material, adhesive type, and printing requirements. This step is crucial because it sets the foundation for your sourcing process. Having precise specifications helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures that suppliers can meet your needs accurately.
- Material Types: Consider whether you need paper, plastic, or eco-friendly options.
- Adhesive Strength: Determine if you need permanent or removable adhesives based on your application.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reliable suppliers in China. Utilize platforms like Alibaba, Made-in-China, and Global Sources to find manufacturers specializing in labels. This step is vital to build a shortlist of potential partners who can fulfill your requirements.
- Supplier Verification: Look for suppliers with verified credentials and good reviews.
- Industry Experience: Focus on suppliers who have a proven track record in your industry.
Step 3: Request Samples for Quality Assessment
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples of their labels. Evaluating samples is essential to assess the quality, durability, and adherence of the labels to your specifications. This step can save you from costly mistakes in bulk orders.
- Quality Check: Examine the print quality, adhesive strength, and overall finish.
- Functionality Testing: Test the labels in real-world conditions to ensure they meet your performance expectations.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management or certifications specific to your industry. This verification is crucial for establishing credibility and ensuring that the supplier adheres to international quality standards.
- Compliance Check: Confirm that the supplier complies with regulations applicable to your market.
- Sustainability Standards: If relevant, check for certifications related to eco-friendliness, such as FSC or REACH.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
After confirming supplier capabilities, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing and terms that align with your budget and timeline.
- Bulk Discounts: Inquire about discounts for larger orders.
- Payment Flexibility: Discuss payment options that work for both parties, such as letters of credit or escrow services.
Step 6: Place a Trial Order
Before committing to a larger order, place a trial order to evaluate the supplier’s performance in fulfilling your requirements. This step is critical to gauge reliability, production timelines, and product quality in a real-world scenario.
- Order Size: Keep the trial order small to minimize risk.
- Delivery Assessment: Monitor the supplier’s adherence to delivery timelines and packaging standards.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Set up a clear communication plan with your supplier to facilitate ongoing discussions and issue resolution. Regular communication helps maintain a strong relationship and ensures that both parties are aligned throughout the sourcing process.
- Preferred Channels: Decide on communication channels (e.g., email, messaging apps).
- Regular Updates: Schedule regular check-ins to discuss production progress and address any concerns.
By following this practical sourcing checklist, international B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of procuring labels from China, ensuring they find the right suppliers and products to meet their business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for label china Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Label China Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of sourcing labels from China is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. For instance, synthetic materials like vinyl or polyester tend to be more expensive than paper labels. Buyers should evaluate the performance needs of their products to select the most cost-effective material.
-
Labor: Labor costs in China can vary based on the region and the skill level required for production. Factories in urban areas may have higher labor costs compared to those in rural regions. Buyers should consider labor costs when negotiating prices.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes factory utilities, maintenance, and administrative expenses. A factory with advanced technologies may charge higher overheads, but it could also ensure better quality and faster production times.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific label shapes or sizes can add to initial costs. Buyers should inquire about these costs upfront, especially for unique label designs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes can incur additional costs. However, investing in quality assurance can prevent costly mistakes and ensure compliance with international standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can fluctuate based on the chosen Incoterms, shipping method, and destination. Buyers should assess logistics costs in relation to their total budget.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding industry standard margins can help in negotiating better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Label Costs in China?
Various factors can influence label pricing, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes typically lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers are often willing to negotiate better prices for larger orders, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate their purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom labels with specific designs or features (like waterproofing or special adhesives) can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define specifications to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Labels that require specific quality certifications (like ISO or CE) may come at a premium. Buyers should assess whether these certifications are necessary for their market.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can significantly impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven quality and service levels.
-
Incoterms: Different Incoterms can affect shipping costs and responsibilities. Understanding these terms can help buyers select the most cost-effective shipping methods.
What Negotiation Strategies Should Buyers Use for Cost-Efficiency?
When sourcing labels from China, buyers can employ several negotiation strategies to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Transparent Communication: Clearly communicate your needs and expectations to suppliers. This transparency can foster trust and lead to better pricing agreements.
-
Leverage Long-term Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers may result in better pricing, preferential treatment, and improved service over time.
-
Analyze Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but the total cost associated with sourcing, including logistics, storage, and potential quality issues. This holistic view can lead to more informed decision-making.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Keeping abreast of market trends and price fluctuations in raw materials can empower buyers during negotiations. This knowledge can help in arguing for better pricing based on market conditions.
-
Be Prepared to Walk Away: Sometimes, the best negotiation tactic is to be willing to walk away if the terms do not meet your expectations. This approach can often prompt suppliers to reconsider their offers.
What Are the Pricing Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific pricing nuances:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rate volatility can impact costs. Buyers should consider hedging strategies to mitigate risks associated with currency fluctuations.
-
Import Duties and Taxes: Different countries impose varying import duties and taxes that can significantly affect the final cost of labels. Buyers should factor these into their total cost calculations.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding local business practices and negotiation styles can be beneficial. Building rapport and trust with suppliers can lead to better deals.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the labels meet the regulatory requirements of your target market. Non-compliance can lead to additional costs and delays.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is important to note that the prices discussed in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Always conduct thorough market research and supplier assessments to obtain the most accurate pricing information tailored to your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing label china With Other Solutions
When evaluating the best options for labeling solutions, it’s essential to consider alternatives to ‘Label China’ that may meet your business needs more effectively. This analysis will provide insights into the performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases for each solution, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions.
Comparison Table of Labeling Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Label China | Alternative 1: Digital Printing Solutions | Alternative 2: Traditional Labeling Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High durability and customization | High-quality prints, fast turnaround | Varies based on material and method |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on volume | Cost-effective for short runs, higher for large volumes | Generally lower for bulk production |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires supplier coordination | User-friendly, minimal setup needed | Labor-intensive, requires skilled workforce |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Low maintenance, but depends on printer upkeep | High maintenance due to manual processes |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale production with diverse designs | Short-run labels, quick changes needed | High-volume, standardized labeling |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Digital Printing Solutions?
Digital printing solutions offer significant advantages, particularly for businesses that require flexibility and speed. They allow for quick changes in design without the need for extensive setup, making them ideal for short-run projects. The cost-effectiveness of digital printing shines in scenarios where small batches are needed, as it reduces waste and setup costs. However, for large-scale productions, the cost may rise significantly, and the durability of printed labels can sometimes be less than that of traditional options.
How Do Traditional Labeling Methods Compare?
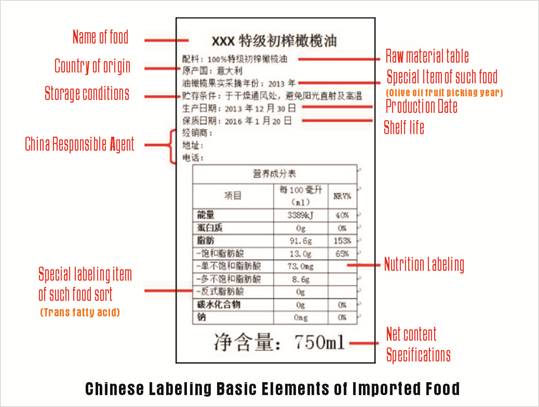
A stock image related to label china.
Traditional labeling methods, such as flexography or offset printing, are well-suited for high-volume production. They generally offer lower costs per unit for large runs, making them an attractive option for businesses with consistent labeling needs. However, these methods can be labor-intensive and require a skilled workforce for setup and operation. Moreover, changes in design can be cumbersome and time-consuming, making them less flexible compared to digital options.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Labeling Solution?
When selecting the appropriate labeling solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, volume requirements, and budget constraints. If your business demands high customization and quick turnaround times, digital printing may be the best fit. Conversely, if you are focused on high-volume production with consistent designs, traditional labeling methods could provide a more cost-effective solution. Evaluating these aspects will help buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe make a choice that aligns with their business goals and operational efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for label china
When navigating the complex world of sourcing label china, understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. Here’s a breakdown of key specifications and common jargon that international B2B buyers should be familiar with.
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of Label China?
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the type of substrate used for labels, which can include paper, vinyl, polyester, or polypropylene. Each material has its own properties regarding durability, resistance to moisture, and suitability for different applications. For example, vinyl labels are ideal for outdoor use due to their weather resistance, while paper labels may be more suitable for indoor applications. Understanding material grades helps buyers choose the right label for their specific needs, impacting product longevity and customer satisfaction.
2. Adhesive Type
The adhesive used on labels is critical for their performance. Common types include permanent, removable, and repositionable adhesives. Permanent adhesives are designed for long-lasting applications, while removable adhesives allow for easy label removal without leaving residue. The choice of adhesive affects how and where the label can be applied, which is crucial for product branding and compliance with regulations.
3. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels indicate the acceptable variation in label dimensions during production. This is particularly important for labels that must fit specific packaging or equipment. For instance, a tolerance of ±0.5mm may be acceptable for most applications, but more stringent requirements may be necessary for precision applications. Understanding these levels ensures that labels will fit correctly and perform as expected.
4. Print Quality
Print quality is assessed by resolution and color accuracy. High-resolution labels (300 DPI or higher) are essential for clear graphics and text, especially for branding purposes. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers can meet their print quality standards to maintain a professional appearance and convey the desired message effectively.
5. Durability Ratings
Durability ratings, such as scratch resistance, water resistance, and UV stability, inform buyers about how well a label will withstand environmental factors. Labels used in harsh conditions, like those exposed to moisture or sunlight, need higher durability ratings. This consideration is crucial for ensuring that labels remain legible and intact throughout their intended lifespan.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Label China Procurement?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or products that are marketed by another company under its own brand. In the context of label china, an OEM might manufacture custom labels for a brand’s product line. Understanding OEM relationships is essential for buyers looking to create unique branding opportunities.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers as it influences inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchasing strategies and avoid overstock or stockouts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. It is an important step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers. A well-structured RFQ can lead to better pricing and favorable terms.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Common terms include FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight). Understanding Incoterms is essential for international buyers to manage risks and costs associated with shipping and logistics effectively.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. This is a critical factor for planning production schedules and inventory management. Buyers should inquire about lead times when negotiating with suppliers to ensure they can meet their delivery timelines.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring they select the most suitable label china products for their business needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the label china Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Label China Sector?
The label manufacturing sector in China is experiencing significant growth driven by various global factors. The increasing demand for customized packaging solutions, particularly in the food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics industries, has propelled the label market. B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should note that the emphasis on digital printing technology is transforming traditional label production methods. This shift allows for shorter production runs, quicker turnaround times, and enhanced design flexibility, catering to the growing trend of personalization in product labeling.
Another critical trend is the integration of smart labeling technologies. QR codes and RFID tags are increasingly being used to enhance traceability and consumer engagement. This is particularly relevant for international buyers who need to comply with stringent regulations regarding product information and supply chain transparency. Moreover, as e-commerce continues to expand, the necessity for effective branding through labels that communicate key product information has never been more crucial.
In terms of sourcing, buyers are advised to engage with suppliers who offer not only competitive pricing but also innovative solutions. Understanding local manufacturing capabilities, as well as logistics and shipping considerations, will be essential in navigating the complexities of sourcing labels from China. Collaborating with suppliers who possess a robust understanding of international markets can significantly enhance supply chain efficiency.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Addressed in the Label China Sector?
Sustainability has become a vital consideration for B2B buyers in the label sector. The environmental impact of label production, including waste generation and resource consumption, is prompting buyers to seek out suppliers committed to sustainable practices. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who utilize eco-friendly materials, such as biodegradable films and recyclable substrates, as well as those who employ water-based inks and adhesives to minimize harmful emissions.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Buyers must assess the supply chains of potential suppliers to ensure compliance with labor standards and fair trade practices. Certifications such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) for paper labels and other ‘green’ certifications can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
By aligning purchasing decisions with sustainability goals, B2B buyers not only enhance their brand reputation but also contribute positively to global environmental initiatives. This alignment is particularly significant for companies looking to appeal to eco-conscious consumers and stakeholders across diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Is the Evolution of the Label China Sector and Its Relevance to B2B Buyers?
The label industry in China has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially characterized by traditional printing methods, the sector has embraced technological advancements, transitioning to digital printing and automated production processes. This evolution has enabled manufacturers to meet the increasing demand for high-quality, customized labels efficiently.
Historically, China has positioned itself as a global leader in manufacturing due to its cost-effective labor and extensive supply chain infrastructure. However, the focus is now shifting towards innovation and sustainability, with many manufacturers investing in cutting-edge technologies and eco-friendly practices. For international B2B buyers, this evolution presents opportunities to partner with suppliers who not only provide competitive pricing but also align with modern business values centered around sustainability and innovation.
Understanding this historical context is essential for buyers aiming to make informed decisions about their sourcing strategies and supplier partnerships in the label sector. As the market continues to evolve, staying abreast of these changes will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in an increasingly globalized economy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of label china
-
How do I ensure the quality of labels sourced from China?
To ensure quality when sourcing labels from China, start by conducting thorough supplier vetting. Request samples before placing bulk orders and assess their print quality, material durability, and adherence to your specifications. Utilize third-party inspection services to evaluate the products before shipment. Additionally, consider suppliers who have quality certifications like ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. -
What are the key factors to consider when choosing a label supplier in China?
When selecting a label supplier in China, evaluate their manufacturing capabilities, product range, and experience in your industry. Look for suppliers with a solid reputation, verified by customer reviews and ratings. Ensure they can meet your specific needs, such as custom designs or materials. Also, inquire about their compliance with international standards and regulations relevant to your market. -
What customization options are available for labels from China?
Many Chinese suppliers offer extensive customization options for labels, including size, shape, material, and printing techniques. You can choose from various finishes such as matte, gloss, or transparent. Additionally, consider options for adhesive strength and weather resistance, depending on your application. Discuss your design requirements with the supplier to explore all available custom features. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for labels from Chinese suppliers?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for labels can vary significantly among suppliers in China. Typically, MOQs range from 1,000 to 10,000 pieces, depending on the complexity of the label and the supplier’s production capabilities. If your needs are lower, some suppliers may offer flexibility, but this could result in higher per-unit costs. Always clarify MOQs during initial discussions to avoid misunderstandings later.
-
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing labels from China?
Payment terms when sourcing labels from China can vary, but common practices include a 30% deposit upfront and the balance before shipment. Some suppliers may offer more favorable terms for larger orders or repeat customers. Be cautious of suppliers asking for full payment in advance, as this can increase risk. Utilize secure payment methods like Alibaba Trade Assurance or PayPal to protect your transactions. -
How can I navigate shipping and logistics for labels sourced from China?
To navigate shipping and logistics for labels sourced from China, consider working with a freight forwarder who can handle the complexities of international shipping. Decide whether you prefer air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness. Ensure that your supplier can provide the necessary documentation, such as commercial invoices and packing lists, to facilitate customs clearance. Factor in delivery times and costs when planning your order. -
What are the common challenges faced when sourcing labels from China, and how can I overcome them?
Common challenges include communication barriers, quality control issues, and potential delays in production or shipping. To overcome these, establish clear communication channels and use detailed specifications to minimize misunderstandings. Regularly follow up with your supplier during production, and utilize third-party inspections to ensure quality. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also help mitigate risks and enhance collaboration. -
How do I handle disputes with a Chinese supplier regarding label quality or delivery?
In the event of a dispute with a Chinese supplier, first, document all communications and agreements related to your order. Attempt to resolve the issue amicably through direct communication, presenting your concerns clearly and providing evidence if necessary. If the issue remains unresolved, consider involving a mediator or using the dispute resolution services provided by platforms like Alibaba. Always aim to maintain a professional tone to preserve the business relationship.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for label china
What Are the Key Takeaways for International B2B Buyers in the Label Industry?
As we conclude our exploration of sourcing labels from China, it is imperative to emphasize the strategic advantages that this market offers to international B2B buyers. The Chinese label manufacturing industry is characterized by its robust supply chain, advanced technology, and competitive pricing. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can leverage these advantages to enhance their product offerings and improve brand visibility.
Why Is Strategic Sourcing Essential for Your Business?
Engaging in strategic sourcing allows businesses to not only reduce costs but also improve quality and efficiency in their labeling processes. By establishing strong partnerships with reliable Chinese suppliers, buyers can ensure consistent quality and timely delivery, which are critical in today’s fast-paced market. Additionally, understanding the regulatory requirements specific to your region will facilitate smoother import processes and compliance.
How Can International Buyers Prepare for Future Opportunities?
Looking ahead, the demand for customized and sustainable labeling solutions is on the rise. International B2B buyers should stay informed about emerging trends and technologies in the label industry, such as eco-friendly materials and smart labels. Embracing these innovations will not only meet consumer expectations but also position your business as a leader in sustainability.
In conclusion, as you navigate the complexities of sourcing labels from China, prioritize strategic partnerships and continuous learning. By doing so, you can unlock new opportunities and drive growth in your business. Engage with trusted suppliers today to position your brand for future success.