Discover Top Benefits of Choosing a Carbon Fiber Supplier (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for carbon fiber supplier
Navigating the global market for carbon fiber suppliers can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, especially those sourcing high-performance materials for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and renewable energy. With the increasing demand for lightweight, durable materials, understanding the nuances of carbon fiber sourcing becomes crucial. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of selecting the right carbon fiber supplier by providing a comprehensive overview of the types of carbon fibers available, their applications across various sectors, and practical strategies for vetting suppliers effectively.
In this guide, you will find actionable insights into the cost structures associated with carbon fiber products, along with tips on negotiating favorable terms with suppliers. Additionally, we will explore the regulatory landscape that influences the carbon fiber market, particularly for buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Turkey and Germany. By equipping yourself with the knowledge presented in this guide, you will empower your organization to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance product performance and sustainability.
The objective is to provide a clear roadmap for navigating this competitive landscape, enabling buyers to secure the best materials while aligning with their corporate sustainability goals. Whether you are an established manufacturer or a startup, understanding the dynamics of the carbon fiber market will position your business for success in today’s environmentally conscious economy.
Understanding carbon fiber supplier Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Suppliers | Provide carbon fiber precursors like polyacrylonitrile (PAN) | Aerospace, automotive, sports gear | Pros: Essential for production; Cons: Limited direct applications for end-users. |
| Manufacturers | Produce finished carbon fiber products in various forms | Construction, automotive, marine | Pros: Wide range of products; Cons: May have long lead times. |
| Distributors | Act as intermediaries, offering various brands and grades | General manufacturing, retail | Pros: Easy access to multiple suppliers; Cons: Potential markup costs. |
| Composite Suppliers | Specialize in carbon fiber composites with resin systems | Aerospace, medical devices | Pros: Tailored solutions; Cons: Higher complexity in sourcing. |
| Technical Service Providers | Offer expertise in carbon fiber applications and processing | R&D, product development | Pros: Invaluable technical support; Cons: May not provide physical products. |
What Are Raw Material Suppliers and Their B2B Relevance?
Raw material suppliers focus on providing the fundamental precursors needed to produce carbon fiber, such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN). These suppliers are crucial for manufacturers aiming to create high-quality carbon fiber products. B2B buyers should consider the purity and consistency of the raw materials, as these factors significantly impact the final product’s performance. Additionally, establishing a relationship with reliable raw material suppliers can lead to better pricing and supply chain stability.
How Do Manufacturers Contribute to the Carbon Fiber Supply Chain?
Manufacturers take raw materials and convert them into finished carbon fiber products, which can range from simple sheets to complex structures. They cater to various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment. Buyers must evaluate manufacturers based on their production capabilities, quality control processes, and ability to meet specific industry standards. Understanding the lead times and production flexibility is also essential when selecting a manufacturer.
Why Choose Distributors for Carbon Fiber Products?
Distributors play a vital role in the carbon fiber supply chain by providing access to multiple brands and product variations. They simplify the purchasing process for businesses looking to source carbon fiber for various applications. Buyers should assess distributors based on their inventory levels, pricing strategies, and the range of products offered. While distributors can offer convenience, buyers must be mindful of potential markup costs that can affect overall procurement budgets.
What Are Composite Suppliers and Their Applications?
Composite suppliers specialize in carbon fiber reinforced composites, which combine carbon fiber with resin systems to create lightweight and strong materials. These suppliers cater to industries like aerospace and medical devices, where performance and reliability are critical. Buyers should focus on the supplier’s expertise in composite formulation and their ability to provide tailored solutions for specific applications. The complexity of sourcing composites necessitates a thorough understanding of the supplier’s capabilities and certifications.
How Do Technical Service Providers Enhance Carbon Fiber Utilization?
Technical service providers offer specialized knowledge and support regarding carbon fiber applications and processing techniques. They assist B2B buyers in research and development, helping to optimize product performance and manufacturing processes. Buyers should consider the level of expertise and support that these providers can offer, as well as their ability to solve specific technical challenges. While they may not supply physical products, their contributions can significantly enhance the value of carbon fiber investments.
Related Video: Carbon Fiber: Everything You Wanted to Know
Key Industrial Applications of carbon fiber supplier
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of carbon fiber supplier | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Aircraft Components (e.g., wings, fuselage) | Lightweight, improved fuel efficiency, and durability | Certification standards, weight specifications, and compliance with aviation regulations |
| Automotive | High-Performance Vehicle Parts (e.g., body panels) | Enhanced performance, reduced emissions, and aesthetic appeal | Material certifications, compatibility with existing designs, and cost-effectiveness |
| Sports Equipment | High-End Sports Gear (e.g., bicycles, tennis rackets) | Superior strength-to-weight ratio, improved performance | Performance testing, customization options, and supplier reliability |
| Wind Energy | Turbine Blades | Increased efficiency and longevity of turbines | Environmental regulations, weight constraints, and sourcing from sustainable suppliers |
| Construction | Structural Reinforcements | Enhanced load-bearing capacity and reduced weight | Compliance with building codes, fire resistance, and long-term durability |
How is Carbon Fiber Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, carbon fiber is utilized for manufacturing critical components such as wings, fuselage, and other structural elements. The lightweight nature of carbon fiber significantly improves fuel efficiency, reducing operational costs for airlines. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and the Middle East, need to consider compliance with stringent certification standards and aviation regulations, ensuring that sourced materials meet safety and performance benchmarks.
What Role Does Carbon Fiber Play in the Automotive Industry?
In automotive applications, carbon fiber is increasingly used for high-performance vehicle parts, including body panels and chassis components. The material’s strength and lightweight characteristics contribute to enhanced vehicle performance and reduced emissions, appealing to environmentally conscious manufacturers. B2B buyers from Europe and South America should focus on material certifications and compatibility with existing vehicle designs to ensure seamless integration.
How is Carbon Fiber Transforming Sports Equipment?
The sports equipment industry leverages carbon fiber for creating high-end gear like bicycles and tennis rackets, capitalizing on its superior strength-to-weight ratio. This results in improved performance and durability, making products more appealing to professional athletes and enthusiasts alike. Buyers in these markets should prioritize performance testing and customization options to meet the specific needs of their target audience.
What are the Benefits of Carbon Fiber in Wind Energy?
In wind energy, carbon fiber is employed in the manufacturing of turbine blades, where its lightweight and durable properties lead to increased efficiency and longevity. This application is crucial as the renewable energy sector seeks to optimize performance and reduce maintenance costs. Buyers must consider environmental regulations and weight constraints when sourcing carbon fiber for this application, ensuring sustainability and compliance with industry standards.
How Does Carbon Fiber Enhance Construction Materials?
Within the construction industry, carbon fiber is used for structural reinforcements, providing enhanced load-bearing capacity while minimizing weight. This is particularly advantageous in high-rise buildings and infrastructure projects. International B2B buyers should focus on compliance with local building codes and fire resistance requirements to ensure the safety and durability of the materials used in their projects.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘carbon fiber supplier’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: High Cost of Carbon Fiber Materials
The Problem:
B2B buyers often encounter the challenge of high costs associated with sourcing carbon fiber materials. This is particularly pronounced for companies in Africa and South America where supply chains may be less developed, leading to inflated prices. Many buyers find themselves struggling to justify these costs against budget constraints, especially when competing with manufacturers in Europe and the Middle East that may have better access to suppliers and more favorable pricing structures.
The Solution:
To mitigate high costs, international buyers should consider a multi-faceted approach. First, conduct thorough market research to identify multiple suppliers within and outside your region. This may include sourcing from countries with a robust carbon fiber production industry, such as Germany or Turkey. Establish relationships with local suppliers who can provide insights into bulk purchasing and potential discounts.
Additionally, engaging in collaborative purchasing with other companies in your sector can drive costs down. Forming a consortium can provide the leverage needed to negotiate better terms. Finally, consider the long-term benefits of investing in carbon fiber. Although the upfront costs are higher compared to traditional materials, the durability and lightweight properties of carbon fiber can lead to significant savings in operational costs over time.

A stock image related to carbon fiber supplier.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality of Carbon Fiber Products
The Problem:
Another common issue faced by B2B buyers is the inconsistency in the quality of carbon fiber products. This inconsistency can stem from variations in manufacturing processes, raw materials, or even supplier practices. For companies in the Middle East, where projects often demand high precision and reliability, receiving subpar materials can lead to project delays and increased costs.
The Solution:
To address quality concerns, buyers should implement a rigorous vetting process when selecting carbon fiber suppliers. Request samples and conduct tests to verify the material’s properties, such as tensile strength and weight. Establish clear quality standards and communicate them to potential suppliers, ensuring they understand your specific requirements.
Additionally, consider suppliers that are certified by recognized industry standards, which can serve as a benchmark for quality assurance. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also foster a mutual understanding of quality expectations, leading to improved consistency over time. Finally, incorporating a quality control process during the procurement phase can help catch discrepancies early and prevent costly mistakes.
Scenario 3: Navigating Regulatory Compliance for Carbon Fiber Use
The Problem:
Navigating the complex landscape of regulatory compliance is a significant pain point for international B2B buyers of carbon fiber products. Different regions, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, have stringent regulations regarding material usage, recycling, and environmental impacts. This can leave buyers confused about what standards to meet, potentially leading to legal challenges or project delays.
The Solution:
To effectively navigate regulatory compliance, B2B buyers must stay informed about the local and international regulations that affect their industry. This can be achieved through regular consultations with legal experts who specialize in trade and environmental regulations. Additionally, suppliers should be vetted not only for their product quality but also for their compliance with relevant regulations.
Investing in training for your procurement team on compliance issues can further streamline this process. Encourage your team to develop a compliance checklist that includes all necessary regulations for carbon fiber usage in your specific market. Lastly, consider engaging with industry associations that can provide resources and updates on regulatory changes, helping you stay ahead of compliance issues before they impact your operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for carbon fiber supplier
When selecting materials for carbon fiber applications, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including material properties, performance characteristics, and compliance with regional standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in conjunction with carbon fiber, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations relevant to buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Epoxy Resins in Carbon Fiber Applications?
Epoxy resins are frequently used as a matrix material in carbon fiber composites due to their excellent adhesion, mechanical properties, and thermal stability. They typically exhibit high tensile strength and rigidity, making them suitable for high-performance applications. Additionally, epoxy resins can withstand temperatures up to 150°C (302°F) and provide good resistance to chemicals and moisture.
Pros:
– Exceptional mechanical strength and stiffness.
– Good chemical resistance and thermal stability.
– Versatile in application, suitable for aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods.
Cons:
– Higher manufacturing complexity due to curing processes.
– Generally more expensive than other resin systems.
– Limited flexibility, which may not be suitable for all applications.
Impact on Application:
Epoxy resins are highly compatible with various media, making them ideal for demanding environments. However, buyers should ensure that the specific epoxy formulation meets the required performance criteria for their applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with standards such as ASTM D638 for tensile properties is crucial. Buyers in Europe, especially in Germany, should also consider the DIN standards for composite materials.
How Do Polyurethane Resins Compare in Carbon Fiber Composites?
Polyurethane resins offer a balance between flexibility and strength, making them suitable for applications requiring impact resistance. They can operate effectively in temperatures ranging from -30°C to 80°C (-22°F to 176°F) and are known for their excellent abrasion resistance.
Pros:
– Good flexibility and impact resistance.
– Lower cost compared to epoxy resins.
– Easier to process, allowing for faster production cycles.
Cons:
– Lower thermal stability compared to epoxy.
– Susceptible to UV degradation without proper additives.
– May not provide the same level of mechanical performance as epoxy.
Impact on Application:
Polyurethane’s flexibility makes it suitable for applications like automotive parts, where impact resistance is critical. However, its lower thermal resistance may limit its use in high-temperature environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that polyurethane formulations comply with local regulations regarding VOC emissions, especially in Europe, where environmental standards are stringent.
What Are the Advantages of Vinyl Ester Resins in Carbon Fiber?
Vinyl ester resins are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and are often used in marine and chemical applications. They can withstand temperatures up to 120°C (248°F) and provide good mechanical properties.
Pros:
– Superior corrosion resistance compared to epoxy.
– Good mechanical properties and thermal stability.
– Lower viscosity allows for easier processing.
Cons:
– Generally more expensive than standard epoxy resins.
– Limited availability in some regions.
– May require specific curing conditions to achieve optimal properties.
Impact on Application:
Vinyl ester resins are particularly effective in applications involving exposure to harsh chemicals or marine environments. Buyers should consider the specific chemical compatibility when selecting this material.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with ASTM D256 for impact resistance is essential. Buyers in the Middle East and Africa should also consider local environmental regulations regarding resin use.
How Do Thermoplastic Composites Enhance Carbon Fiber Applications?
Thermoplastic composites, such as polyamide and polypropylene, offer unique advantages, including reprocessability and toughness. They can be processed at lower temperatures, making them suitable for applications requiring rapid production cycles.
Pros:
– Recyclable and can be reshaped without degradation.
– High impact resistance and toughness.
– Faster processing times compared to thermosetting resins.
Cons:
– Generally lower mechanical properties than thermosetting resins.
– Limited temperature resistance, typically up to 100°C (212°F).
– May require specialized processing equipment.
Impact on Application:
Thermoplastic composites are ideal for applications in automotive and consumer goods where weight reduction and recyclability are priorities. However, their lower thermal stability may limit their use in high-performance environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should evaluate compliance with standards such as ISO 527 for tensile properties. In Europe, adherence to REACH regulations regarding material safety is also vital.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Carbon Fiber Suppliers
| Material | Typical Use Case for carbon fiber supplier | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy Resins | Aerospace and automotive components | Exceptional mechanical strength | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
| Polyurethane Resins | Automotive parts requiring impact resistance | Good flexibility and lower cost | Lower thermal stability | Medium |
| Vinyl Ester Resins | Marine and chemical applications | Superior corrosion resistance | Limited availability | High |
| Thermoplastic Composites | Automotive and consumer goods | Recyclable and faster processing | Lower mechanical properties | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of common materials used in carbon fiber applications, equipping international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions tailored to their specific market needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for carbon fiber supplier
What Are the Main Stages of Carbon Fiber Manufacturing?
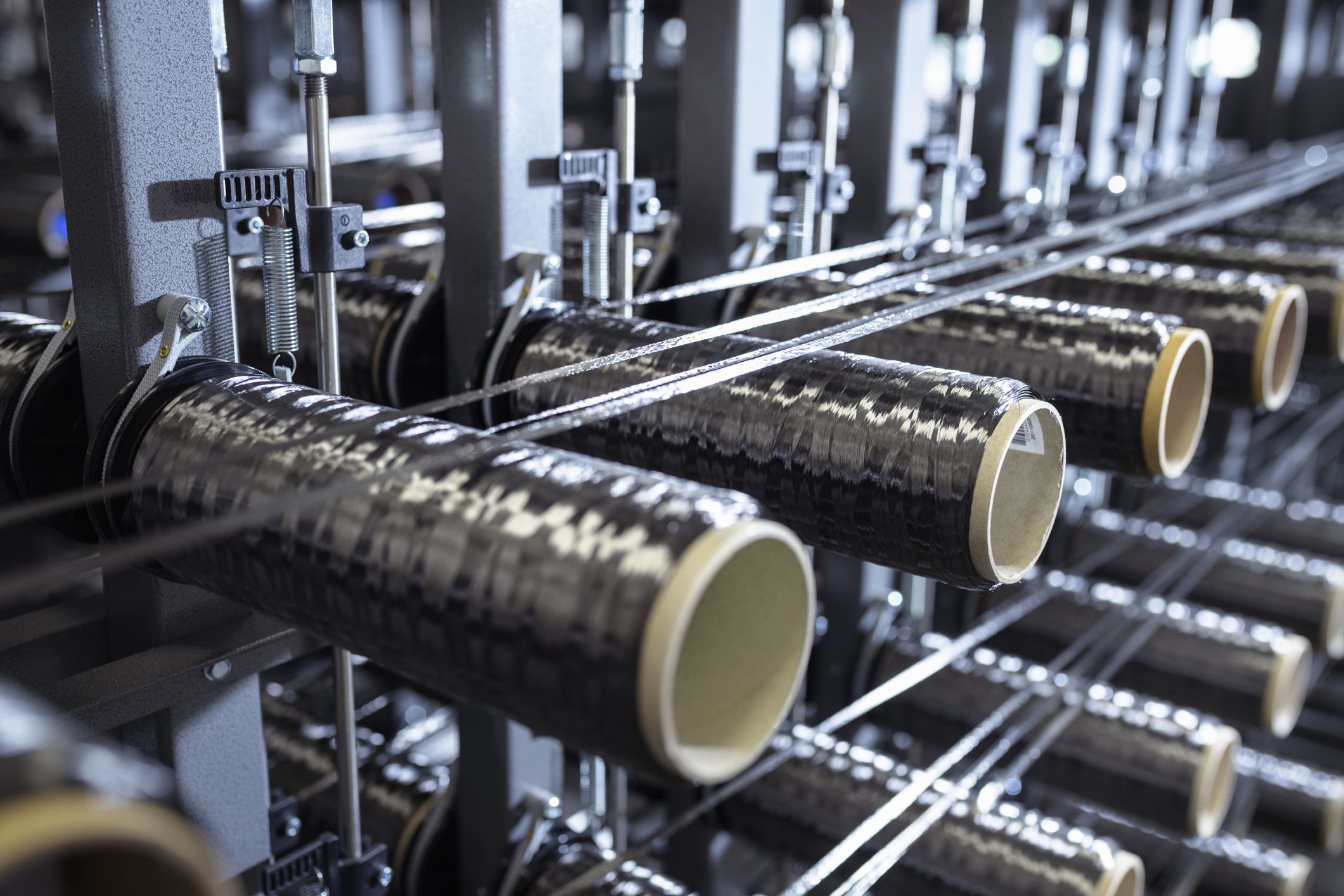
A stock image related to carbon fiber supplier.
The manufacturing process of carbon fiber involves several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality materials suitable for various applications. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing from international suppliers.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the carbon fiber manufacturing process is the preparation of raw materials. Typically, polyacrylonitrile (PAN) is the primary precursor used. The PAN is subjected to processes such as spinning, which transforms it into fibers. The quality of the precursor significantly influences the final product’s strength and rigidity.
Key techniques in this stage include:
– Polymer spinning: This involves dissolving PAN in a solvent and extruding it through spinnerets to form filaments.
– Stabilization: The fibers are heated in air to stabilize them chemically, which prepares them for the carbonization process.
2. Forming
Once the fibers are prepared, they undergo a forming process. This step involves aligning the fibers to optimize their strength characteristics.
Techniques used in the forming stage include:
– Filament winding: This involves wrapping fibers around a mold to create composite shapes.
– Pultrusion: A continuous process that pulls fibers through a resin bath and then through a heated die to form solid shapes.
3. Assembly
In the assembly stage, the formed carbon fiber components are combined with other materials, such as resins or adhesives, to create composite structures. This stage is crucial for ensuring that the final product meets specific performance standards.
Key methods include:
– Layup: Manually placing layers of carbon fiber and resin into a mold.
– Vacuum bagging: A technique that removes air from the assembly to enhance bonding and reduce voids.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves finishing processes that enhance the appearance and performance of the carbon fiber products. This may include cutting, sanding, and applying protective coatings.
Techniques in this stage may involve:
– Surface treatment: Improving adhesion properties through chemical or mechanical processes.
– Quality coating: Applying a protective layer to enhance durability and resistance to environmental factors.
How Do Quality Assurance Measures Ensure Product Integrity?
Quality assurance (QA) is a pivotal aspect of the carbon fiber manufacturing process. For international B2B buyers, understanding the QA framework is essential to ensure that the products meet industry standards and specifications.
Relevant International Standards
Suppliers often adhere to various international quality standards to maintain product integrity. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: A widely recognized standard for quality management systems that ensures consistent product quality and customer satisfaction.
- ISO 14001: Focuses on effective environmental management, crucial for suppliers aiming to minimize their ecological footprint.
- Specific Industry Standards: Depending on the application, additional certifications may be required, such as CE marking for European markets or API standards for oil and gas applications.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is integrated at multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial check ensures that raw materials meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during manufacturing to monitor process stability and product quality.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive evaluation of the finished products to ensure they meet the defined specifications before shipment.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Carbon Fiber Production?
To guarantee that carbon fiber products meet the required performance criteria, several testing methods are employed:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the strength and elongation of carbon fibers under stress.
- Flexural Testing: Assesses the material’s ability to withstand bending forces.
- Impact Testing: Determines the toughness of the material by measuring its resistance to impact forces.
- Thermal Analysis: Evaluates the thermal stability and decomposition temperatures of the fibers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the QC processes of a carbon fiber supplier is crucial. Here are actionable strategies:
Conduct Supplier Audits
Regular audits are essential for assessing a supplier’s compliance with quality standards. Buyers should request to conduct on-site audits to evaluate the manufacturing processes, equipment, and quality management systems in place.
Request Quality Reports
Buyers should ask for detailed quality reports that outline the testing methods used, results obtained, and any corrective actions taken for non-conformities. This transparency helps build trust between buyers and suppliers.
Engage Third-Party Inspectors
Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s QC processes. These inspectors can conduct random checks and verify that the products meet the required specifications.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International Buyers?
When sourcing carbon fiber products from different regions, buyers must be aware of specific nuances in QC practices:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different countries may have varying regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact. It’s important for buyers to ensure that their suppliers comply with the regulations relevant to their target market.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural nuances can help buyers communicate their quality expectations more effectively. For instance, in regions like Turkey or Germany, the emphasis on documentation and formal processes may differ.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should prioritize suppliers who maintain a transparent supply chain, as this enhances traceability and accountability in quality assurance.
By gaining a deeper understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting carbon fiber suppliers, ultimately leading to successful partnerships and high-quality product outcomes.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘carbon fiber supplier’
In the competitive landscape of carbon fiber procurement, international B2B buyers must adopt a systematic approach to ensure they select the right supplier. This practical sourcing guide provides a step-by-step checklist designed to help you navigate the complexities of sourcing carbon fiber. By following these steps, you can mitigate risks, ensure quality, and establish fruitful partnerships.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements for carbon fiber products. This includes dimensions, tensile strength, weight, and any specific performance characteristics needed for your application.
– Tip: Create a comprehensive specification document to share with potential suppliers, ensuring they understand your needs from the outset.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a strong reputation in the carbon fiber industry. Utilize online directories, industry publications, and trade shows to gather a list of potential candidates.
– Consider: Look for suppliers who have experience in your specific market segment, as they will be more familiar with your needs and regulations.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Confirm that potential suppliers possess the necessary certifications and comply with international standards. This may include ISO 9001 for quality management or specific certifications relevant to your industry.
– Why It Matters: Compliance ensures that the products you receive meet safety and quality benchmarks, reducing the risk of costly failures.
Step 4: Request Samples and Test Quality
Once you’ve shortlisted suppliers, request samples of their carbon fiber products. Testing these samples against your specifications will provide insight into their quality and performance.
– Actionable Insight: Perform independent testing if possible to verify the material’s characteristics align with your requirements.
Step 5: Assess Supplier Capabilities and Reliability
Inquire about the supplier’s production capabilities, lead times, and ability to scale with your business needs. Reliable suppliers should demonstrate flexibility and the capacity to meet fluctuating demands.
– Key Questions: Ask about their production processes, technology used, and contingency plans for supply chain disruptions.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Ensure that you understand all costs involved, including shipping and potential tariffs, especially when dealing with international suppliers.
– Best Practice: Aim for a transparent negotiation process where both parties feel valued, setting the stage for a strong business relationship.
Step 7: Establish a Clear Communication Plan
Once you’ve selected a supplier, establish a communication plan that outlines how you will interact throughout the partnership. Regular updates and feedback loops are essential for addressing issues promptly.
– Tip: Use project management tools to track progress and maintain open lines of communication, ensuring alignment on expectations and deliverables.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process, ensuring they select the right carbon fiber supplier that meets their technical and business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for carbon fiber supplier Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Carbon Fiber Supplier Sourcing?
When sourcing carbon fiber, understanding the cost structure is essential for international B2B buyers. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: The primary expense often relates to the carbon fiber itself, which can vary significantly based on the type (e.g., standard, intermediate, or high modulus). Bulk purchasing can lead to reduced prices, making it advantageous for buyers who can meet minimum order quantities (MOQs).
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for the production and handling of carbon fiber materials. Labor costs can fluctuate based on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing processes involved.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs associated with factory operations, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help lower these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling is often necessary for specialized applications, contributing to the initial setup costs. Buyers should consider whether the supplier can absorb these costs or if they will be passed on.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is vital, especially for applications in sectors like aerospace and automotive. This involves testing and inspection processes, which can increase costs but are necessary to meet safety standards.
-
Logistics: The cost of transporting carbon fiber materials can vary widely depending on the distance, shipping methods, and whether the supplier covers these costs. Buyers should factor in logistics when evaluating total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on supplier reputation, market demand, and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Carbon Fiber Procurement?
Several factors can influence the pricing of carbon fiber, which international buyers must consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes usually lead to lower unit prices. Buyers should assess their needs to negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can drive up costs. Buyers should clarify their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The quality of raw materials and any necessary certifications (e.g., ISO) can significantly affect pricing. Ensuring that suppliers meet required standards is crucial for project success.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier experience, reputation, and reliability can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting overall costs.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Their Carbon Fiber Sourcing Costs?
For international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are actionable tips:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage your purchasing power. Suppliers are often willing to negotiate terms, especially for large orders or long-term contracts.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also logistics, maintenance, and potential rework costs. This holistic view can uncover hidden savings.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware that prices can vary based on market conditions, currency fluctuations, and geopolitical factors. Regularly review supplier pricing and market trends to make informed decisions.
-
Evaluate Multiple Suppliers: Obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing and terms. This can provide leverage in negotiations and help identify the best value.
- Build Strong Relationships: Cultivating a good relationship with suppliers can lead to better terms, priority service, and insights into upcoming price changes.
Conclusion
While sourcing carbon fiber involves various cost components and price influencers, international B2B buyers can optimize their procurement strategies by understanding these elements. By negotiating effectively and focusing on the total cost of ownership, buyers can make more informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Always consider that indicative prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, so continuous monitoring is essential for maintaining cost efficiency.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing carbon fiber supplier With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Carbon Fiber Suppliers
In the quest for advanced materials, international B2B buyers are increasingly exploring various alternatives to carbon fiber. These alternatives can provide similar benefits in terms of performance and weight reduction, while potentially offering different cost structures and application scenarios. This analysis will delve into two notable alternatives: fiberglass and aramid fibers, providing a detailed comparison to help buyers make informed decisions.
Comparison Table of Carbon Fiber and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Carbon Fiber Supplier | Fiberglass | Aramid Fibers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent stiffness | Good tensile strength, heavier | Excellent impact resistance, moderate weight |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to manufacturing complexity | Lower cost, widely available | Moderate cost, varies with application |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized handling and curing processes | Easier to work with, less specialized equipment needed | Requires specific processing techniques |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance but sensitive to impact damage | Good durability, less sensitive | Moderate maintenance, can degrade under UV |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, high-performance automotive | Construction, marine applications | Bulletproof vests, aerospace components |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Fiberglass?
Fiberglass is a composite material made from glass fibers and resin. It is known for its affordability and ease of manufacturing, making it a popular choice in various industries.
Pros:
– Cost-Effective: Fiberglass is typically much cheaper than carbon fiber, allowing companies to reduce material costs significantly.
– Ease of Use: It is easier to mold and shape, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from construction to automotive.
Cons:
– Lower Performance: Although fiberglass has decent tensile strength, it does not match the performance metrics of carbon fiber, particularly in weight-to-strength ratios.
– Weight: Fiberglass is generally heavier than carbon fiber, which may be a drawback in industries where weight is critical, such as aerospace.
How Do Aramid Fibers Compare to Carbon Fiber?
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are known for their high strength and resistance to abrasion and impact. They are commonly used in applications requiring durability and flexibility.
Pros:
– Impact Resistance: Aramid fibers excel in applications where impact resistance is crucial, such as personal protective equipment and certain aerospace components.
– Weight: While they are heavier than carbon fibers, they offer a good balance of weight and strength.
Cons:
– Cost Variability: The cost of aramid fibers can vary widely based on the application and the specific type of fiber used, which may complicate budgeting.
– Processing Complexity: They require specific processing techniques that may not be readily available in all manufacturing environments.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When evaluating alternatives to carbon fiber suppliers, B2B buyers should consider their specific needs, including application requirements, budget constraints, and manufacturing capabilities. Conducting a thorough assessment of each alternative’s performance characteristics and cost-effectiveness will help businesses select the most suitable material for their projects. Additionally, engaging with suppliers for insights on material properties and processing can provide valuable information for making a well-informed decision. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on balancing performance needs with financial considerations and operational capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for carbon fiber supplier
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Carbon Fiber?
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific formulation of carbon fiber, which can significantly impact its strength, stiffness, and weight. Common grades include standard modulus and intermediate modulus, with higher grades providing increased performance. Understanding material grades is crucial for B2B buyers as it directly affects the final product’s performance in applications like aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment.
2. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength is a measure of how much load a carbon fiber can withstand while being stretched before failing. This property is vital in applications where high strength-to-weight ratios are needed. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that provide detailed tensile strength specifications to ensure the material meets the requirements of their specific projects.
3. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in the dimensions of the carbon fiber products, such as thickness and width. In B2B transactions, precise tolerances are essential for ensuring that components fit correctly in larger assemblies, particularly in industries like aerospace and automotive where precision is critical. Buyers should inquire about tolerance levels to avoid costly rework or product failures.
4. Fiber Diameter
The diameter of carbon fibers can vary, typically ranging from 5 to 15 micrometers. This property influences the fiber’s mechanical properties and how it interacts with resin systems during composite manufacturing. B2B buyers must consider fiber diameter when selecting materials for specific applications, as it can affect the overall performance and durability of the final product.
5. Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity indicates how well carbon fiber can conduct heat. This property is particularly important for applications in electronics and automotive industries, where heat dissipation is critical. Buyers should assess the thermal properties of carbon fiber to ensure they align with the thermal management needs of their applications.
Which Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand When Sourcing Carbon Fiber?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding this term is essential for B2B buyers as it can dictate the quality and compatibility of carbon fiber products with existing equipment. Buyers should look for OEM-certified suppliers to ensure they receive high-quality materials.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers as it affects purchasing decisions, inventory management, and cash flow. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs to avoid overstocking or underordering.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process where a buyer requests pricing and availability for specific products from suppliers. Utilizing RFQs can help B2B buyers compare prices and terms across different suppliers, ensuring they get the best deal for their carbon fiber sourcing needs.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the delivery of goods. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Buyers should familiarize themselves with terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) to manage their logistics effectively.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is crucial for planning and production schedules. Buyers should communicate their timeline requirements clearly to suppliers to ensure timely delivery and avoid production delays.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing carbon fiber, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the carbon fiber supplier Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Carbon Fiber Supplier Sector?
The global carbon fiber market is currently experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries such as aerospace, automotive, and renewable energy. According to recent market analyses, the sector is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 10% over the next five years. Key drivers include the push for lightweight materials that enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, aligning with global sustainability goals.
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial. Emerging technologies such as advanced manufacturing processes and automation are reshaping sourcing strategies. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that leverage digital platforms for inventory management and supply chain transparency. This shift not only enhances efficiency but also facilitates real-time collaboration with suppliers, which is vital for meeting the rapid pace of market demands.
Moreover, geopolitical factors and trade policies can significantly influence sourcing trends. For instance, European buyers may face different tariffs and regulations compared to those sourcing from South America or Africa. It’s essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about these regulations, as they can impact overall procurement costs and timelines.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influence Carbon Fiber Supply Chains?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of procurement strategies in the carbon fiber supplier sector. The environmental impact of carbon fiber production, particularly regarding energy consumption and carbon emissions, has prompted buyers to seek out suppliers committed to sustainable practices. This includes the use of renewable energy in production processes and the development of recycled carbon fibers, which can significantly reduce waste.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as stakeholders are increasingly scrutinizing supply chains for social responsibility. Buyers are encouraged to partner with suppliers who prioritize fair labor practices and ethical sourcing of raw materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Oeko-Tex (for textiles) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Furthermore, as climate regulations tighten globally, suppliers that adopt green certifications and sustainable materials will likely enjoy a competitive advantage. B2B buyers should prioritize these suppliers, not only to comply with regulations but also to enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Carbon Fiber Industry Relevant to B2B Buyers?
The carbon fiber industry has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1960s. Initially developed for aerospace applications due to its high strength-to-weight ratio, the material has gradually found its way into various sectors, including automotive and sports equipment.
In recent years, advancements in manufacturing techniques, such as the introduction of automated fiber placement and 3D printing, have reduced production costs and expanded the accessibility of carbon fiber to smaller businesses. This evolution has opened new opportunities for B2B buyers, enabling them to incorporate carbon fiber into innovative products without the prohibitive costs that once defined the sector.
Today, as the industry continues to innovate, B2B buyers must remain agile, adapting their sourcing strategies to leverage the latest technological advancements while also prioritizing sustainability and ethical practices in their supply chains. Understanding the historical context of carbon fiber can aid buyers in making informed decisions as they navigate this dynamic market landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of carbon fiber supplier
-
How do I choose the right carbon fiber supplier for my business needs?
Choosing the right carbon fiber supplier involves evaluating several key factors. Start by assessing the supplier’s experience and expertise in the industry, including their production capacity and technological capabilities. Request samples to gauge quality, and check for certifications that demonstrate compliance with international standards. Additionally, consider their ability to offer customization options, as well as their responsiveness and reliability in communication. Finally, review customer testimonials and case studies to understand their track record with businesses similar to yours. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for carbon fiber products?
Minimum order quantities for carbon fiber products can vary significantly among suppliers, typically ranging from a few kilograms to several tons. Smaller suppliers may offer lower MOQs, which can be advantageous for startups or businesses testing new applications. Conversely, larger suppliers might have higher MOQs but can provide economies of scale. When sourcing, inquire about flexibility in MOQs and whether they can accommodate smaller orders for prototypes or specialized projects without compromising on quality. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with a carbon fiber supplier?
When negotiating payment terms with a carbon fiber supplier, consider options such as net 30, 60, or 90 days, depending on your cash flow needs. It’s also essential to discuss upfront payments, especially for custom orders. Ensure that the payment methods are secure and convenient, including options like bank transfers, credit cards, or letters of credit. Additionally, clarify any penalties for late payments and potential discounts for early settlements, as these can significantly impact your overall costs. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing carbon fiber?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing carbon fiber, implement a robust vetting process for potential suppliers. Request documentation of their quality control processes, including certifications like ISO 9001. Conduct on-site inspections or audits if possible, and ask for third-party test results of their products. Establish clear specifications and testing standards in your purchase agreements, and consider implementing a quality assurance plan that includes regular inspections and feedback loops to address any quality issues promptly. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing carbon fiber?
When importing carbon fiber, logistics considerations are crucial for timely delivery and cost management. Assess shipping options that align with your budget and urgency, such as air freight for speed versus ocean freight for cost savings. Be aware of customs regulations and tariffs in your country, as these can affect overall costs. Work closely with your supplier to ensure proper documentation is provided to facilitate smooth customs clearance, and consider partnering with a logistics provider experienced in handling international shipments of specialized materials. -
How does the carbon fiber supply chain impact pricing for buyers?
The carbon fiber supply chain is complex and can significantly impact pricing for buyers. Factors such as raw material availability, production processes, and transportation costs all play a role. Global events, such as trade disputes or supply shortages, can further influence prices. Buyers should stay informed about market trends and potential disruptions and consider building long-term relationships with suppliers to negotiate better pricing and terms. Additionally, bulk purchasing or entering into long-term contracts can help mitigate price volatility. -
What customization options are typically available when ordering carbon fiber products?
Customization options for carbon fiber products can include variations in weave patterns, resin types, thickness, and shapes. Many suppliers offer tailored solutions to meet specific application requirements, such as aerospace, automotive, or sporting goods. When discussing customization, clearly articulate your needs and provide detailed specifications. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s ability to produce prototypes or small batches for testing before committing to larger orders, which can help ensure that the final product meets your expectations. -
How do carbon taxes and sustainability initiatives affect carbon fiber sourcing?
Carbon taxes and sustainability initiatives are increasingly influencing sourcing decisions for carbon fiber. As governments implement regulations to combat climate change, suppliers may face additional costs associated with carbon emissions, which can be passed on to buyers. Companies committed to sustainability should seek suppliers that prioritize eco-friendly practices, such as using recycled materials or low-emission production methods. Understanding the regulatory landscape in your region can help you make informed sourcing decisions that align with your company’s sustainability goals while potentially reducing future compliance costs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for carbon fiber supplier
As the demand for lightweight and high-strength materials like carbon fiber continues to rise across various industries, strategic sourcing has become a critical component for international B2B buyers. By focusing on long-term partnerships with reliable carbon fiber suppliers, businesses can enhance their supply chain resilience, reduce costs, and improve product quality. Buyers must prioritize suppliers who not only provide competitive pricing but also demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, particularly in light of increasing regulations around carbon emissions and environmental impact.
How Can B2B Buyers Leverage Global Trends in Carbon Fiber Sourcing?
Navigating the complexities of the carbon fiber market requires an understanding of regional dynamics and emerging trends. For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, engaging with suppliers who are aligned with global sustainability goals can open new opportunities. This strategic approach not only meets regulatory requirements but also positions companies as leaders in innovation and sustainability.
In conclusion, the outlook for carbon fiber sourcing is promising, with significant growth anticipated in various sectors. By taking proactive steps today—such as conducting thorough market research, fostering supplier relationships, and prioritizing sustainability—international B2B buyers can secure a competitive advantage. Embrace the future of sourcing by partnering with carbon fiber suppliers who align with your strategic goals and values.