Improve Quality with Top Automotive Electronic Manufacturer (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for automotive electronic manufacturer
Navigating the complexities of sourcing automotive electronic manufacturers can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, especially when considering the unique challenges faced in markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As the automotive industry increasingly integrates advanced electronic systems, understanding how to effectively identify and partner with reliable manufacturers becomes crucial. This guide aims to demystify the process of sourcing automotive electronic components, encompassing a variety of types and applications, from infotainment systems to advanced driver-assistance technologies.
Through this comprehensive resource, we will explore essential topics such as supplier vetting strategies, cost considerations, and emerging trends in automotive electronics. By providing actionable insights tailored to the specific needs of buyers in diverse regions, this guide empowers decision-makers to make informed purchasing choices. Whether you are looking to enhance your supply chain resilience or stay ahead of technological advancements, our insights will equip you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the global market confidently.
Ultimately, this guide serves as a vital tool for international B2B buyers seeking to build strong relationships with automotive electronic manufacturers, ensuring not only quality and innovation but also alignment with regional market demands. As you embark on this journey, remember that informed decisions are the cornerstone of successful partnerships in the dynamic automotive landscape.
Understanding automotive electronic manufacturer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) | Produce parts for vehicle assembly; strict compliance with industry standards | Complete vehicle production, large-scale manufacturing | Pros: High reliability, extensive warranties. Cons: Higher costs, longer lead times. |
| Tier 1 Suppliers | Directly supply OEMs with critical components; often involved in design and development | Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), infotainment systems | Pros: Close collaboration with OEMs, innovative solutions. Cons: May require minimum order quantities, potentially higher prices. |
| Tier 2 and Tier 3 Suppliers | Provide components to Tier 1 suppliers; often specialize in niche products | Specialized electronic components, sensors | Pros: Cost-effective solutions, flexibility in orders. Cons: Less direct support for OEMs, variable quality control. |
| Aftermarket Manufacturers | Focus on replacement parts and upgrades for existing vehicles; less stringent regulations | Vehicle upgrades, replacement parts | Pros: Competitive pricing, wide product variety. Cons: Quality may vary, limited compatibility with certain models. |
| Specialty Electronics Firms | Develop niche products for specific automotive applications; often utilize advanced technology | Electric vehicles (EVs), autonomous driving technologies | Pros: Cutting-edge technology, tailored solutions. Cons: Higher costs, limited product range. |
What Are the Characteristics of Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs)?
OEMs are the backbone of the automotive supply chain, producing essential components used in new vehicle assembly. They are known for their adherence to strict industry standards and regulations, ensuring that their products are reliable and safe. For B2B buyers, partnering with OEMs often means securing high-quality components, although this comes with a higher price tag and longer lead times. When considering OEMs, it’s crucial to evaluate their reputation, warranty offerings, and capacity for large-scale production.
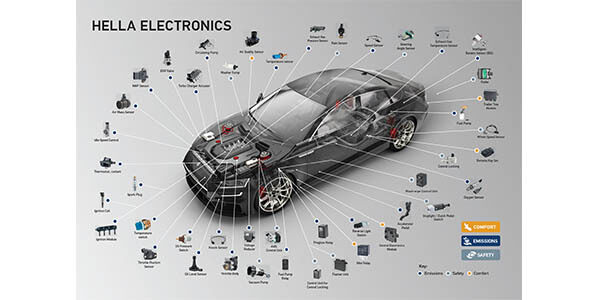
A stock image related to automotive electronic manufacturer.
How Do Tier 1 Suppliers Differ from Other Manufacturers?
Tier 1 suppliers play a critical role by directly supplying OEMs with major components, including advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and infotainment systems. These manufacturers often engage in the design and development phases alongside OEMs, fostering innovation and collaboration. For B2B buyers, the advantage of working with Tier 1 suppliers lies in their ability to provide cutting-edge solutions that enhance vehicle performance. However, they may require minimum order quantities and can command higher prices, which are important factors to consider when negotiating contracts.
What Should Buyers Know About Tier 2 and Tier 3 Suppliers?
Tier 2 and Tier 3 suppliers provide essential components to Tier 1 suppliers and often specialize in niche electronic products, such as sensors and connectors. These manufacturers offer greater flexibility and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for businesses looking to optimize their supply chains without compromising on quality. However, B2B buyers should be cautious about the variable quality control associated with these suppliers. It is advisable to conduct thorough evaluations and establish clear quality expectations when engaging with Tier 2 and Tier 3 suppliers.
Why Consider Aftermarket Manufacturers for Automotive Electronics?
Aftermarket manufacturers focus on producing replacement parts and upgrades for existing vehicles, catering to a growing demand for vehicle customization and maintenance. They typically offer competitive pricing and a wide range of products, making them appealing to cost-conscious B2B buyers. However, the quality of aftermarket parts can vary significantly, and compatibility with specific vehicle models may be limited. Buyers should prioritize reputable aftermarket manufacturers and consider product reviews and certifications to ensure quality.
What Unique Solutions Do Specialty Electronics Firms Provide?
Specialty electronics firms develop niche automotive products, often leveraging advanced technology to create solutions for electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving systems. These manufacturers are known for their innovative approaches and ability to cater to specific needs within the automotive sector. While they offer cutting-edge technology and tailored solutions, the costs can be higher, and their product ranges may be limited compared to larger manufacturers. B2B buyers should assess their specific requirements and budget constraints when considering partnerships with specialty electronics firms.
Related Video: Automotive Electrical System Basics – EricTheCarGuy
Key Industrial Applications of automotive electronic manufacturer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Automotive Electronic Manufacturer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) | Enhances vehicle safety and reduces accident rates | Compliance with local regulations and safety standards |
| Electric Vehicles | Battery Management Systems (BMS) | Maximizes battery life and performance, reducing operational costs | Compatibility with various battery technologies and sizes |
| Fleet Management | Telematics and Vehicle Tracking Systems | Improves operational efficiency and reduces fuel consumption | Scalability and integration with existing fleet software |
| Heavy Equipment | Engine Control Units (ECUs) | Optimizes engine performance and fuel efficiency | Durability and robustness for harsh working conditions |
| Public Transportation | Passenger Information Systems (PIS) | Enhances passenger experience and operational efficiency | User-friendly interface and multilingual support |
How Are Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) Transforming Automotive Safety?
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) are becoming integral in modern vehicles, aiming to enhance safety through features like lane departure warnings and adaptive cruise control. For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing ADAS components requires attention to local regulatory standards and safety certifications. Manufacturers must ensure that their systems are compatible with the specific vehicle models prevalent in these markets, addressing challenges such as varying infrastructure and driving conditions.
What Role Do Battery Management Systems (BMS) Play in Electric Vehicle Performance?
Battery Management Systems (BMS) are critical in electric vehicles, ensuring optimal battery performance and longevity. For buyers in South America and Europe, the focus should be on sourcing BMS that can handle diverse battery chemistries and configurations. This includes evaluating manufacturers’ capabilities in providing real-time monitoring and diagnostics, which can lead to significant cost savings through improved energy efficiency and reduced maintenance needs.
How Can Telematics Improve Fleet Management Efficiency?
Telematics and vehicle tracking systems provide fleet managers with real-time data on vehicle location, speed, and fuel consumption. This technology is particularly beneficial for businesses in Africa and South America, where logistics can be challenging. Buyers should consider sourcing telematics solutions that offer scalability and can integrate seamlessly with existing fleet management software. Ensuring robust data security and compliance with local data protection regulations is also crucial.
Why Are Engine Control Units (ECUs) Essential for Heavy Equipment Optimization?
Engine Control Units (ECUs) are pivotal in optimizing the performance of heavy equipment by managing engine functions to enhance efficiency and reduce emissions. For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, sourcing ECUs that are durable and capable of functioning in extreme conditions is essential. Additionally, manufacturers must provide support for software updates and troubleshooting to maintain performance over time, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
How Do Passenger Information Systems (PIS) Enhance Public Transportation?
Passenger Information Systems (PIS) are vital for improving the user experience in public transportation by providing real-time updates on schedules and routes. For international buyers from Europe and Africa, sourcing PIS requires consideration of user-friendly interfaces and multilingual support to cater to diverse populations. Additionally, systems should be adaptable to various transport modes, ensuring efficient integration with existing infrastructure.
Related Video: Fully automated cable harness production in the automotive industry (EN)
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘automotive electronic manufacturer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Compliance and Regulatory Challenges in Automotive Electronics
The Problem:
B2B buyers in the automotive electronics sector often face significant challenges related to compliance with varying regulations across different regions. For instance, a company in South America may struggle to meet the stringent European Union regulations for electronic components, which can lead to delays in product launch and increased costs. Moreover, the complexity of certifications, such as ISO and IATF standards, can create confusion, especially for buyers who are not familiar with the specific requirements for their target markets.
The Solution:
To effectively navigate these compliance and regulatory challenges, it is crucial for B2B buyers to conduct thorough research on the specific regulations applicable to their target markets. Engage with automotive electronic manufacturers that have a proven track record of compliance in various regions. Request detailed documentation of their certifications and ask for case studies that demonstrate their understanding of international standards. Additionally, consider collaborating with local consultants or legal experts who specialize in automotive regulations to ensure that all products meet necessary compliance requirements before they are introduced to the market. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also enhances the reliability of your supply chain.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Supply Chain Disruptions in Automotive Electronics
The Problem:
Supply chain disruptions have become increasingly common, particularly in the automotive sector, where timely delivery of electronic components is crucial. B2B buyers may encounter delays due to geopolitical issues, natural disasters, or supplier insolvency. For example, a buyer in Africa may depend on electronic components sourced from Asia, but shipping delays or tariffs can create bottlenecks that jeopardize production schedules and customer satisfaction.
The Solution:
To alleviate the impact of supply chain disruptions, it is advisable for B2B buyers to diversify their supplier base. Instead of relying on a single source, establish relationships with multiple manufacturers across different regions. This not only provides alternatives in case of disruptions but can also create competitive pricing opportunities. Furthermore, implementing robust inventory management practices, such as just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems, can help maintain optimal stock levels while minimizing excess. Utilize technology platforms that offer real-time tracking and forecasting capabilities to better anticipate and respond to potential supply chain issues. By adopting these strategies, buyers can enhance resilience and maintain smoother operations.
Scenario 3: Addressing Quality Assurance and Reliability Concerns
The Problem:
Quality assurance is a top concern for B2B buyers in the automotive electronics industry. The risk of receiving defective components can lead to costly recalls and damage to a brand’s reputation. Buyers from the Middle East, for instance, may have experienced instances where components did not meet performance specifications, leading to safety concerns and operational failures in vehicles.
The Solution:
To mitigate quality assurance risks, B2B buyers should prioritize manufacturers with rigorous quality control processes in place. Request detailed information about the manufacturer’s testing protocols, quality certifications (such as ISO 9001), and customer feedback. Establishing a close relationship with suppliers can also facilitate better communication regarding quality expectations. Additionally, consider implementing a vendor management system that includes regular performance evaluations and audits of your suppliers. This proactive approach ensures that all electronic components meet the highest standards before they are integrated into final products, ultimately protecting both the buyer’s brand and their customers’ safety.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for automotive electronic manufacturer
A stock image related to automotive electronic manufacturer.
When selecting materials for automotive electronics manufacturing, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that affect product performance, durability, and compliance with industry standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in automotive electronics, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What are the Key Properties of Polycarbonate in Automotive Electronics?
Polycarbonate (PC) is a popular choice for automotive electronic housings and components due to its excellent impact resistance and thermal stability. It typically operates effectively at temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C, making it suitable for various automotive environments. Additionally, polycarbonate exhibits good electrical insulation properties and is resistant to UV radiation, which is crucial for components exposed to sunlight.
Pros and Cons of Polycarbonate:
– Pros: High impact resistance, lightweight, and good thermal stability.
– Cons: It can be more expensive than other plastics and may require specific molding techniques, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Polycarbonate is particularly compatible with electronic components that require durability and resistance to environmental stressors. However, it may not be suitable for applications involving high chemical exposure.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM D256 for impact resistance and consider local regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact.
How Does Aluminum Enhance Automotive Electronic Components?
Aluminum is widely used in automotive electronics for its lightweight properties and excellent thermal conductivity. It typically has a melting point of around 660°C and can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for heat sinks and other components that dissipate heat.
Pros and Cons of Aluminum:
– Pros: Lightweight, excellent thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance when anodized.
– Cons: Higher cost compared to some plastics and can be more challenging to machine.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s thermal properties make it ideal for applications requiring effective heat management, such as power electronics and battery management systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the need for compliance with standards like ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions and consider the availability of anodizing services in their region.
Why is FR-4 Glass Epoxy Board Essential for Circuit Boards?
FR-4 is a composite material made from woven glass fiber and epoxy resin, commonly used for printed circuit boards (PCBs) in automotive electronics. It has excellent dielectric properties, withstanding temperatures up to 130°C, and is highly resistant to moisture and chemicals.
Pros and Cons of FR-4:
– Pros: Excellent electrical insulation, good mechanical strength, and moisture resistance.
– Cons: It can be brittle and may not perform well under extreme thermal cycling.
Impact on Application: FR-4 is essential for applications requiring high reliability and stability in electrical performance, such as control units and sensor systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with IPC standards for PCB manufacturing and consider the availability of local suppliers who can meet these specifications.
What Role Does Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) Play in Automotive Sealing?
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) are increasingly used in automotive electronics for sealing and cushioning applications. They offer flexibility and resilience, with temperature resistance typically ranging from -40°C to 120°C.
Pros and Cons of TPE:
– Pros: Excellent flexibility, good weather resistance, and ease of processing.
– Cons: Generally lower thermal stability compared to other materials and can be more expensive.
Impact on Application: TPEs are particularly suitable for applications that require sealing against moisture and dust, enhancing the longevity of electronic components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider local climate conditions when selecting TPE grades and ensure compliance with relevant automotive standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Automotive Electronics
| Material | Typical Use Case for automotive electronic manufacturer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polycarbonate | Housings and protective covers for electronic components | High impact resistance | Higher manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Aluminum | Heat sinks and structural components | Lightweight and excellent thermal conductivity | More challenging to machine | High |
| FR-4 Glass Epoxy Board | Printed circuit boards (PCBs) | Excellent electrical insulation | Brittle under thermal cycling | Medium |
| Thermoplastic Elastomer | Sealing and cushioning applications | Excellent flexibility and weather resistance | Lower thermal stability | Medium |
By understanding the properties and applications of these materials, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their product requirements and regional standards, ultimately enhancing the performance and reliability of automotive electronic components.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for automotive electronic manufacturer
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing in Automotive Electronics?
The manufacturing process for automotive electronics involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure high quality and reliability in the final product. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Automotive Electronics?
Material preparation is the foundational step where raw materials are sourced, inspected, and processed. This stage typically involves:
- Sourcing Quality Components: Buyers should ensure that suppliers utilize high-quality materials, such as semiconductors, circuit boards, and connectors, that meet international standards.
- Initial Inspection: Conducting Incoming Quality Control (IQC) to verify that the materials comply with specified requirements and standards before they enter the production line.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Automotive Electronics?
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage utilizes various techniques to shape components. Common techniques include:
- Etching and Deposition: For printed circuit boards (PCBs), manufacturers often use photolithography and chemical etching to create intricate circuit patterns.
- Molding and Casting: For plastic components, injection molding is a prevalent technique that ensures precision and repeatability.
These techniques are vital for achieving the required specifications for automotive electronics, especially in applications requiring durability and performance under varying environmental conditions.
How Does Assembly Work in Automotive Electronics Manufacturing?
The assembly stage combines different electronic components into a cohesive unit. This process often involves:
- Surface Mount Technology (SMT): This technique allows for the placement of components directly onto the surface of PCBs, which is crucial for compact designs in automotive applications.
- Manual and Automated Assembly: Many manufacturers use a mix of manual labor and automated machines to ensure efficiency while maintaining quality.
Quality assurance during assembly is critical, as improper assembly can lead to product failures. Therefore, it’s essential for B2B buyers to understand the assembly process and verify that suppliers have robust protocols in place.
What Finishing Processes Are Important for Automotive Electronics?
Finishing processes are essential for ensuring that the final product meets both aesthetic and functional requirements. Key finishing techniques include:
- Coating and Encapsulation: Applying protective coatings to electronic components to enhance durability and resistance to moisture and heat.
- Final Inspection and Testing: Conducting Final Quality Control (FQC) to ensure that each unit meets the specified performance criteria before delivery.
Buyers should inquire about the specific finishing techniques used by suppliers, as these can significantly impact the longevity and reliability of automotive electronics.
What Are the Key Quality Control Standards for Automotive Electronics?
Quality control is critical in the automotive electronics sector, given the high stakes involved in vehicle safety and performance. International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, while industry-specific standards like CE marking and API certifications ensure compliance with safety and performance requirements.
How Do Suppliers Implement Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Ensures that incoming materials meet quality standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitors the manufacturing process to identify defects during production.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducts comprehensive testing on finished products to verify compliance with specifications.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the reliability of automotive electronics. These include:
- Functional Testing: Verifying that each component operates correctly under specified conditions.
- Environmental Testing: Assessing the product’s performance under extreme conditions, such as temperature fluctuations and humidity.
- Durability Testing: Evaluating the product’s longevity and resistance to wear and tear.
B2B buyers should request detailed testing reports from suppliers to confirm that these methods are being properly implemented.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to stringent quality control practices, B2B buyers can take several actionable steps:
- Conduct Audits: Regularly auditing suppliers’ facilities can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including inspection and testing results.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
- Understanding Local Standards: Different regions may have varying regulations and standards that suppliers must adhere to. It’s essential to verify that suppliers comply with both local and international standards.
- Cultural Considerations: Communication barriers and cultural differences can affect quality expectations. Buyers should establish clear specifications and maintain open lines of communication.
- Logistical Challenges: International shipping can introduce risks related to product handling. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust packaging and shipping practices to mitigate these risks.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in automotive electronics is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions and foster successful partnerships with suppliers, ultimately leading to high-quality products that meet the rigorous demands of the automotive industry.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘automotive electronic manufacturer’
Introduction
Sourcing automotive electronic components is a critical process for B2B buyers, especially in dynamic markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This checklist serves as a practical guide to help international buyers navigate the complexities of selecting the right manufacturers. By following these steps, you can ensure a streamlined procurement process that meets your technical and business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to potential manufacturers, clearly outline the technical specifications of the electronic components you require. This includes factors such as voltage requirements, durability standards, and compatibility with existing systems. A well-defined specification not only aids in obtaining accurate quotes but also minimizes the risk of product mismatches later in the process.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research for Suppliers
Engage in thorough market research to identify reputable automotive electronic manufacturers. Utilize online platforms, industry reports, and trade shows to gather a list of potential suppliers. Pay attention to their production capabilities, market presence, and specialization in automotive electronics, as these factors will significantly impact the quality and reliability of the products you source.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Consider the following:
– Track Record: Look for suppliers with a proven history of delivering high-quality products on time.
– Customer Feedback: Analyze reviews and testimonials to gauge customer satisfaction and reliability.
Step 4: ✅ Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the manufacturers you are considering hold relevant industry certifications, such as ISO 9001 or IATF 16949. These certifications indicate adherence to quality management systems and automotive industry standards. Additionally, check for compliance with local regulations and international safety standards, as this can prevent future legal and operational issues.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before making large orders, request samples or prototypes of the electronic components. This step allows you to assess product quality, functionality, and compatibility with your existing systems. During this phase, pay attention to:
– Performance Testing: Conduct your own tests to verify that the samples meet your technical specifications.
– Material Quality: Inspect the materials used, as this can impact the longevity and performance of the components.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a potential supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Be transparent about your budget and expectations while also seeking value for your investment. Consider including clauses for warranties and after-sales support to safeguard your procurement interests.
Step 7: Establish a Clear Communication Plan
Effective communication is vital for a successful supplier relationship. Establish a clear communication plan that outlines points of contact, reporting structures, and timelines for updates. Regular check-ins can help address any issues promptly and ensure that both parties remain aligned throughout the procurement process.
By following this step-by-step checklist, international B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategy for automotive electronic manufacturers, leading to successful partnerships and high-quality product acquisitions.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for automotive electronic manufacturer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Automotive Electronics Manufacturing?
When sourcing automotive electronics, understanding the cost structure is paramount. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly influences the overall cost. High-quality components such as semiconductors, capacitors, and circuit boards can be more expensive but are critical for performance and reliability.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region, impacting the total manufacturing cost. Skilled labor may demand higher wages, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, where labor regulations are stringent. Consideration of local labor markets in Africa and South America may reveal opportunities for cost savings.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can mitigate overhead costs, making it essential to evaluate potential suppliers’ production capabilities.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom parts. Buyers should assess whether the tooling can be amortized over large production runs to reduce per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are vital in the automotive sector to ensure compliance with safety standards. While this adds to costs, it can prevent more expensive recalls and brand damage in the long run.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs can vary widely based on the geographical location of suppliers and the shipping methods chosen. Understanding the logistics landscape in your sourcing region is crucial for accurate budgeting.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically incorporate their profit margins into pricing, which can differ based on market conditions and supplier competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Automotive Electronics Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of automotive electronics:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) significantly affect pricing. Higher volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs, allowing buyers to negotiate better terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts tailored to specific requirements can incur additional costs. Buyers should clarify their needs upfront to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The use of premium materials and the acquisition of quality certifications (like ISO/TS 16949) can increase costs but are essential for compliance and performance assurance.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and financial stability can impact pricing. Conducting due diligence on potential partners is critical.
-
Incoterms: The terms of trade (Incoterms) dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping. Understanding these can prevent hidden costs and clarify liability during transportation.
What Buyer Tips Should Be Considered for Cost-Efficiency?
For B2B buyers navigating the complex landscape of automotive electronics sourcing, consider the following actionable insights:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage your purchasing power, particularly if you are a larger buyer. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to more favorable terms and pricing.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the TCO, which includes maintenance, logistics, and potential failure costs. This broader view can highlight the true value of a supplier.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Be aware of regional differences in pricing structures. For instance, suppliers in Africa may have different pricing dynamics compared to those in Europe or the Middle East. Currency fluctuations and local economic conditions can also affect final prices.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Keeping abreast of industry developments can provide leverage in negotiations and help identify emerging suppliers who may offer competitive pricing.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for automotive electronics can fluctuate based on market conditions, material costs, and supplier negotiations. It is advisable for buyers to obtain detailed quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing. Regular market analysis will aid in making informed sourcing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing automotive electronic manufacturer With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives for Automotive Electronic Manufacturing Solutions
In the dynamic landscape of automotive electronics, international B2B buyers must consider various solutions that cater to their specific needs. While traditional automotive electronic manufacturers provide robust products and services, alternative technologies and methods can also achieve similar objectives, sometimes offering unique advantages. This section provides a comparative analysis of automotive electronic manufacturers against two viable alternatives: Custom Electronics Development and Modular Electronics Platforms.
| Comparison Aspect | Automotive Electronic Manufacturer | Custom Electronics Development | Modular Electronics Platforms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High performance with proven reliability in mass production. | Tailored solutions can outperform standard products for specific needs. | Variable performance, depending on module integration. |
| Cost | Generally higher upfront costs due to mass production and quality assurance. | Potentially higher costs due to R&D and prototyping phases. | Cost-effective for modular designs but may require additional investment in integration. |
| Ease of Implementation | Streamlined due to established processes and support. | Complex, requiring significant collaboration and time to develop. | Moderate; easier to implement but depends on compatibility with existing systems. |
| Maintenance | Supported by manufacturer with established service networks. | Maintenance can be challenging without proper support systems. | Modular systems can be easier to maintain and upgrade. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for large-scale production with standardized needs. | Best for specialized applications requiring unique functionalities. | Suitable for projects needing flexibility and scalability. |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Custom Electronics Development?
Custom electronics development offers tailored solutions designed to meet specific requirements. The primary advantage of this approach is its adaptability; businesses can create unique functionalities that standard products cannot provide. However, this method often involves higher costs and longer lead times due to the research and development phase. Additionally, the complexity of integration and potential lack of support can pose challenges for companies unfamiliar with bespoke solutions.
How Do Modular Electronics Platforms Compare?
Modular electronics platforms present a flexible alternative by allowing manufacturers to assemble components based on specific needs. This approach can be cost-effective, especially for projects requiring customization without starting from scratch. The ease of upgrading and replacing individual modules can lead to lower long-term maintenance costs. However, the performance may vary significantly based on how well the modules integrate with one another, and there may be compatibility issues with existing systems.
Conclusion: Which Solution Should B2B Buyers Choose for Automotive Electronics?
When selecting the right solution for automotive electronics, B2B buyers must evaluate their specific needs carefully. If the goal is to achieve high performance in large-scale production, sticking with established automotive electronic manufacturers might be the best choice. However, for businesses with unique requirements or the need for flexibility, exploring custom electronics development or modular platforms can yield significant advantages. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for automotive electronic manufacturer
What Are the Essential Technical Properties for Automotive Electronic Manufacturing?
When selecting automotive electronic components, understanding key technical properties is crucial for ensuring quality, reliability, and performance. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– The material grade of electronic components, such as circuit boards and connectors, indicates the quality and durability of the materials used. Higher-grade materials often result in enhanced performance and longevity, which is vital for automotive applications where failure can lead to serious safety issues. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who utilize high-grade materials to ensure compliance with industry standards. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. In automotive electronics, precise tolerances are essential for compatibility and functionality within complex systems. Understanding tolerance levels can help buyers select components that will fit seamlessly into their designs, reducing the risk of errors during assembly and minimizing the potential for costly rework. -
Operating Temperature Range
– Automotive electronics must function effectively under varying temperature conditions, from extreme cold to high heat. Buyers should look for components that specify a wide operating temperature range to ensure reliability in different climates, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, where temperature variations can be significant. -
Electrical Ratings
– Electrical ratings, including voltage, current, and power specifications, are critical for assessing whether a component can handle the demands of the automotive system. Understanding these ratings helps buyers ensure that the components will not only perform effectively but also comply with safety regulations. -
Life Cycle Testing
– Life cycle testing evaluates the durability and reliability of components under real-world conditions over time. B2B buyers should seek manufacturers that provide data on life cycle testing to confirm that their products can withstand the rigors of automotive use, thereby reducing the likelihood of failure.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in Automotive Electronics?
Navigating the landscape of automotive electronic manufacturing requires familiarity with key trade terminology. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding the OEM landscape is crucial for buyers, as it influences sourcing decisions and impacts product quality and compatibility. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchasing strategy, manage inventory, and negotiate better terms with suppliers, especially for larger orders typical in the automotive sector. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs to compare prices, terms, and conditions from multiple manufacturers, ensuring they secure the best deal while maintaining quality standards. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping, including who pays for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms can help buyers avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions across borders, which is particularly relevant for international buyers from diverse regions. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving it. Understanding lead times is essential for effective supply chain management, allowing buyers to plan production schedules and avoid delays in their automotive projects.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing automotive electronic components, ensuring they partner with reliable manufacturers and secure high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the automotive electronic manufacturer Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics in the Automotive Electronic Manufacturing Sector?
The automotive electronic manufacturing sector is undergoing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. Key global drivers include the growing demand for electric vehicles (EVs), enhanced vehicle connectivity, and increasing automation in production processes. International B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of the rapid integration of smart technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) into automotive electronics. These technologies not only enhance vehicle performance but also improve safety features, which are becoming paramount in modern automotive design.
Emerging B2B sourcing trends indicate a shift towards agile supply chains that can adapt to fluctuating market demands. International buyers should consider strategic partnerships with local suppliers who can offer flexibility and shorter lead times. Additionally, the focus on cost-efficiency and innovation has prompted many manufacturers to invest in research and development (R&D) for next-generation electronic components, such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and battery management systems (BMS). This emphasis on innovation presents opportunities for international buyers to source cutting-edge technologies that can differentiate their offerings in competitive markets.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Automotive Electronics Industry?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become critical considerations for international B2B buyers in the automotive electronics sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including electronic waste and carbon emissions, has prompted manufacturers to adopt more sustainable practices. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to reducing their environmental footprint through innovative materials and manufacturing techniques.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers should look for partners who adhere to internationally recognized standards and certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the Responsible Business Alliance (RBA) Code of Conduct. Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials, such as recyclable plastics and eco-friendly metals, is gaining traction. These materials not only comply with environmental regulations but also appeal to consumers who are increasingly concerned about sustainability. By sourcing from manufacturers that prioritize ethical practices, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing demand for responsible products.
How Has the Automotive Electronics Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the automotive electronics sector has been marked by rapid technological advancements and changing consumer expectations. Initially, automotive electronics focused on basic functionalities, such as ignition systems and dashboard displays. However, as vehicles became more complex, the demand for advanced electronic systems surged, leading to innovations in areas like infotainment, navigation, and safety features.
The introduction of electric vehicles has further accelerated this evolution, necessitating the development of sophisticated electronic components that can manage battery performance and energy efficiency. Today, the automotive electronics industry is at the forefront of integrating advanced technologies, setting the stage for a future where vehicles are not only more efficient but also smarter and more connected. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is essential for making informed sourcing decisions that align with current trends and consumer demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of automotive electronic manufacturer
-
How do I ensure quality when sourcing automotive electronics from manufacturers?
To ensure quality when sourcing automotive electronics, start by conducting thorough research on potential suppliers. Look for manufacturers with ISO certifications and positive industry reviews. Request product samples to evaluate their performance and reliability. Establish clear quality assurance protocols and consider third-party inspections to verify compliance with industry standards. Engaging in regular communication and site visits can also help build trust and ensure that quality is consistently maintained throughout the production process. -
What are the key factors to consider when selecting an automotive electronics supplier?
When selecting an automotive electronics supplier, consider factors such as their experience in the industry, production capabilities, and technological expertise. Evaluate their compliance with international regulations and standards, especially those relevant to your target market. Assess their ability to offer customization options and flexibility in order quantities. Furthermore, consider their logistics capabilities and whether they have a reliable supply chain to ensure timely delivery. Finally, review their financial stability and customer support services. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for automotive electronic components?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for automotive electronic components can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the specific product. Typically, MOQs can range from 100 to 1,000 units for standard products. However, for highly specialized or customized components, MOQs may be higher. When negotiating with suppliers, discuss your specific needs and explore options for smaller orders, especially if you’re a new buyer or entering a new market. Some manufacturers may be willing to accommodate lower MOQs for long-term partnerships. -
How can I negotiate favorable payment terms with automotive electronics manufacturers?
To negotiate favorable payment terms with automotive electronics manufacturers, start by demonstrating your credibility as a buyer. Present your business history, financial stability, and potential for future orders. Propose a payment structure that aligns with your cash flow, such as partial payments upfront with the remainder upon delivery. Consider leveraging trade finance options or establishing a letter of credit to mitigate risk for both parties. Building a strong relationship with the manufacturer can also lead to more favorable terms over time. -
What are the best practices for vetting automotive electronics suppliers?
Best practices for vetting automotive electronics suppliers include conducting background checks and verifying their business licenses and certifications. Look for reviews and testimonials from other international buyers, particularly those in your region. Request references and follow up to gain insights into their reliability and quality. Additionally, assess their production capabilities and technology by visiting their facility if possible. Engaging a local sourcing agent can also provide valuable insights into the supplier’s reputation and practices. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping when sourcing automotive electronics internationally?
Handling logistics and shipping when sourcing automotive electronics internationally requires careful planning. Start by understanding the shipping regulations and customs requirements of both the exporting and importing countries. Choose a reliable freight forwarder with experience in automotive electronics to manage the shipping process. Consider the shipping method (air vs. sea) based on cost and urgency. Ensure that all documentation, such as invoices and packing lists, is accurate to avoid delays. Lastly, factor in lead times for production and delivery when planning your inventory. -
What customization options should I ask for when sourcing automotive electronics?
When sourcing automotive electronics, inquire about customization options that align with your specific needs. This may include modifications to hardware, firmware, or software to ensure compatibility with your vehicles or applications. Discuss branding opportunities, such as custom labeling or packaging. Clarify whether the manufacturer can accommodate changes in design or functionality as your market demands evolve. Ensure that you understand any additional costs or lead times associated with customization, and consider how these options will impact your overall supply chain. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from an automotive electronics manufacturer?
Quality assurance measures to expect from an automotive electronics manufacturer should include comprehensive testing protocols, such as functional, environmental, and durability tests. Manufacturers should have a clear quality management system in place, often certified by relevant industry standards like ISO/TS 16949 for automotive suppliers. Expect regular quality audits and reports detailing compliance with specifications. Additionally, inquire about traceability systems that allow tracking of components through the production process, ensuring accountability and transparency in quality management.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for automotive electronic manufacturer
In today’s rapidly evolving automotive landscape, strategic sourcing has emerged as a critical component for manufacturers of automotive electronics. By leveraging global supply chains and optimizing procurement processes, businesses can enhance their competitiveness while ensuring product quality and innovation. International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must prioritize partnerships that not only offer cost efficiency but also align with sustainability goals and technological advancements.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Drive Value for International Buyers?
Investing in strategic sourcing allows buyers to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions, particularly in light of geopolitical uncertainties and fluctuating market demands. By diversifying suppliers and exploring emerging markets, companies can secure a robust supply chain while fostering collaboration with innovative partners.
What Is the Future Outlook for Automotive Electronic Manufacturers?
Looking ahead, the automotive electronic sector is poised for significant growth driven by the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and smart technologies. Buyers should remain agile, continuously evaluating their sourcing strategies to adapt to market trends and technological shifts. Embracing digital tools for procurement and supply chain management can further enhance efficiency and responsiveness.
In conclusion, the future of automotive electronics manufacturing hinges on strategic sourcing as a pathway to resilience and success. International B2B buyers are encouraged to actively seek partnerships that align with their strategic goals, ensuring they remain at the forefront of this dynamic industry. Engaging in proactive sourcing strategies today will pave the way for sustainable growth and innovation in the automotive electronics sector.