Free Empirical Rule Calculators: Our Top 5 Picks for 2025
Finding the Best Empirical Rule Calculator: An Introduction
When it comes to statistical analysis, the empirical rule is a fundamental concept that many users need to understand and apply in various contexts. However, finding a reliable and effective empirical rule calculator can be a challenge. With a plethora of options available online, users may find themselves overwhelmed by the choices, each claiming to offer the best features and results. This article aims to simplify that search by reviewing and ranking the top empirical rule calculators currently available.
The Importance of a Quality Calculator
A good empirical rule calculator not only saves time but also ensures accuracy in calculations. The empirical rule, often referred to as the 68-95-99.7 rule, helps users determine the distribution of data points within standard deviations from the mean in a normal distribution. This rule is crucial for various applications, including data analysis, research, and forecasting. Therefore, choosing the right calculator is essential for obtaining reliable results.
Criteria for Ranking
In this review, we will evaluate each calculator based on several key criteria:
-
Accuracy: The primary function of any calculator is to provide correct results. We will assess how accurately each tool applies the empirical rule.
-
Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface is vital for ensuring that users can navigate the tool without confusion. We will examine the design and intuitiveness of each calculator.
-
Features: Additional functionalities, such as the ability to handle different distributions or provide visual representations, will also be considered.
By focusing on these criteria, this article will help you identify the best empirical rule calculators, allowing you to make informed decisions without wasting time on subpar tools. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or just someone curious about statistics, our rankings will guide you to the most efficient resources available online.
Our Criteria: How We Selected the Top Tools
Criteria for Selecting the Best Empirical Rule Calculators
When evaluating the top empirical rule calculators, we focused on several key criteria that ensure each tool meets the needs of users ranging from students to professionals. Here’s a breakdown of the essential factors we considered in our selection process:
-
Accuracy and Reliability
– The primary function of any calculator is to provide accurate results. We assessed each tool’s ability to correctly compute the ranges of data that fall within one, two, and three standard deviations from the mean. This includes verifying that the outputs align with the established empirical rule percentages of 68%, 95%, and 99.7%. -
Ease of Use
– A user-friendly interface is crucial for any online tool. We examined how intuitive each calculator is, focusing on the clarity of the input fields and the simplicity of the calculation process. A good calculator should allow users to quickly enter data and receive results without unnecessary complications. -
Key Features
– Effective empirical rule calculators should offer specific inputs that enhance usability, including:- Mean (μ): The average value of the dataset.
- Standard Deviation (σ): A measure of the spread of the dataset.
- Options for additional calculations, such as probabilities of specific data points falling within defined ranges.
- Visual aids or graphs that illustrate the normal distribution and the empirical rule can also enhance understanding.
-
Cost (Free vs. Paid)
– We evaluated whether the calculators were free to use or if they required a subscription or one-time fee. Free tools are generally more accessible, but we also considered any premium features that may justify a cost in certain calculators. -
Additional Educational Resources
– Tools that provide supplementary information about the empirical rule, such as explanations of the underlying concepts, worked examples, or links to related calculators, were prioritized. This aspect not only aids in the calculation process but also enhances the user’s understanding of statistical principles. -
Mobile Compatibility
– With the increasing use of mobile devices, we assessed whether the calculators are optimized for mobile use. A responsive design ensures that users can easily access and utilize the tools on various devices without losing functionality. -
User Reviews and Feedback
– We also considered user feedback and ratings from previous users to gauge overall satisfaction and identify any common issues. This qualitative data helps ensure that our recommendations are based on real-world experiences.
By applying these criteria, we were able to curate a list of the best empirical rule calculators that cater to a wide range of user needs, ensuring both accuracy and ease of use for anyone looking to understand their data better.
The Best Empirical Rule Calculators of 2025
1. Empirical Rule Calculator
The Empirical Rule Calculator on Omni Calculator is designed to help users easily compute the mean and standard deviation of a dataset, facilitating the application of the empirical rule in statistics. By allowing users to input their values, the tool efficiently calculates the mean (μ) and standard deviation (σ), providing a straightforward way to analyze data distributions and understand the likelihood of values falling within certain ranges.
- Website: omnicalculator.com
- Established: Approx. 11 years (domain registered in 2014)
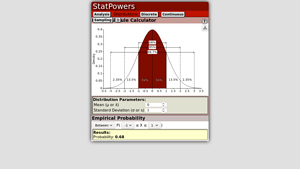
2. Empirical Rule Calculator
The Empirical Rule Calculator from StatPowers is a versatile online tool designed to help users understand and apply the Empirical Rule in statistics. It provides functionality for calculating various sampling distributions, including mean, sum, and proportion, making it useful for statistical analysis. With its user-friendly interface, the calculator simplifies complex statistical concepts, allowing users to easily interpret data and make informed decisions based on empirical findings.
- Website: statpowers.com
- Established: Approx. 7 years (domain registered in 2018)
4. Empirical Rule Calculator (68
The Empirical Rule Calculator from Inch Calculator is a valuable tool designed to help users determine the distribution of data within a dataset according to the 68-95-99.7 rule. This calculator efficiently calculates the percentage of data that falls within one, two, and three standard deviations from the mean, providing clear insights into data variability and aiding in statistical analysis for various applications.
- Website: inchcalculator.com
- Established: Approx. 12 years (domain registered in 2013)
5. Empirical Rule Calculator Mean Standard Deviation
The Empirical Rule Calculator from Statistics Helper is a valuable online tool designed to assist users in applying the empirical rule in statistics. This calculator enables users to determine the mean and standard deviation of a data set, illustrating how 68% of data points lie within one standard deviation from the mean. Its user-friendly interface makes it accessible for both students and professionals looking to simplify statistical analysis.
- Website: statisticshelper.com
- Established: Approx. 7 years (domain registered in 2018)
How to Get the Most Accurate Results
Double-Check Your Inputs
One of the simplest yet most crucial steps to ensure accurate results when using an empirical rule calculator is to double-check your inputs. The calculators typically require two key pieces of information: the mean (μ) and the standard deviation (σ) of your dataset. Inputting incorrect values can lead to misleading outputs. Always verify that you are using the correct data points and that your calculations for the mean and standard deviation are accurate before entering them into the tool. If you’re unsure about your calculations, consider using dedicated calculators for mean and standard deviation to confirm your values.
Understand the Underlying Assumptions
The empirical rule, also known as the 68-95-99.7 rule, applies specifically to normally distributed data. Before using the calculator, it’s important to understand that this rule assumes a bell-shaped curve, where most data points cluster around the mean. If your dataset is skewed or has outliers, the empirical rule may not provide accurate insights. Familiarize yourself with the characteristics of your data distribution and consider visualizing your data using graphs, such as histograms, to assess its normality before applying the empirical rule.
Use Multiple Tools for Comparison
While many online calculators can provide you with empirical rule results, it’s beneficial to use multiple tools for comparison. Different calculators might have varying interfaces, additional features, or even slightly different algorithms for handling data. By entering your data into multiple calculators, you can cross-verify the results and gain a more comprehensive understanding of your dataset. If discrepancies arise, review the inputs and underlying assumptions of each tool to identify potential sources of error.
Interpret the Results with Context
Once you have obtained results from the empirical rule calculator, take the time to interpret them within the context of your dataset. The outputs will indicate the ranges where approximately 68%, 95%, and 99.7% of your data points lie. Consider how these ranges align with your expectations or previous analyses. For instance, if you are analyzing test scores, think about how the calculated ranges reflect student performance and whether they suggest any trends or outliers in your data.
Seek Additional Resources
If you find yourself struggling with the concepts of the empirical rule or the calculations involved, don’t hesitate to seek additional resources. Many calculators provide links to related articles or tutorials that can help deepen your understanding of statistical concepts. Websites that focus on statistics education often offer explanations, examples, and practice problems that can enhance your knowledge and confidence in using these tools effectively.
By following these tips, you can maximize the accuracy and usefulness of the empirical rule calculators, leading to better insights from your data analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the empirical rule and how does it work?
The empirical rule, also known as the 68-95-99.7 rule, is a statistical principle that describes how data is distributed in a normal distribution. According to this rule:
– Approximately 68% of the data falls within one standard deviation (σ) from the mean (μ).
– About 95% of the data falls within two standard deviations from the mean.
– Nearly 99.7% of the data falls within three standard deviations from the mean.
This rule helps to summarize the distribution of data points in a normally distributed dataset, allowing users to understand how much of their data is expected to fall within certain ranges.
2. How do I use an empirical rule calculator?
Using an empirical rule calculator is straightforward. You typically need to input two key values:
– Mean (μ): The average of your dataset.
– Standard Deviation (σ): A measure of the spread of your data.
Once you enter these values, the calculator will automatically compute and display the ranges for the data that fall within 68%, 95%, and 99.7% of the mean. This allows you to quickly visualize how your data is distributed without manually calculating the ranges.
3. What kind of data can I analyze with an empirical rule calculator?
An empirical rule calculator is most effective for datasets that follow a normal distribution. This means the data should be symmetrically distributed around the mean, forming a bell-shaped curve. Common examples include test scores, heights, and other measurements where the majority of values cluster around the average, with fewer values at the extremes.
4. Why is the empirical rule important in statistics?
The empirical rule is crucial because it provides a quick way to understand the distribution of data without requiring extensive analysis. It helps statisticians and researchers to:
– Identify the spread of data points.
– Determine probabilities associated with certain ranges of data.
– Spot outliers that fall outside the expected ranges.
This rule is widely used in various fields, including education, psychology, and quality control, to make informed decisions based on statistical data.
5. Can the empirical rule be applied to non-normal distributions?
While the empirical rule is specifically designed for normal distributions, some insights can still be drawn from it for non-normal distributions. However, the percentages (68%, 95%, 99.7%) may not hold true. In such cases, other statistical methods or transformations might be needed to properly analyze the data. If you suspect your data is not normally distributed, consider using other tools or tests to assess its distribution before applying the empirical rule.
Important Disclaimer
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information and reviews in this guide are for educational purposes only and are based on publicly available information. We are not affiliated with any of the tools mentioned. Features and pricing may change. Always conduct your own research before choosing a tool for your needs.