Discover Top Benefits of Sourcing a Microscope Manufacturer (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for microscope manufacturer
In today’s rapidly evolving scientific landscape, sourcing the right microscope manufacturer can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers. With a plethora of options available, international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must navigate a complex market to identify suppliers that align with their specific needs. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, addressing critical aspects such as the various types of microscopes, their applications across industries, effective supplier vetting processes, and factors influencing cost.
As a decision-maker, understanding the nuances of microscope procurement is essential to making informed purchasing choices. Whether you are seeking high-precision optical microscopes for research labs or digital models for educational institutions, this guide will empower you with actionable insights. We delve into the key considerations for evaluating manufacturers, including quality assurance, technological advancements, and after-sales support—elements that are crucial for ensuring long-term satisfaction and operational efficiency.
By equipping yourself with the knowledge contained in this guide, you will be better positioned to assess potential suppliers and negotiate favorable terms. The aim is to facilitate a seamless sourcing experience that ultimately enhances your organization’s capabilities, driving innovation and success in your respective field.
Understanding microscope manufacturer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optical Microscopes | Utilize visible light and lenses for magnification | Education, Research Labs | Pros: Simple to use, cost-effective. Cons: Limited magnification compared to digital options. |
| Electron Microscopes | Use electron beams for high-resolution imaging | Material Science, Nanotechnology | Pros: Extremely high magnification, detailed imaging. Cons: Expensive, complex operation. |
| Digital Microscopes | Integrate cameras for digital imaging and analysis | Quality Control, Telemedicine | Pros: Easy data sharing, enhanced image processing. Cons: May require software training. |
| Confocal Microscopes | Use laser scanning for 3D imaging | Biomedical Research, Drug Development | Pros: High-resolution 3D images, reduces background noise. Cons: High cost, requires technical expertise. |
| Stereomicroscopes | Provide 3D imaging through lower magnification | Assembly, Repair, Fieldwork | Pros: User-friendly, great depth perception. Cons: Limited magnification, not suitable for fine details. |
What Are the Characteristics of Optical Microscopes?
Optical microscopes are fundamental tools in laboratories and educational settings, utilizing visible light to magnify samples. They are characterized by their simple design, which includes lenses and light sources. These microscopes are suitable for observing biological specimens, slides, and other transparent materials. When purchasing, buyers should consider factors such as magnification power, ease of use, and maintenance costs, making them ideal for budget-conscious organizations.
How Do Electron Microscopes Stand Out?
Electron microscopes are advanced instruments that employ electron beams instead of light, allowing for incredibly high magnification and resolution. They are essential in fields such as material science and nanotechnology for analyzing microstructures. While they offer unparalleled detail, buyers must be aware of their high cost and the complexity of operation, necessitating skilled personnel for effective use. Organizations should evaluate their specific research needs against the investment required.
What Are the Benefits of Digital Microscopes?
Digital microscopes combine optical systems with digital cameras, enabling real-time imaging and data analysis. They are widely used in quality control and telemedicine, where remote diagnostics are crucial. The ability to capture, store, and share images digitally enhances collaboration and documentation. However, potential buyers should consider the training needed for software use and the overall cost of ownership, balancing these with the benefits of modern imaging technology.
Why Choose Confocal Microscopes for Research?
Confocal microscopes are specialized devices that utilize laser scanning to create high-resolution, three-dimensional images of specimens. They are particularly valuable in biomedical research and drug development, where precise imaging is critical. While they provide superior image quality and the ability to reduce background noise, the high price point and requirement for technical expertise can be barriers for some organizations. Buyers should assess their research goals and budget when considering this option.
How Do Stereomicroscopes Facilitate Fieldwork?
Stereomicroscopes are designed for low magnification and provide a three-dimensional view of larger samples, making them ideal for assembly, repair, and fieldwork applications. Their user-friendly nature and excellent depth perception are significant advantages, especially in practical settings. However, they are not suitable for fine detail work due to their limited magnification capabilities. Buyers should weigh the benefits of ease of use against the need for higher magnification in specific applications.
Key Industrial Applications of microscope manufacturer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Microscope Manufacturer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Cellular Analysis in Pathology | Enhances diagnostic accuracy, leading to better patient outcomes. | Quality assurance, regulatory compliance, and service support. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Drug Development and Quality Control | Ensures product safety and efficacy through detailed analysis. | Precision in imaging, reliability, and availability of consumables. |
| Material Science | Failure Analysis of Materials | Identifies defects and enhances material performance. | Technical support, customization options, and warranty terms. |
| Education and Research | Advanced Microscopy for Research and Teaching | Facilitates cutting-edge research and enhances learning experiences. | Training resources, ease of use, and compatibility with existing systems. |
| Electronics | Failure Analysis in Semiconductor Manufacturing | Minimizes production downtime and improves yield rates. | Availability of parts, technical specifications, and service responsiveness. |
How is Microscope Technology Used in Healthcare?
In the healthcare sector, microscope manufacturers provide advanced imaging solutions for cellular analysis in pathology. These microscopes allow pathologists to identify cellular abnormalities and diagnose diseases with greater accuracy. For international buyers, particularly in Africa and the Middle East, sourcing reliable and high-quality microscopes is crucial to ensure compliance with local healthcare regulations. Additionally, buyers should consider the availability of service support and training to maximize the equipment’s potential.
What Role Do Microscopes Play in Pharmaceuticals?
Microscopes are vital in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly during drug development and quality control. They enable detailed analysis of samples to ensure that medications are safe and effective. For buyers in South America and Europe, it is essential to prioritize microscopes that offer precision imaging and reliability. Furthermore, understanding the supplier’s reputation for customer service and availability of consumables can significantly impact the success of pharmaceutical operations.
How Are Microscopes Applied in Material Science?
In material science, microscopes are instrumental in conducting failure analysis of materials. They help identify defects and assess the performance of materials under various conditions. Buyers from diverse regions, including Europe and Africa, should seek microscopes that provide customization options to meet specific analytical needs. The ability to receive technical support and warranty services is also critical to ensure long-term reliability and performance.
What Benefits Do Microscopes Offer in Education and Research?
Microscopes are essential tools in educational institutions and research facilities, facilitating advanced microscopy techniques for both teaching and groundbreaking research. They enhance the learning experience and contribute to significant scientific advancements. B2B buyers from the Middle East and South America should focus on sourcing user-friendly models that come with comprehensive training resources. This ensures that both educators and students can effectively utilize the technology for optimal results.
How Do Microscopes Contribute to Electronics Manufacturing?
In the electronics industry, microscopes are crucial for failure analysis in semiconductor manufacturing. They help detect defects that can lead to production downtime, thus improving overall yield rates. For international buyers, particularly from Europe and Asia, sourcing microscopes that are readily available with spare parts and technical specifications is vital. Additionally, understanding the supplier’s service responsiveness can greatly enhance operational efficiency in electronics production.
Related Video: Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) | Principle, Instrumentation, Working & Applications
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘microscope manufacturer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Identifying the Right Microscope for Specific Applications
The Problem:
B2B buyers often struggle to find the appropriate microscope for their specific applications, such as clinical diagnostics, materials analysis, or educational purposes. This challenge is compounded by the vast array of options available, each with unique specifications, features, and price points. Without adequate knowledge, buyers may end up purchasing a microscope that does not meet their needs, leading to wasted resources and dissatisfaction.
The Solution:
To address this issue, buyers should begin by conducting a thorough needs assessment to identify the specific requirements of their application. This includes determining the required magnification, resolution, and any specialized features such as fluorescence or phase contrast capabilities. After establishing these criteria, buyers should consult with reputable microscope manufacturers or distributors who can provide expert guidance tailored to their application.
Utilizing online resources, such as comparison charts and product demos, can also facilitate informed decision-making. Additionally, engaging in discussions with peers or industry forums can yield valuable insights into the performance of various microscope models. By taking these steps, buyers can ensure they select a microscope that aligns with their operational needs and budget.
Scenario 2: Concerns Over Microscope Maintenance and Longevity
The Problem:
Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the concern about the maintenance and longevity of microscopes. Many buyers fear that the equipment will require costly repairs or have a short lifespan, particularly in high-use environments such as laboratories or educational institutions. This concern can lead to hesitation in investment and ultimately result in settling for lower-quality alternatives.
The Solution:
To mitigate these concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing microscopes from manufacturers known for their durability and customer support. Investigating warranty options and the availability of replacement parts can provide additional reassurance. Buyers should also inquire about the manufacturer’s maintenance recommendations and whether they offer training programs for proper usage and care.
Establishing a routine maintenance schedule can significantly extend the life of a microscope. This includes regular cleaning, calibration, and inspections, which can often be performed in-house or through a service contract with the manufacturer. By investing in quality equipment and adhering to maintenance best practices, buyers can reduce the total cost of ownership and enhance the longevity of their microscopes.
Scenario 3: Navigating International Shipping and Customs Challenges
The Problem:
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa and South America, navigating the complexities of shipping and customs clearance can be daunting. This often results in delays, unexpected costs, and potential damage to sensitive equipment like microscopes. Such issues can disrupt operations and lead to lost business opportunities.
The Solution:
To overcome these challenges, buyers should work closely with their microscope manufacturer to understand the shipping options available, including the use of specialized carriers experienced in handling delicate instruments. It is essential to establish clear communication regarding packaging standards to ensure the equipment is safeguarded during transit.
Additionally, buyers should familiarize themselves with the customs regulations of their country, including any necessary documentation and import duties. Engaging a local customs broker can streamline the process, helping to avoid potential pitfalls. Lastly, considering purchasing from manufacturers with a solid reputation for international logistics can further alleviate these concerns, as they may have established systems in place to manage shipping effectively. By taking proactive measures, buyers can ensure a smoother acquisition process and avoid disruptions to their operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for microscope manufacturer
What Are the Key Materials Used in Microscope Manufacturing?
When selecting materials for microscope manufacturing, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the industry, focusing on their performance characteristics, suitability for applications, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Perform as a Material for Microscopes?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has a good strength-to-weight ratio. It can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which enhances portability. However, it may not be as durable as heavier metals like steel, particularly under extreme conditions. Additionally, while it is relatively easy to machine, the surface finish may require additional coatings for enhanced performance.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including biological specimens and chemicals used in microscopy. However, care must be taken to avoid prolonged exposure to highly corrosive substances.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards for aluminum grades, such as ASTM or ISO. In Europe, adherence to EU regulations regarding material safety is essential.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Microscope Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and durability. It can handle high temperatures and pressures, making it ideal for robust applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of stainless steel is its long lifespan and resistance to rust and corrosion, which is vital in laboratory environments. However, it is heavier than aluminum and can be more expensive, impacting overall manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for components that require high precision and stability, such as the microscope frame and internal mechanisms. Its compatibility with various chemicals used in microscopy is also a significant benefit.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East should consider the impact of high humidity and temperature on stainless steel performance. Compliance with international standards like ASTM A276 is critical for ensuring quality.
Why Is Glass an Essential Material in Microscope Design?
Key Properties: Optical glass is specifically engineered for clarity, refractive index, and minimal distortion. It can withstand moderate thermal stress but is susceptible to scratches.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of glass is its optical clarity, essential for high-quality imaging. However, it is fragile and can be more expensive than other materials, requiring careful handling during manufacturing and assembly.
Impact on Application: Glass is used in lenses and slides, directly affecting the quality of the images produced. It is compatible with various biological and chemical samples, making it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from Europe should be aware of the stringent regulations regarding glass safety and quality, such as compliance with EN standards. In regions like Africa, sourcing high-quality glass can be challenging, impacting overall production.
How Does Plastic Compare in Microscope Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Plastics, particularly high-performance polymers, are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can be molded into complex shapes. They typically have lower thermal and chemical resistance compared to metals and glass.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastic is its cost-effectiveness and versatility in design. However, it may lack the durability and rigidity required for certain applications, leading to potential performance issues over time.
Impact on Application: Plastic components are often used in non-critical areas, such as housing and knobs. They are compatible with many media but may not withstand harsh laboratory conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in South America should evaluate the availability of high-quality plastics that meet international standards like ISO 9001. Understanding local manufacturing capabilities and limitations is vital for ensuring product quality.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Microscope Manufacturing
| Material | Typical Use Case for microscope manufacturer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Frames and lightweight components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable than steel | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Structural components and mechanisms | High strength and corrosion resistance | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Glass | Lenses and optical components | Superior optical clarity | Fragile and prone to scratches | High |
| Plastic | Housing and non-critical components | Cost-effective and versatile | Less durable and lower thermal resistance | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions when sourcing materials for microscope manufacturing. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material is crucial for optimizing product performance and ensuring compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for microscope manufacturer
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing for Microscopes?
The manufacturing process for microscopes involves several critical stages that ensure precision and quality. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
1. Material Preparation
The first stage involves sourcing high-quality materials, including glass, metal, and plastics. Manufacturers often use optical glass that has been specially treated to minimize defects and enhance clarity. Suppliers must provide material certifications to verify that the components meet industry standards, such as optical quality grades.
2. Forming Techniques: How Are Microscope Components Created?
Various forming techniques are employed to create the intricate components of a microscope.
-
Precision Machining: This involves cutting and shaping metal components, such as the microscope body and stage, using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines for high accuracy.
-
Glass Molding and Grinding: Optical components are formed through precise molding and grinding processes, which ensure that lenses are free from distortions.
-
Injection Molding: For plastic components, injection molding is commonly used to create parts like casing and knobs, ensuring uniformity and structural integrity.
3. Assembly: What Is the Process for Assembling Microscopes?
After the components are formed, they undergo assembly, where different parts are meticulously combined. This stage is crucial, as any misalignment can affect the microscope’s performance.
-
Sub-Assembly: Smaller units, such as optical systems and mechanical stages, are often assembled separately before being integrated into the main body.
-
Alignment and Calibration: Optical alignment is critical and requires specialized tools and skilled technicians to ensure that all components work together effectively. Calibration checks are performed to guarantee that the microscope meets specifications.
What Are the Finishing Processes for Microscopes?
Finishing processes contribute to the final appearance and functionality of microscopes.
-
Coating: Lenses may receive anti-reflective coatings to improve light transmission and reduce glare, enhancing image quality.
-
Surface Treatment: Metal parts might undergo anodizing or powder coating to prevent corrosion and improve aesthetics.
-
Final Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to ensure that all components meet quality standards before packaging and shipping.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Microscope Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that every microscope produced meets international and industry-specific standards.
Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance
International standards like ISO 9001 play a significant role in quality management systems. Compliance with these standards indicates that a manufacturer maintains effective processes for consistent quality.
-
CE Marking: For European markets, CE marking confirms that the product meets health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: In certain applications, particularly in life sciences and industrial uses, manufacturers may also comply with API (American Petroleum Institute) standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to ensure product quality at various stages.
1. Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
IQC involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival. This step verifies that the materials meet the required specifications before they enter the production line. Suppliers must provide documentation, such as certificates of analysis, to confirm compliance.
2. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During the manufacturing process, IPQC checks are performed to monitor ongoing operations. This includes:
-
Dimensional Checks: Regular measurements of components to ensure they remain within specified tolerances.
-
Visual Inspections: Spot checks for defects or irregularities in materials and assembly.
3. Final Quality Control (FQC)
FQC is the last line of defense before products are shipped. This stage involves comprehensive testing, including:
-
Functional Testing: Ensuring that all features of the microscope operate correctly.
-
Performance Testing: Evaluating optical performance under various conditions to guarantee image quality.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to verify the quality control processes of microscope manufacturers.
1. Conducting Supplier Audits
Audits provide an in-depth look at a supplier’s manufacturing practices and quality assurance protocols. Buyers should request audits that assess compliance with international standards, including documentation review and facility inspections.
2. Reviewing Quality Assurance Reports
Manufacturers should be willing to provide detailed reports on their quality assurance processes, including historical data on defect rates and customer complaints. This transparency can help buyers gauge the reliability of the supplier.

A stock image related to microscope manufacturer.
3. Utilizing Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a manufacturer’s quality control measures. These services typically include pre-shipment inspections, which can help mitigate risks associated with product defects.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control and certifications is crucial, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
-
Regional Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations governing laboratory equipment.
-
Language Barriers: Documentation and certifications may be in different languages. Buyers should ensure they receive translated documents or summaries to avoid misunderstandings.
-
Cultural Differences: Building relationships with suppliers can often require navigating cultural nuances. Open communication and clarity about expectations can help mitigate potential issues.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols of microscope manufacturers, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they select reliable partners that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘microscope manufacturer’
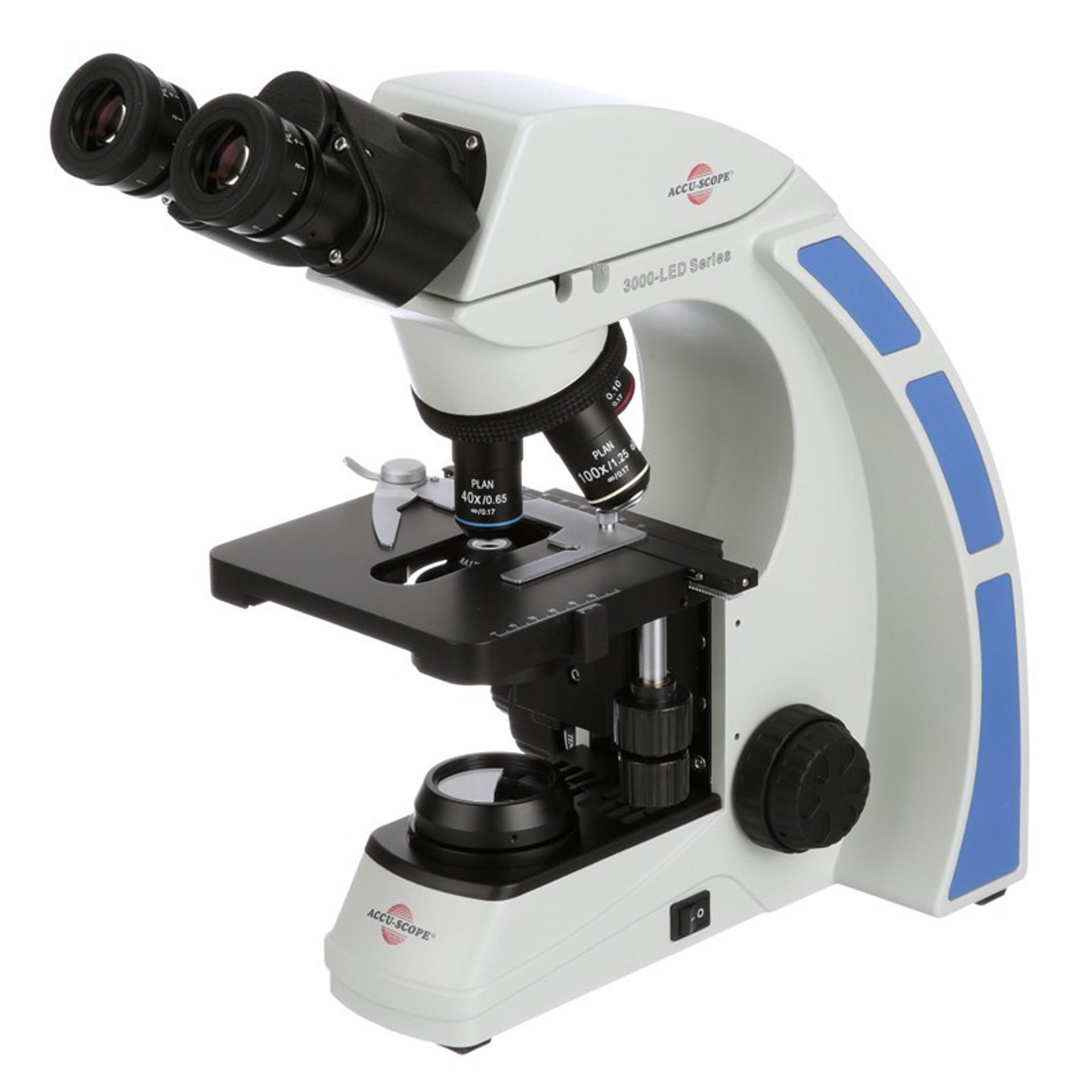
A stock image related to microscope manufacturer.
In the competitive landscape of sourcing microscopes, international B2B buyers must navigate various challenges to ensure they select the right manufacturer. This checklist serves as a practical guide to streamline the procurement process, ensuring you secure high-quality products that meet your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specifications your microscopes must meet. This includes magnification ranges, types of illumination (e.g., LED, halogen), and any specific features such as digital imaging capabilities. Precise specifications help avoid miscommunication with suppliers and ensure that the products align with your operational requirements.
- Consider end-user needs: Determine who will be using the microscopes and for what applications, as this will influence your technical requirements.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research on Potential Suppliers
Research potential microscope manufacturers to understand their market presence, product offerings, and reputation. Utilize online resources, industry reports, and trade shows to gather insights on various suppliers.
- Focus on regional suppliers: For buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, consider local manufacturers to reduce shipping costs and lead times.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Standards
Verify that the manufacturers comply with international quality standards, such as ISO 9001. Certifications ensure that the products are manufactured under strict quality control processes, which is crucial for sensitive applications.
- Ask for documentation: Request copies of relevant certifications and quality assurance procedures to assess their commitment to quality.
Step 4: Request Product Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, ask for samples of the microscopes. Testing samples allows you to evaluate the performance and quality of the products firsthand.
- Assess usability and functionality: Ensure that the microscopes meet your operational needs by testing them in real-world scenarios.
Step 5: Check References and Customer Feedback
Ask for references from previous clients, particularly those in your industry or region. This step provides insights into the manufacturer’s reliability and customer service.
- Look for case studies: Reviewing case studies can illustrate how the supplier has successfully supported similar businesses.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, negotiate the terms of your purchase, including pricing, payment terms, delivery timelines, and warranty conditions. Clear terms help prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smooth procurement process.
- Consider long-term partnerships: Discuss potential for ongoing support and maintenance agreements to enhance your relationship with the supplier.
Step 7: Finalize and Document the Agreement
After negotiations, finalize the agreement and ensure all terms are documented. This formal contract should include all agreed-upon specifications, pricing, delivery schedules, and warranties.
- Review legal implications: Consult with legal counsel to ensure the contract protects your interests and complies with international trade laws.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing microscopes, ensuring they partner with reputable manufacturers that meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for microscope manufacturer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Microscope Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure of microscope manufacturing is critical for international B2B buyers. The primary components contributing to the overall cost include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost. High-quality optics, specialized glass, and durable metals can increase expenses. Buyers should consider suppliers who offer both quality and cost-effectiveness.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in the production of microscopes. Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region and the level of expertise required. Countries with a high skill base may command higher wages but can also ensure superior craftsmanship.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturers often have lower overhead costs, enabling them to pass savings on to buyers.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, particularly for custom designs. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs and consider how these will affect overall pricing, especially for smaller orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures that microscopes meet necessary specifications and certifications, which can add to the cost. However, investing in quality control can reduce returns and improve customer satisfaction in the long run.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on the destination and shipping method. Buyers should consider Incoterms to clarify who bears the cost and risk during transit.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin on top of their costs. Understanding the margin expectations in different regions can help buyers negotiate better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Microscope Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of microscopes in the B2B market:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to optimize pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specialized specifications can significantly increase costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of custom features against their budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (such as ISO or CE) can elevate prices. Buyers should assess whether the benefits of certified products justify the additional costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and operational efficiency can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for reliability, while newer players might offer competitive rates to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, risks, and insurance, which can significantly impact total expenses.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs in Microscope Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the following strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate Terms: Leverage your purchasing power to negotiate better pricing and payment terms. Don’t hesitate to discuss discounts for larger orders or long-term contracts.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Evaluate maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime associated with different suppliers to determine the best overall value.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local economic factors. Familiarize yourself with the pricing landscape in your target market to better gauge fair pricing.
-
Engage Multiple Suppliers: Solicit quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing and services. This will not only provide insights into market rates but also enhance your negotiating leverage.
-
Evaluate Long-term Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service in the future. Consider suppliers who demonstrate reliability and a willingness to collaborate on pricing strategies.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for microscopes can vary widely based on specifications, order size, and supplier conditions. This analysis provides a framework for understanding costs and pricing but does not guarantee specific pricing outcomes. Always request detailed quotes from suppliers to obtain accurate pricing tailored to your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing microscope manufacturer With Other Solutions
When considering the procurement of microscopy solutions, it’s essential for B2B buyers to explore various alternatives. This analysis highlights how traditional microscope manufacturers compare to other viable technologies and methods, assisting international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe in making informed decisions.
Comparison Table of Microscope Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Microscope Manufacturer | Digital Imaging Systems | Smartphone Microscopy Kits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-resolution imaging, suitable for detailed analysis | Advanced imaging capabilities, often with software integration for enhanced data analysis | Moderate resolution, suitable for basic imaging tasks |
| Cost | Generally high initial investment | Varies widely; can be high due to software requirements | Low-cost, accessible for basic uses |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized setup and training | Moderate; may need technical expertise for software | Very easy; typically involves a simple attachment to a smartphone |
| Maintenance | Requires regular calibration and professional servicing | Software updates needed; hardware maintenance can be minimal | Minimal maintenance; smartphones are commonly used and supported |
| Best Use Case | Research labs, educational institutions, and industries needing high-precision analysis | Laboratories focusing on real-time imaging and data sharing | Fieldwork, educational settings, and informal use |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Digital Imaging Systems?
Digital imaging systems provide an innovative alternative to traditional microscopy, leveraging high-definition cameras and advanced software. The primary advantage of these systems lies in their ability to capture high-resolution images and integrate data analysis tools, enhancing research capabilities. However, they often require a significant investment in software and may necessitate technical expertise for optimal use. This makes them suitable for specialized laboratories that prioritize data sharing and real-time imaging but may not be the best fit for smaller operations or those with limited budgets.
How Do Smartphone Microscopy Kits Compare?
Smartphone microscopy kits offer a cost-effective and user-friendly alternative for basic imaging tasks. These kits typically consist of a lens attachment that transforms a smartphone into a microscope, making them ideal for educational settings and fieldwork. The primary advantage is their affordability and ease of use, allowing users to capture images quickly without extensive training. However, the resolution and imaging capabilities are generally inferior to those of traditional microscopes and digital imaging systems, making them less suitable for high-precision scientific applications.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Microscopy Solution?
When selecting the appropriate microscopy solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific needs, budget constraints, and the intended application. Traditional microscope manufacturers excel in high-performance environments where precision is paramount. In contrast, digital imaging systems are advantageous for labs seeking integration with data analysis software. Meanwhile, smartphone microscopy kits are perfect for educational purposes and basic imaging tasks, offering a low-cost entry point for less demanding applications. Evaluating these factors will enable buyers to choose a solution that aligns with their operational requirements and budgetary constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for microscope manufacturer
What are the Essential Technical Properties of Microscopes?
When considering the procurement of microscopes, international B2B buyers must understand several critical specifications that influence performance, reliability, and application suitability. Here are some essential technical properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality and type of materials used in the construction of the microscope. Common materials include aluminum, stainless steel, and high-grade plastics. The choice of material affects not only the durability of the microscope but also its weight and ease of use. For instance, microscopes made from high-grade materials are less prone to corrosion, which is vital in humid environments typical in some regions of Africa and South America.
2. Optical Resolution
Optical resolution is the ability of a microscope to distinguish between two close objects. This specification is typically expressed in micrometers (µm). A higher resolution allows for more detailed imaging, which is crucial for applications in research and quality control. Buyers should ensure that the resolution meets their specific application needs, especially in fields like biology and materials science.
3. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the acceptable limits of variation in a microscope’s components. It is essential for maintaining precision during use. High tolerances indicate that parts fit together more accurately, which is critical for optical performance. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers evaluate the quality of the microscope and its potential longevity in various operational settings.
4. Magnification Power
Magnification power is a key specification that indicates how much larger an object appears through the microscope compared to its actual size. This is usually expressed as a ratio (e.g., 40x, 100x). Different applications may require different magnification powers; hence, buyers should assess their specific needs to ensure they select a microscope with appropriate magnification capabilities.
5. Illumination Type
The type of illumination—such as LED, halogen, or fluorescent—affects the clarity and contrast of the images produced. LED illumination, for instance, offers longer life and lower heat output, making it suitable for prolonged use. Choosing the right illumination type can enhance usability and the overall quality of observations.
What are Common Trade Terms in Microscope Manufacturing?
Understanding trade terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the microscope industry. Here are several commonly used terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In microscopy, an OEM may create components like lenses or illumination systems that are then assembled into a final product by another brand. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify quality sources and potential customization options.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory planning, particularly for businesses in emerging markets where initial capital may be limited. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their operational needs without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer submits to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it formalizes the procurement process, allowing for comparison of different suppliers’ offerings. Crafting a precise RFQ can lead to better pricing and service agreements.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify aspects such as shipping costs, insurance, and liability. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth logistics when importing microscopes from different regions.
5. Warranty Period
The warranty period is the duration during which the manufacturer is responsible for repairing or replacing defective products. This term is vital for buyers to understand, as it reflects the manufacturer’s confidence in their product quality. A longer warranty period can provide peace of mind, particularly for significant investments in scientific equipment.
In conclusion, understanding these technical properties and trade terms can empower B2B buyers in making informed decisions regarding microscope procurement, ensuring they select products that meet their operational needs while optimizing their investment.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the microscope manufacturer Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers and Trends in the Microscope Manufacturing Sector?
The microscope manufacturing sector is currently experiencing transformative growth driven by several global factors. Advances in technology, such as automation and artificial intelligence, are enhancing product capabilities, making microscopes more efficient and user-friendly. Additionally, the rising demand for high-resolution imaging in sectors like healthcare, education, and research is propelling market expansion. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the need for advanced diagnostic tools, emphasizing the importance of robust microscopy solutions in laboratories and hospitals.
International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly looking for suppliers that not only offer high-quality products but also innovative solutions tailored to their unique market needs. Trends such as digital microscopy and cloud-based data management are becoming crucial in procurement decisions. Furthermore, there is a growing interest in integrated systems that combine microscopy with other technologies, such as spectroscopy, to provide comprehensive analytical capabilities.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Microscope Manufacturing Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a central theme in the sourcing strategies of international B2B buyers. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the importance of ethical supply chains are now critical considerations. Suppliers that prioritize sustainable practices, such as reducing carbon footprints, utilizing eco-friendly materials, and ensuring responsible waste management, are more likely to attract discerning buyers.
Buyers are increasingly seeking certifications that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and FSC certification for sourced materials. Moreover, the use of ‘green’ materials in the manufacturing of microscopes is gaining traction. This shift not only fulfills regulatory requirements but also aligns with the corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals of many organizations, fostering brand loyalty and consumer trust.
What Is the Historical Context of Microscope Manufacturing Relevant to Today’s Market?
The microscope has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 16th century, initially serving as a vital tool for scientific discovery. The introduction of optical advancements in the 19th century laid the groundwork for modern microscopy, enabling detailed biological and material analyses. Over the decades, the sector has witnessed continuous innovation, from the development of electron microscopes in the 20th century to the integration of digital technologies in contemporary devices.
Today, this historical context informs the current landscape, where buyers are not only looking for advanced technical specifications but also a legacy of reliability and innovation. Understanding the evolution of the microscope manufacturing sector can empower international buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with manufacturers that have a proven track record of quality and innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of microscope manufacturer
-
How do I choose the right microscope manufacturer for my needs?
Choosing the right microscope manufacturer involves assessing your specific requirements, such as the type of microscopy (light, electron, etc.), application (research, clinical, industrial), and budget. Research potential manufacturers by reviewing their product offerings, certifications, and customer reviews. Additionally, consider their ability to provide technical support and after-sales service. Engaging with industry peers or attending trade shows can also help you gather insights on reliable manufacturers that align with your needs. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing microscopes internationally?
When sourcing microscopes internationally, key factors to consider include the manufacturer’s reputation, compliance with international standards, and the quality of their products. Understand the logistics involved, including shipping times and costs, as well as potential customs duties and regulations in your country. Evaluate the manufacturer’s experience in exporting to your region, as this can impact the efficiency of the procurement process. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for microscopes from manufacturers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for microscopes can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and the type of microscope. Some manufacturers may offer MOQs as low as one unit for specialized models, while others may require larger orders for bulk pricing. It’s essential to communicate directly with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that fit your budget and needs, especially if you’re a smaller buyer. -
How can I ensure the quality of microscopes when purchasing from a manufacturer?
To ensure quality when purchasing microscopes, request product samples or demonstration units to evaluate performance firsthand. Verify the manufacturer’s certifications, such as ISO or CE, which indicate adherence to quality standards. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes, including testing protocols and warranty policies. Establishing a solid communication channel for support and feedback can also help ensure ongoing satisfaction with the product. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing microscopes from manufacturers?
Payment terms can vary among microscope manufacturers, but common practices include partial upfront payments (e.g., 30-50%) followed by the balance upon delivery or after inspection. Some manufacturers may offer net 30 or net 60 terms for established buyers. It’s crucial to clarify payment methods (wire transfer, credit terms) and negotiate terms that suit your financial capabilities while ensuring secure transactions. -
How do I vet a microscope manufacturer before making a purchase?
Vetting a microscope manufacturer involves several steps: researching their history, checking for customer testimonials and case studies, and validating their certifications and industry partnerships. Request references from previous clients and assess their responsiveness and willingness to provide detailed information about their products. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities if feasible or attending industry expos where they showcase their equipment. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing microscopes from abroad?
Logistics considerations include understanding shipping options, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may apply to your import. Collaborate with a freight forwarder experienced in handling sensitive laboratory equipment to ensure safe and timely delivery. Be aware of lead times, which can be affected by manufacturing schedules and shipping routes. Additionally, plan for proper storage conditions upon arrival to maintain the microscopes’ integrity. -
Can I customize my microscope order to meet specific requirements?
Many microscope manufacturers offer customization options to tailor products to specific applications or user needs. Customizations may include modifications to optics, accessories, or software features. When discussing your order, clearly outline your requirements and ask about the manufacturer’s capabilities for customization. Keep in mind that bespoke solutions may come with longer lead times and higher costs, so it’s essential to factor this into your planning.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for microscope manufacturer
As international B2B buyers navigate the complex landscape of microscope procurement, the importance of strategic sourcing cannot be overstated. Key takeaways from this guide emphasize the need for a thorough understanding of supplier capabilities, the significance of quality assurance, and the advantages of establishing strong relationships with manufacturers. By prioritizing these elements, buyers can ensure they are making informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and support long-term success.
What should B2B buyers consider for future sourcing of microscopes? Embracing technological advancements and sustainability practices in the sourcing process will be crucial. Buyers should remain vigilant about emerging trends and innovations within the microscopy field, as these can provide competitive advantages and align with global sustainability goals.
Looking ahead, now is the time for B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to leverage strategic sourcing as a vital tool for growth. By investing in robust supplier partnerships and staying informed about market dynamics, businesses can position themselves for success in a rapidly evolving marketplace. Engage with leading microscope manufacturers today to explore how tailored solutions can meet your specific needs and propel your organization forward.