Discover Top Benefits from Your Garbage Truck Manufacturer (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for garbage truck manufacturer
Navigating the complexities of sourcing garbage trucks can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With increasing urbanization and a heightened focus on sustainable waste management, the demand for efficient, reliable, and environmentally friendly garbage trucks has never been greater. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the global market for garbage truck manufacturers, equipping buyers with the insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
Within these pages, you’ll find detailed analyses of various types of garbage trucks—ranging from rear loaders to front loaders and automated side loaders—each suited for different waste management applications. We will delve into critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers, including certifications, technological innovations, and after-sales support. Understanding the cost structures involved in purchasing and maintaining these vehicles is also crucial; thus, we will provide a breakdown of expected expenses, financing options, and potential ROI.
By leveraging the knowledge and strategies outlined in this guide, international buyers can navigate the intricacies of the global garbage truck market with confidence. Whether you are based in South Africa, Argentina, or the Middle East, this resource is designed to empower you to identify the best manufacturers that meet your specific operational needs and sustainability goals.
Understanding garbage truck manufacturer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Front Loader Garbage Trucks | Equipped with a front-loading mechanism for efficient collection | Urban waste management, commercial sectors | Pros: High efficiency, suitable for tight spaces. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Rear Loader Garbage Trucks | Traditional design with a rear-loading hopper | Residential waste collection, recycling | Pros: Cost-effective, simple operation. Cons: Less efficient in urban areas. |
| Side Loader Garbage Trucks | Side-loading mechanism allows for curbside collection | Municipal waste services, large volume collections | Pros: Reduces worker injury risk, efficient for high-density areas. Cons: Requires more space for operation. |
| Automated Garbage Trucks | Incorporates robotics for automated waste collection | Smart city initiatives, large municipalities | Pros: Labor-saving, increases safety. Cons: High maintenance costs, technical complexity. |
| Compactor Garbage Trucks | Built-in compaction system for efficient waste handling | Industrial waste management, large events | Pros: Maximizes load capacity, reduces trips. Cons: Heavier, may require more power. |
What Are the Characteristics of Front Loader Garbage Trucks?
Front loader garbage trucks are distinguished by their front-loading mechanism, which enables them to lift and dump waste containers from the front. These trucks are particularly suitable for urban waste management and commercial sectors, where efficiency and speed are crucial. When considering a front loader, B2B buyers should evaluate the truck’s lifting capacity and compatibility with existing waste containers to ensure seamless integration into their operations.
How Do Rear Loader Garbage Trucks Operate?
Rear loader garbage trucks are characterized by their traditional design, featuring a rear-loading hopper. They are commonly used for residential waste collection and recycling efforts. Their straightforward operation makes them a cost-effective choice for municipalities and smaller waste management companies. Buyers should consider the volume of waste generated in their area and the potential for route optimization to maximize the efficiency of rear loaders.
What Are the Advantages of Side Loader Garbage Trucks?
Side loader garbage trucks utilize a side-loading mechanism that allows for curbside waste collection without requiring workers to leave the vehicle. This design is particularly beneficial for municipal waste services in high-density urban areas. While they reduce the risk of worker injuries and enhance operational efficiency, buyers need to assess the space required for maneuvering these trucks in their designated routes.
Why Choose Automated Garbage Trucks?
Automated garbage trucks leverage robotics to facilitate waste collection, making them ideal for smart city initiatives and large municipalities. These vehicles can significantly reduce labor costs and improve safety by minimizing human interaction with the waste collection process. However, potential buyers should weigh the higher initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs against the long-term savings and efficiency gains.
What Makes Compactor Garbage Trucks Unique?
Compactor garbage trucks are equipped with a built-in compaction system that compresses waste to maximize load capacity. This feature is especially useful for industrial waste management and large events where the volume of waste can be substantial. While compactor trucks can reduce the number of trips required for waste disposal, buyers must consider their weight and power requirements, as these factors can influence operational costs and logistics.
Related Video: Types of “Garbage Truck” 3
Key Industrial Applications of garbage truck manufacturer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of garbage truck manufacturer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waste Management | Collection and transportation of municipal waste | Efficient waste disposal, improved public health | Compliance with local regulations, vehicle capacity, reliability |
| Construction and Demolition | Removal of construction debris and hazardous waste | Timely project completion, reduced site hazards | Durability for rough terrain, specialized containers, safety features |
| Recycling Facilities | Sorting and transporting recyclable materials | Enhanced recycling rates, lower landfill costs | Compatibility with recycling processes, material types, volume capacity |
| Municipal Services | Street cleaning and litter collection | Improved urban cleanliness, enhanced community image | Versatility in operations, ease of maintenance, local service support |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Disposal of industrial waste and by-products | Compliance with environmental regulations, waste reduction | Customization options, load capacity, sustainability practices |
How Do Garbage Truck Manufacturers Support Waste Management?
Garbage truck manufacturers play a pivotal role in waste management by providing vehicles specifically designed for the collection and transportation of municipal waste. These trucks are essential for maintaining public health by ensuring timely waste disposal, thus minimizing the risk of disease outbreaks. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing trucks that comply with local environmental regulations is crucial. Buyers should also consider the reliability and service availability of manufacturers in their region to ensure operational efficiency.
What Are the Applications of Garbage Trucks in Construction and Demolition?
In the construction and demolition industry, garbage trucks are utilized for the removal of debris, including hazardous waste. Their use helps ensure that projects are completed on time by maintaining a clean and safe working environment. International buyers, especially from the Middle East, should prioritize trucks that are durable enough to handle rough terrains and heavy loads. Additionally, specialized containers for different types of waste can enhance operational efficiency and safety on job sites.
How Do Recycling Facilities Benefit from Garbage Truck Manufacturers?
Recycling facilities rely on garbage trucks for the sorting and transportation of recyclable materials. These trucks enable facilities to enhance recycling rates and reduce landfill costs, making them crucial for sustainable operations. Buyers from Europe should focus on sourcing trucks that are compatible with their specific recycling processes and material types. Understanding the volume capacity needed for efficient operations is also essential for maximizing the benefits of these vehicles.
What Role Do Garbage Trucks Play in Municipal Services?
Municipal services utilize garbage trucks for street cleaning and litter collection, contributing to improved urban cleanliness and enhancing the community’s image. These trucks must be versatile enough to operate in various urban environments and be easy to maintain. For B2B buyers in regions like South Africa, ensuring that the manufacturer offers local service support can significantly impact the long-term operational effectiveness of these vehicles.
How Are Garbage Trucks Used in Industrial Manufacturing?
In industrial manufacturing, garbage trucks are critical for the disposal of industrial waste and by-products. Their use helps companies comply with environmental regulations while also reducing waste. Buyers should look for manufacturers that offer customization options to meet specific waste disposal needs, as well as trucks with adequate load capacity to handle the volume of waste generated. Sustainability practices in manufacturing can also influence purchasing decisions, making it essential for buyers to align with environmentally responsible suppliers.
Related Video: From Waste to Wonder: The Surprising Uses of Carbon Dioxide
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘garbage truck manufacturer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Limited Budget Constraints in Garbage Truck Procurement
The Problem:
B2B buyers, especially in regions with developing waste management systems like Africa and South America, often face significant budget constraints. For instance, a municipal buyer in South Africa may have a limited financial allocation for waste management vehicles, making it challenging to procure high-quality garbage trucks without exceeding budget limits. This situation can lead to compromised vehicle specifications, ultimately affecting operational efficiency and reliability.
The Solution:
To address budget constraints, buyers should consider exploring flexible financing options, such as leasing garbage trucks instead of outright purchases. This approach allows municipalities or companies to manage cash flow more effectively while still acquiring the necessary equipment. Additionally, buyers should thoroughly research manufacturers that offer tiered pricing or bulk purchasing discounts. Engaging directly with manufacturers to discuss customized packages that fit within their budget can also yield better options. Lastly, investing in durable and fuel-efficient models may have a higher upfront cost but can lead to long-term savings through reduced maintenance and operational costs.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Regulatory Compliance Challenges in Waste Management
The Problem:
In regions like Europe and the Middle East, waste management regulations can be stringent and complex. Buyers often struggle to ensure that the garbage trucks they purchase comply with local environmental laws and standards. For example, a buyer in Argentina might face challenges related to emissions standards and waste segregation requirements, which can complicate the procurement process and lead to potential legal issues if compliance is not met.
The Solution:
To navigate regulatory compliance, it is crucial for B2B buyers to conduct thorough research on local laws and regulations before engaging with manufacturers. They should seek out manufacturers that have a proven track record of compliance with international and local standards, as these companies will typically provide documentation and certifications that can simplify the approval process. Additionally, buyers should consider collaborating with local waste management authorities during the procurement phase to ensure that the selected garbage trucks meet all necessary regulations. This proactive approach not only mitigates compliance risks but also fosters a stronger partnership with regulatory bodies.
Scenario 3: Addressing Maintenance and Downtime Issues with Garbage Trucks
The Problem:
A common pain point for buyers, particularly in the Middle East and Africa, is the high maintenance costs and unexpected downtime associated with garbage trucks. For instance, a waste management company in the Middle East might experience frequent breakdowns due to harsh environmental conditions, leading to service delays and increased operational costs. This scenario not only affects the company’s bottom line but also damages its reputation among residents and local governments.
The Solution:
To minimize maintenance issues, B2B buyers should prioritize purchasing garbage trucks from manufacturers known for their reliability and after-sales support. Before making a purchase, it is advisable to request case studies or testimonials from other customers in similar environments. Additionally, buyers should invest in comprehensive training programs for their maintenance teams to ensure they are equipped to handle common repairs and maintenance tasks. Establishing a proactive maintenance schedule can significantly reduce downtime; manufacturers often provide maintenance packages that include regular check-ups and parts replacement, which can further enhance vehicle reliability and lifespan. By focusing on these proactive strategies, buyers can create a more efficient waste management operation with fewer interruptions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for garbage truck manufacturer
When selecting materials for garbage truck manufacturing, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, limitations, and the specific needs of international markets. The choice of material can significantly affect the truck’s performance, longevity, and compliance with local regulations. Below is an analysis of three common materials used in the manufacturing of garbage trucks, providing actionable insights for B2B buyers.
What are the Key Properties of Steel for Garbage Truck Manufacturing?
Steel is one of the most widely used materials in garbage truck manufacturing due to its strength and versatility. Key properties include high tensile strength, excellent impact resistance, and good weldability. Steel can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its durability, which ensures a long service life even under harsh conditions. However, steel is prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which can lead to increased maintenance costs over time. Additionally, while steel is generally cost-effective, the manufacturing complexity increases with the need for protective coatings or treatments.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various waste types, including municipal solid waste and industrial refuse. Its robustness allows for the construction of sturdy containers and chassis that can handle heavy loads.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN for steel quality. Additionally, understanding the local climate’s impact on corrosion resistance is essential for selecting the right steel grade.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Garbage Trucks?
Aluminum is gaining popularity in garbage truck manufacturing due to its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. Key properties include a high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent thermal conductivity.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its lightweight, which can lead to improved fuel efficiency and payload capacity. However, aluminum can be more expensive than steel and may require specialized welding techniques, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in urban garbage collection where frequent stops and starts occur.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions like Europe and the Middle East, where fuel efficiency standards are stringent, aluminum may be a preferred choice. Buyers should also consider local recycling capabilities, as aluminum is highly recyclable, aligning with sustainability goals.
What Role Does Composite Materials Play in Garbage Truck Manufacturing?
Composite materials, which combine different substances to enhance properties, are increasingly being used in garbage truck manufacturing. Key properties include high strength, low weight, and excellent resistance to corrosion and environmental degradation.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of composites is their ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions without significant wear. However, they can be more expensive to produce and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which can complicate supply chains.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for components exposed to corrosive elements, such as waste containers and body panels. Their lightweight nature also contributes to overall vehicle efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa and South America should assess the availability of composite materials and the expertise required for their manufacturing. Compliance with international standards for composites is also essential for ensuring product quality.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Garbage Truck Manufacturing
| Material | Typical Use Case for garbage truck manufacturer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Chassis and structural components | High durability and strength | Prone to corrosion without treatment | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight bodies and containers | Improved fuel efficiency | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Composite | Waste containers and body panels | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher production costs and complexity | High |
In conclusion, the selection of materials for garbage truck manufacturing should be guided by performance requirements, cost considerations, and compliance with local standards. By understanding the properties and implications of each material, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for garbage truck manufacturer
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Garbage Truck Production?
Manufacturing garbage trucks involves several critical stages, each contributing to the final product’s quality and performance. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Understanding these processes helps B2B buyers assess potential suppliers effectively.
How Is Material Prepared for Garbage Truck Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. High-quality raw materials, such as steel and composite materials, are selected based on durability and weight specifications. Suppliers often conduct rigorous testing to ensure materials meet necessary strength and corrosion resistance standards. Buyers should inquire about the sourcing of materials and whether they comply with international standards like ISO 9001.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Garbage Truck Manufacturing?
Once materials are prepared, the next step involves forming them into specific shapes. Common techniques include:
- Stamping: Used to create panels and components through a pressing process.
- Welding: Critical for joining different parts, ensuring structural integrity.
- Bending: Allows for the creation of complex shapes necessary for truck frames.
Understanding the forming techniques helps buyers gauge the production capabilities and potential limitations of their suppliers.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Garbage Truck Manufacturing?
After the components are formed, they undergo assembly. This stage combines various elements such as the chassis, hydraulic systems, and bodywork. Assembly often follows a standardized workflow to ensure consistency and efficiency.
What Are Common Quality Control Checkpoints During Assembly?
Quality control (QC) is integral at every stage of manufacturing. During assembly, various checkpoints are established:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Ensures that all incoming parts meet specifications before they are used in assembly.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitors the assembly process to catch any defects in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducted after assembly to verify that the final product meets all specifications.
B2B buyers should ask suppliers about their QC processes and how they handle discrepancies.
What Finishing Techniques Enhance the Quality of Garbage Trucks?
Finishing processes significantly impact the durability and appearance of garbage trucks. Techniques used include:
- Painting: Provides protection against corrosion and enhances aesthetics. Many manufacturers use eco-friendly paints to align with international environmental standards.
- Coating: Additional protective coatings can be applied to critical areas to enhance longevity.
- Polishing: Improves surface quality and can be essential for specific components.
Buyers should evaluate the finishing techniques employed by suppliers to ensure they meet their operational requirements.
How Does Quality Assurance Align with International Standards?
Quality assurance in garbage truck manufacturing is governed by several international standards. ISO 9001 is a fundamental quality management standard that ensures consistent quality in production processes.
What Industry-Specific Certifications Should B2B Buyers Look For?
Apart from ISO standards, garbage truck manufacturers may hold industry-specific certifications, including:
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for manufacturers that incorporate hydraulic components.
B2B buyers from regions like Africa and South America should verify these certifications to ensure that suppliers meet their specific regulatory requirements.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Control?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to ensure product quality. Common techniques include:
- Hydraulic Testing: Ensures that hydraulic systems function correctly and safely.
- Load Testing: Verifies that the truck can handle its designated weight without structural failure.
- Visual Inspections: Used at multiple stages to identify any visible defects.
By understanding these testing methods, buyers can better assess the reliability of a manufacturer‘s quality assurance processes.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are several actionable steps:
- Request Documentation: Buyers should ask for detailed QC reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC.
- Conduct Audits: On-site audits can provide valuable insights into the manufacturing and QC processes.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Hiring independent inspectors can validate the supplier’s claims and provide an unbiased assessment of quality standards.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of Regarding Quality Control?
B2B buyers from diverse regions, such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East, may encounter various nuances in quality control. It is essential to consider local regulations and standards that may differ from international norms.
How Do Cultural and Regulatory Differences Impact Quality Assurance?
Cultural differences can influence supplier communication and the interpretation of quality standards. Buyers should ensure that they clearly articulate their expectations and understand the supplier’s capabilities and limitations. Additionally, regulatory requirements in different regions can affect certification and compliance, making it crucial for buyers to stay informed about the specific standards applicable in their markets.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in garbage truck production is vital for international B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, assembly processes, and quality control standards, buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. Engaging with manufacturers who adhere to international standards and conducting thorough audits can further enhance the reliability of the procurement process.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘garbage truck manufacturer’
Introduction
Sourcing garbage trucks is a critical undertaking for municipalities, waste management companies, and private sector organizations in need of reliable waste collection solutions. This guide provides a practical checklist to help international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigate the complexities of sourcing a garbage truck manufacturer. By following these steps, you will ensure a thorough evaluation process that aligns with your operational needs and budget.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the first and most vital step in the procurement process. Consider the types of waste you will be collecting, the volume capacity required, and the truck’s operational environment.
- Key considerations:
- Payload capacity
- Engine type (diesel vs. electric)
- Chassis configuration (front loader, rear loader, etc.)
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct comprehensive research to identify potential garbage truck manufacturers. Utilize industry reports, trade shows, and online marketplaces to gather a list of suppliers.
- Focus on:
- Supplier reputation and history in the market
- Range of products offered
- Geographic presence and support capabilities in your region
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Before proceeding with any supplier, verify their certifications and compliance with local and international standards. This ensures the manufacturer meets safety, environmental, and operational regulations.
- Look for:
- ISO certifications
- Compliance with emission standards relevant to your region
- Any industry-specific certifications
Step 4: Request and Review Quotes
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that outline pricing, delivery timelines, and warranty information.
- Important aspects to review:
- Cost breakdown (manufacturing, shipping, and installation)
- Payment terms and conditions
- Warranty and service agreements
Step 5: Conduct Supplier Visits or Virtual Tours
If feasible, arrange to visit the manufacturing facility or request a virtual tour. This provides insight into their production processes, quality control measures, and overall operational standards.

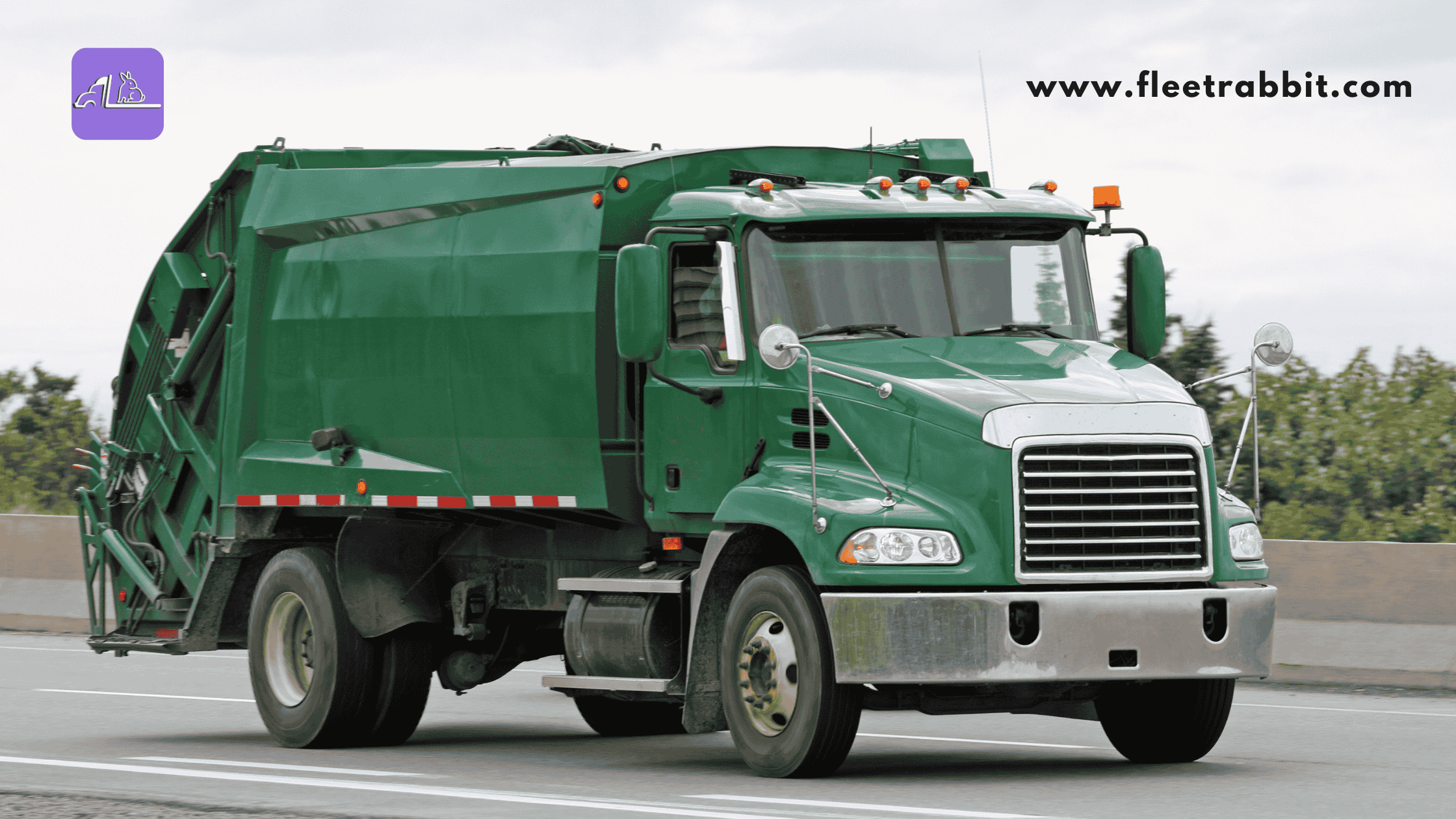
A stock image related to garbage truck manufacturer.
- What to assess:
- Quality of machinery and equipment used
- Workforce qualifications and training
- Safety protocols in place
Step 6: Check References and Customer Feedback
Reach out to existing customers or check online reviews to gauge the supplier’s reliability and customer service. Understanding the experiences of others can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s performance.
- Key questions to ask:
- How satisfied were they with the product quality?
- How responsive was the supplier to issues post-purchase?
- Would they recommend this manufacturer?
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize the Contract
Once you’ve evaluated all options, enter negotiations with your preferred supplier. Ensure that all terms, including pricing, delivery, and after-sales support, are clearly outlined in the contract.
- Considerations during negotiation:
- Flexibility in payment schedules
- Options for future purchases or upgrades
- Penalties for non-compliance or delays
By following this structured checklist, international B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for garbage truck manufacturers, ensuring they select a partner that meets their operational needs and delivers value.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for garbage truck manufacturer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Garbage Trucks?
Understanding the cost structure of garbage truck manufacturing is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The raw materials used in manufacturing garbage trucks, such as steel, aluminum, and specialized plastics, significantly influence overall costs. Fluctuations in global material prices can impact the final pricing, so it’s essential to keep track of market trends.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can affect the total cost of production. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but it’s important to consider the skill level and efficiency of the workforce.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs, making it vital to evaluate a manufacturer’s operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: The cost of molds, dies, and other tooling necessary for production can be significant. Customization may require additional tooling expenses, which should be factored into the total cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing strict quality control measures is essential to ensure the reliability and safety of garbage trucks. However, higher QC standards can lead to increased costs, which are a worthwhile investment for long-term performance.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary greatly based on the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer’s location. Understanding the logistics involved, including transportation modes and potential tariffs, is crucial for accurate cost estimation.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the industry standard for margins can provide insight into whether a quote is competitive.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Garbage Truck Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of garbage trucks, including:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate for better pricing based on their purchasing capacity.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can drive up costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certified components generally come at a premium. It’s essential to balance quality with cost to ensure the trucks meet operational requirements without overspending.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and financial stability of a supplier can impact pricing. Established manufacturers may charge more due to their proven track record, but they also bring reliability and service.
-
Incoterms: The terms of sale (Incoterms) dictate who bears the costs and risks associated with shipping. Understanding these terms can help buyers better manage logistics costs.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing Garbage Trucks?
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing garbage trucks, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Terms and Prices: Don’t accept the first price offered. Engage in negotiations to explore discounts or favorable payment terms that can enhance your overall cost structure.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, fuel efficiency, and resale value. A cheaper truck may incur higher long-term costs, so thorough evaluation is essential.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have unique pricing dynamics due to local economic conditions, tariffs, and demand-supply variations. Conduct market research to identify competitive pricing in your target region.
-
Consider Local Partnerships: Establishing relationships with local distributors or manufacturers may reduce shipping costs and lead to better service and support.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Regularly monitor material costs and market conditions. This knowledge enables buyers to make informed purchasing decisions and negotiate better deals.
Disclaimer on Pricing Information
Pricing for garbage trucks can vary significantly based on the factors outlined above. The figures provided are indicative and should be confirmed directly with manufacturers for accuracy. Always conduct due diligence when evaluating pricing to ensure a fair and competitive quote.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing garbage truck manufacturer With Other Solutions
Understanding the Importance of Alternatives in Waste Management Solutions
When considering the procurement of waste management vehicles, specifically garbage trucks, it is crucial for B2B buyers to explore various alternatives. This analysis will not only illuminate the strengths and weaknesses of traditional garbage truck manufacturers but also present other innovative solutions that may better align with specific operational needs and budgetary constraints. By understanding the complete landscape of waste collection technologies, international buyers can make informed decisions that optimize efficiency and cost-effectiveness in their operations.
Comparison Table of Garbage Truck Manufacturer vs. Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Garbage Truck Manufacturer | Automated Waste Collection System | Refuse Collection Through Third-Party Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High capacity and reliability for large-scale operations | Efficient in densely populated areas with high-frequency collection | Variable performance based on service provider capability |
| Cost | High initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs | Moderate setup cost, lower ongoing operational costs | Pay-per-service model can be cost-effective for smaller municipalities |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires significant infrastructure and training | Easier to implement in urban areas with existing technology | Minimal setup required; dependent on service provider availability |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance and skilled personnel | Lower maintenance needs due to automated systems | Outsourced maintenance, typically included in service fees |
| Best Use Case | Large municipalities and regions with high waste volumes | Urban areas with high population density | Small municipalities or businesses that generate less waste |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Automated Waste Collection Systems?
Automated Waste Collection Systems utilize advanced technologies such as pneumatic tubes and robotics to streamline the waste collection process. One of the primary advantages of this method is its efficiency in urban environments where space is limited. By minimizing the need for large trucks, these systems can reduce traffic congestion and enhance collection frequency. However, the initial setup can be moderately costly and requires careful planning and infrastructure adjustments, which may not be feasible for all municipalities, especially in developing regions.
How Do Third-Party Refuse Collection Services Compare?
Refuse Collection Through Third-Party Services offers a flexible approach to waste management, particularly for smaller municipalities or businesses that do not generate large volumes of waste. This model allows organizations to pay for services as needed, potentially saving costs on upfront investments in garbage trucks and maintenance. However, the quality and reliability of service can vary significantly depending on the provider, which poses a risk for municipalities that require consistent waste management solutions. This option may also limit control over the collection process and scheduling.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Waste Management Solution?
When selecting the appropriate waste management solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, budgetary constraints, and long-term goals. For larger municipalities with high waste volumes, investing in garbage trucks may provide the most reliable service. In contrast, urban areas with dense populations might benefit from automated systems that enhance efficiency. Alternatively, smaller organizations could explore third-party services for a cost-effective and flexible solution. Ultimately, understanding the trade-offs between these alternatives is essential for making a choice that aligns with both current needs and future growth.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for garbage truck manufacturer
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Garbage Trucks?
When considering the procurement of garbage trucks, understanding critical technical properties is essential for ensuring performance, durability, and compliance with local regulations. Here are some of the key specifications to evaluate:
1. Material Grade
Garbage trucks are typically constructed from high-strength steel or aluminum alloys to withstand harsh operating conditions. The material grade affects the truck’s weight, fuel efficiency, and resistance to corrosion. For international buyers, selecting a manufacturer that utilizes high-grade materials can lead to longer vehicle lifespans and reduced maintenance costs.
2. Payload Capacity
This specification refers to the maximum weight the truck can safely carry, including the weight of the garbage and the container. Understanding payload capacity is critical for efficiency in waste management operations, as it directly influences the number of trips required to complete collection routes. Buyers should ensure that the payload capacity aligns with their operational needs and local regulations.
3. Engine Power and Fuel Efficiency
The engine power, often measured in horsepower (HP), determines the truck’s ability to navigate various terrains and handle heavy loads. Fuel efficiency, measured in miles per gallon (MPG), is also a vital consideration, especially in regions where fuel costs are high. Manufacturers that offer advanced engine technologies can provide significant operational cost savings.
4. Tipping Mechanism
The tipping mechanism is a crucial feature that enables the efficient unloading of waste. There are various types, including rear, side, or front loaders. Understanding the different mechanisms and their suitability for specific waste management operations is essential. Buyers should consider which type best suits their collection routes and the types of waste being collected.
5. Durability and Maintenance Intervals
Durability refers to the truck’s ability to withstand wear and tear over time, while maintenance intervals indicate how often the truck requires servicing. These factors can significantly impact total cost of ownership. Buyers should inquire about the manufacturer’s warranty and recommended maintenance schedules to ensure long-term reliability.
What Common Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know?
Familiarity with industry jargon can greatly enhance communication and negotiation with manufacturers. Here are some common terms every B2B buyer should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the garbage truck industry, understanding whether a manufacturer is an OEM can indicate the quality and reliability of the components used in the truck.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest amount of product that a supplier is willing to sell. For international buyers, understanding the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. This term can also influence negotiation strategies when placing bulk orders.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. It is a vital tool for B2B buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals. Crafting a comprehensive RFQ can lead to more favorable terms and pricing.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms, such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), is essential for clarifying shipping costs and responsibilities, ensuring smoother transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time from placing an order to receiving the goods. For garbage truck procurement, understanding lead times is essential for planning and ensuring that waste management operations run smoothly. Manufacturers with shorter lead times can provide more agility in meeting urgent needs.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their waste management operations while ensuring compliance with local standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the garbage truck manufacturer Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Garbage Truck Manufacturing Sector?
The global garbage truck manufacturing sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by a combination of technological advancements, regulatory changes, and shifting consumer expectations. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
One of the primary drivers of market growth is the increasing emphasis on urbanization and population growth, which has resulted in heightened demand for efficient waste management solutions. In many African and South American cities, rapid urbanization has led to an urgent need for modern waste collection systems. Additionally, the Middle East is investing heavily in infrastructure to support smart city initiatives, integrating advanced garbage trucks equipped with IoT technologies that optimize route efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Emerging trends in B2B technology include the adoption of electric and hybrid garbage trucks, reflecting a global shift toward sustainability. In Europe, for example, regulatory frameworks are pushing for greener fleets, while manufacturers are responding by developing models that reduce emissions and fuel consumption. Moreover, automated waste collection systems are gaining traction, offering increased efficiency and safety for operators.
For buyers in these regions, staying abreast of these trends is vital. Engaging with manufacturers that prioritize innovation and sustainability can not only enhance operational efficiency but also align with broader environmental goals.
How Is Sustainability Impacting Sourcing Decisions in the Garbage Truck Manufacturing Sector?
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it is a driving force shaping sourcing decisions within the garbage truck manufacturing sector. As environmental concerns escalate globally, buyers are increasingly prioritizing ethical sourcing and the environmental impact of their purchases. This shift is particularly pronounced in Europe, where stringent regulations require compliance with sustainability standards.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers must consider the lifecycle of garbage trucks, from the materials used in manufacturing to the end-of-life recycling processes. Engaging with manufacturers that utilize sustainable materials—such as recycled steel and eco-friendly components—can help mitigate environmental impact. Furthermore, certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) signal a manufacturer’s commitment to sustainability.
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in South America and Africa, sourcing from companies that adhere to ethical practices not only supports environmental stewardship but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty. By demanding transparency in sourcing and favoring manufacturers with green certifications, buyers can contribute to a more sustainable future while also reaping the benefits of operational efficiencies.
What Is the Evolution of Garbage Truck Manufacturing and Its Relevance to Today’s Buyers?
The garbage truck manufacturing sector has undergone a remarkable evolution over the past few decades, transitioning from basic mechanical vehicles to advanced, technology-driven solutions. Early models primarily focused on functionality, with little regard for efficiency or environmental impact. However, as cities around the world have expanded and waste management needs have become more complex, manufacturers have adapted by integrating cutting-edge technologies.
In the late 20th century, innovations such as hydraulic systems and automated collection mechanisms began to emerge, significantly improving operational efficiency. Today, the focus has shifted towards sustainability and smart technologies, including GPS tracking and route optimization software, which are essential for modern waste management.
For international B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is critical. It highlights the importance of investing in garbage trucks that are not only fit for current waste management needs but are also adaptable to future challenges. This historical perspective can guide buyers in making choices that align with both immediate operational requirements and long-term sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of garbage truck manufacturer
-
How do I determine the right specifications for a garbage truck?
To identify the right specifications for a garbage truck, start by assessing your operational needs, including the types of waste you will be collecting and the volume. Consider the truck’s payload capacity, body type (such as rear-loader or side-loader), and engine specifications suitable for your terrain. Additionally, evaluate local regulations regarding waste collection and emissions standards. Engaging with experienced manufacturers can also provide insights into customization options that align with your specific requirements. -
What factors should I consider when selecting a garbage truck manufacturer?
When selecting a garbage truck manufacturer, consider their industry reputation, experience, and customer reviews. Evaluate their compliance with international quality standards such as ISO certifications. Additionally, investigate their manufacturing capabilities and technology used, as well as their after-sales support, warranty, and availability of spare parts. Building relationships with manufacturers who understand the unique challenges of your region, whether it’s Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, can also enhance your purchasing experience. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for garbage trucks?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for garbage trucks can vary significantly between manufacturers. Many will have a standard MOQ, often influenced by production capacity and shipping logistics. For international buyers, MOQs may also be affected by trade agreements or regional demand. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers, as some may offer flexibility, particularly for first-time buyers or smaller municipalities looking to upgrade their fleet. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing garbage trucks internationally?
Payment terms can differ based on the manufacturer and the size of your order. Common terms include a deposit upfront (typically 20-30%) with the balance due upon delivery or prior to shipping. Some manufacturers may offer financing options or extended payment terms for larger orders. Always clarify these terms during negotiations and ensure they are documented in your contract to avoid misunderstandings later. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when buying garbage trucks?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed product specifications and quality certifications from the manufacturer. Consider visiting their production facilities or asking for third-party inspection services to verify the manufacturing processes. Additionally, seek feedback from other customers who have purchased similar models. Establishing a clear agreement on quality standards and testing procedures before finalizing your order will also help ensure that the trucks meet your operational requirements.
A stock image related to garbage truck manufacturer.
-
What are the logistics considerations when importing garbage trucks?
Logistics for importing garbage trucks involve several key factors, including transportation methods, customs clearance, and local regulations. Assess the best shipping options (e.g., container shipping versus roll-on/roll-off) based on cost and delivery time. Work with a freight forwarder experienced in heavy machinery to navigate customs procedures efficiently. Be aware of any import duties or taxes that may apply in your country, and ensure that all necessary documentation is in order to avoid delays. -
Can I customize my garbage truck for specific waste management needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for garbage trucks to meet specific waste management needs. Customizations can include specialized bodies for different types of waste, enhanced lifting mechanisms, or additional safety features. Discuss your requirements with the manufacturer during the design phase to ensure that the modifications can be integrated effectively. This will help ensure that the truck operates efficiently within your local context and waste management practices. -
What are the best practices for maintaining garbage trucks?
Regular maintenance is essential for the longevity and performance of garbage trucks. Establish a routine maintenance schedule that includes checks on the engine, hydraulic systems, brakes, and tires. Ensure that drivers are trained in basic maintenance and reporting issues promptly. Keep a detailed maintenance log to track repairs and servicing. Additionally, partnering with the manufacturer for ongoing support and utilizing genuine spare parts will help maintain the truck’s operational efficiency and safety standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for garbage truck manufacturer
In today’s dynamic market, international B2B buyers must recognize the importance of strategic sourcing when procuring garbage trucks. By aligning procurement strategies with local needs and sustainability goals, companies can enhance their operational efficiency while reducing costs. Key takeaways include the necessity for thorough supplier evaluations, the exploration of local manufacturing options to mitigate logistics costs, and the importance of ensuring compliance with regional regulations and environmental standards.
What are the future trends in garbage truck manufacturing? As the industry evolves, innovations such as electric and hybrid models are gaining traction, particularly in regions like Europe and South America, where environmental regulations are tightening. Buyers should stay informed about these advancements and consider how they align with their operational goals and sustainability commitments.
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of garbage trucks not only fosters cost efficiency but also encourages the adoption of sustainable practices. International buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are encouraged to leverage these insights, explore partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize innovation, and commit to a procurement strategy that supports both economic and environmental objectives. The future of waste management is here—embrace it for a cleaner, more efficient tomorrow.