Pet Bottle Blowing Machines: The Ultimate 2025 Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for PET Bottle Blowing Machines
In the high-stakes manufacturing landscapes of the USA and Europe, production efficiency is not just a metric—it is the defining factor of competitiveness. As consumer demand for versatile, sustainable packaging accelerates, facilities must rely on PET bottle blowing machines that deliver absolute precision, speed, and reliability.
However, scaling production is rarely straightforward. Manufacturers often face the “efficiency paradox”: balancing high-speed output with the need for intricate bottle designs and eco-friendly lightweighting. Furthermore, sourcing equipment is no longer about buying a standalone machine; it is about finding a comprehensive solution that integrates seamlessly from blowing to filling and labeling. A misstep in equipment selection can lead to costly downtime, inconsistent bottle quality, and inflated energy costs.
Drawing on industry standards and over 25 years of global engineering expertise, this guide provides a roadmap for procurement teams and plant managers. We move beyond basic specifications to analyze the operational realities of modern PET production.
This guide covers:
- Technological Integration: How modern blow molding units interface with complete filling lines.
- Selection Criteria: Evaluating speed (BPH), energy efficiency, and mold flexibility.
- Global Partnership: Why support across 80+ countries matters for long-term maintenance and commissioning.
- ROI Analysis: Balancing initial investment with long-term operational costs.
Prepare to optimize your production line with solutions designed for the most demanding markets.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Top 10 Pet Bottle Blowing Machines Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. SMF – Blowing machines for bottle production
Domain: smfgmbh.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: We specialize in: production of PET bottle blow molding machines, bottle stackers, conveyors. Check out our offer & contact us….
2. Top 10 Extrusion Blow Molding Machine Manufacturers – MAIWEI
Domain: maiwei-machine.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Here is a curated list of the top 10 extrusion blow molding machine manufacturers worldwide, based on their technological advancements, market presence, ……
3. 10 Best Water Bottle Blowing Machine Brands in 2025 – MEPER
Domain: meper-blowmolding.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Waton Machinery Co., Ltd. is a leading manufacturer of high-speed PET blow molding machines in China. With a strong focus on quality and ……
4. China Top PET Bottle Blowing Machine Manufacturers Suppliers …
Domain: eceng-petblowing.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Eceng Machinery: Professional and reliable top pet bottle blowing machine manufacturers and suppliers in China. There are a great selection of top pet ……

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. SEGS Series PET Bottle Blowing Machine – High Stability & Efficiency
Domain: stableblowing.com
Registered: 2025 (0 years)
Introduction: Rating 5.0 (1) We are Shenbao Machinery, a leading manufacturer of PET stretch blow molding machines. Our SEGS Series is designed to offer high stability and ease of ……
6. Pet Plast India Inc.
Domain: petbottleplant.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Pet Plast India Inc., an ISO 9001:2008 certified company, is the reliable Manufacturer and Supplier of a wide range of PET/PP/PC Blowing Machines (Fully auto ……
7. Pet Blow Molding Machine Manufacturers in Toronto
Domain: petallmfg.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Pet All Manufacturing Inc. is a manufacturer and supplier of pet blow molding molding machines in North America, Latin America, and Europe….
Understanding pet bottle blowing machines Types and Variations
Understanding PET Bottle Blowing Machines: Types and Variations
Selecting the right machinery is critical for optimizing production efficiency and meeting specific packaging requirements. In the PET manufacturing sector, equipment is generally categorized by its mechanical architecture (Linear vs. Rotary) and its level of integration (Standalone vs. Combi).
The following section outlines the primary variations of PET blow molding machinery available for the US and European markets, informed by modern industry standards for efficiency and precision.
Quick Comparison: PET Blowing Machine Types
| Machine Type | Key Features | Primary Applications | Pros & Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Stretch Blow Molding | Modular design; servo-driven systems; high flexibility for mold changes. | SMEs; specialized custom shapes; production runs requiring frequent format changes. | Pros: Lower capital cost, high flexibility, easy maintenance. Cons: Lower total output speed compared to rotary. |
| Rotary Stretch Blow Molding | Continuous motion; high-speed output; typically hydraulic or hybrid drive. | Large-scale beverage production (water, CSD); high-volume standardized bottle runs. | Pros: Maximum efficiency (BPH), consistent quality at speed. Cons: Higher footprint, expensive tooling changes. |
| Integrated Combi Lines (Blow-Fill-Cap) | Unites blowing, filling, and capping in a single compact block; eliminates intermediate conveying. | Complete bottling plants; sensitive beverages (juices, dairy) requiring hygiene. | Pros: Compact footprint, energy efficiency, reduced contamination risk. Cons: High initial investment; fault in one unit stops the whole line. |
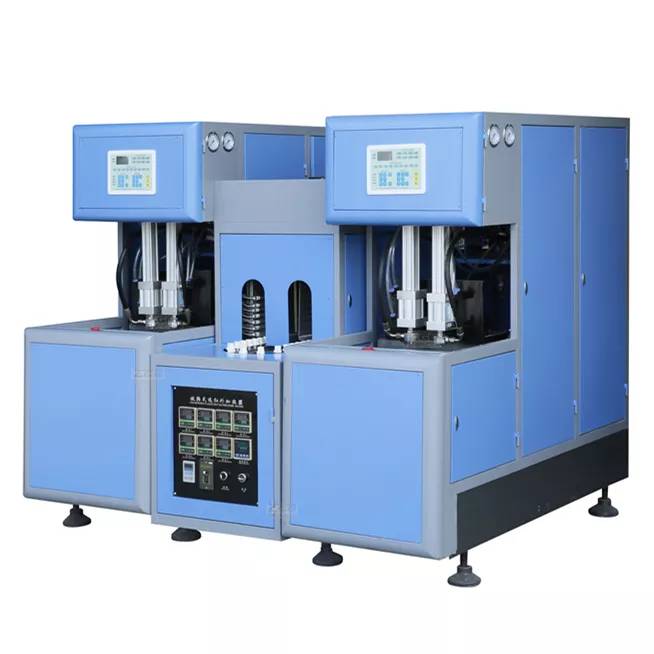
1. Linear Stretch Blow Molding Machines
Linear machines are the workhorses of the flexible packaging industry. As the name suggests, preforms move through the machine in a linear path. These systems are particularly aligned with manufacturers who prioritize versatility over raw speed.
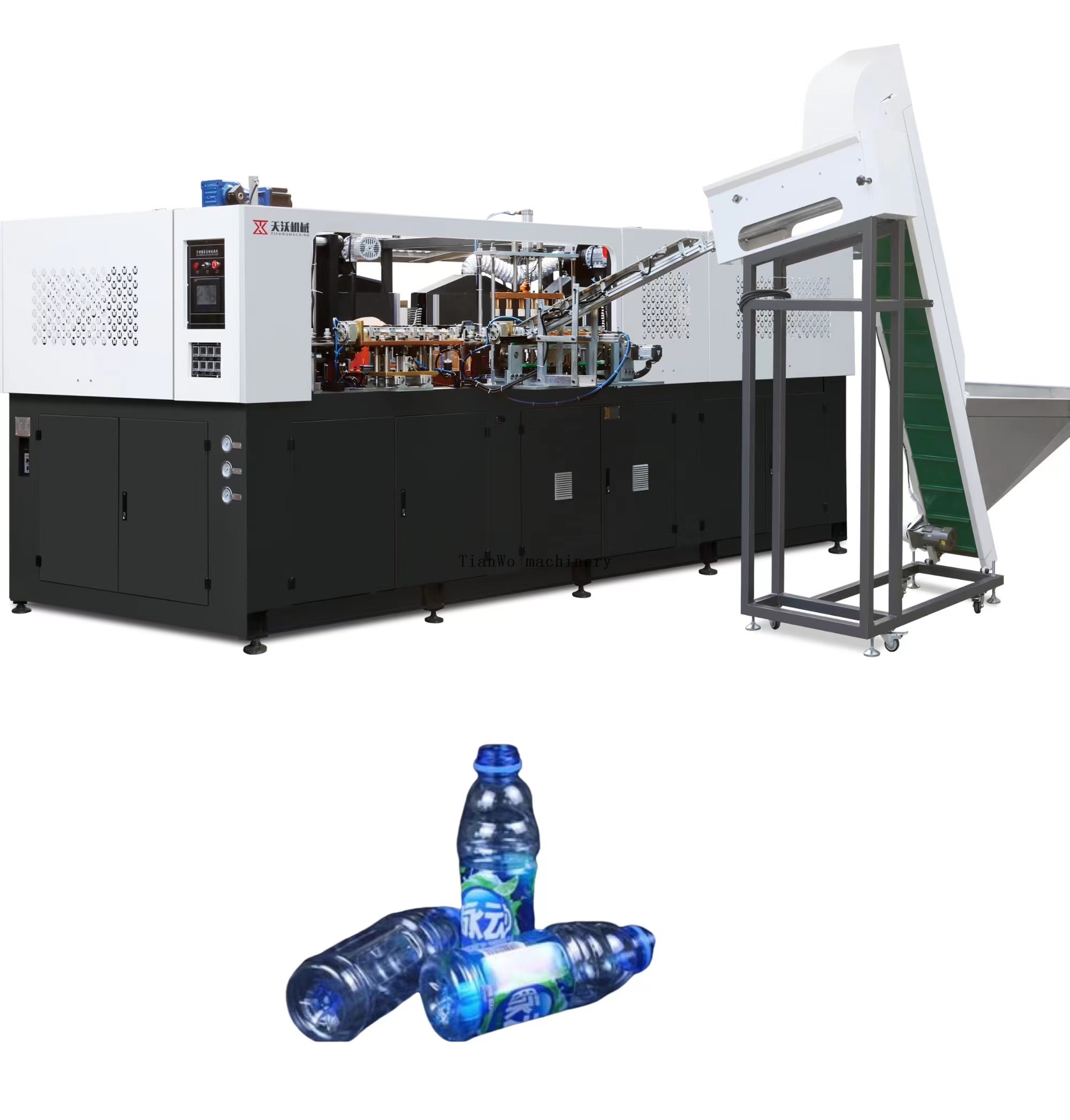

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Mechanism: Preforms are loaded, heated, and blown in a step-by-step linear sequence. Modern iterations often utilize all-electric servo drives to ensure precision and reduce energy consumption.
- Best For: Manufacturers producing a wide variety of bottle shapes (“Every shape, every vision”) or those requiring frequent mold changeovers. They are ideal for SKUs ranging from small single-serve bottles to large 5L containers.
- Market Relevance: In the European and US markets, linear machines are favored by contract packers and brands with diverse product portfolios who need to switch between designs quickly without extensive downtime.
2. Rotary Stretch Blow Molding Machines
Rotary machines are designed for speed and volume. In these systems, the molds are mounted on a rotating wheel, allowing for a continuous production flow.
- Mechanism: The continuous motion eliminates the start-stop cycle of linear machines, allowing for significantly higher production rates (often exceeding 14,000 to 80,000+ BPH).
- Best For: High-volume production of standardized containers, such as water and carbonated soft drinks (CSD).
- Market Relevance: These are the standard for major beverage corporations where “highest efficiency” and reliability are the primary KPIs. While the initial capital expenditure is higher, the cost-per-bottle drops significantly at high volumes.
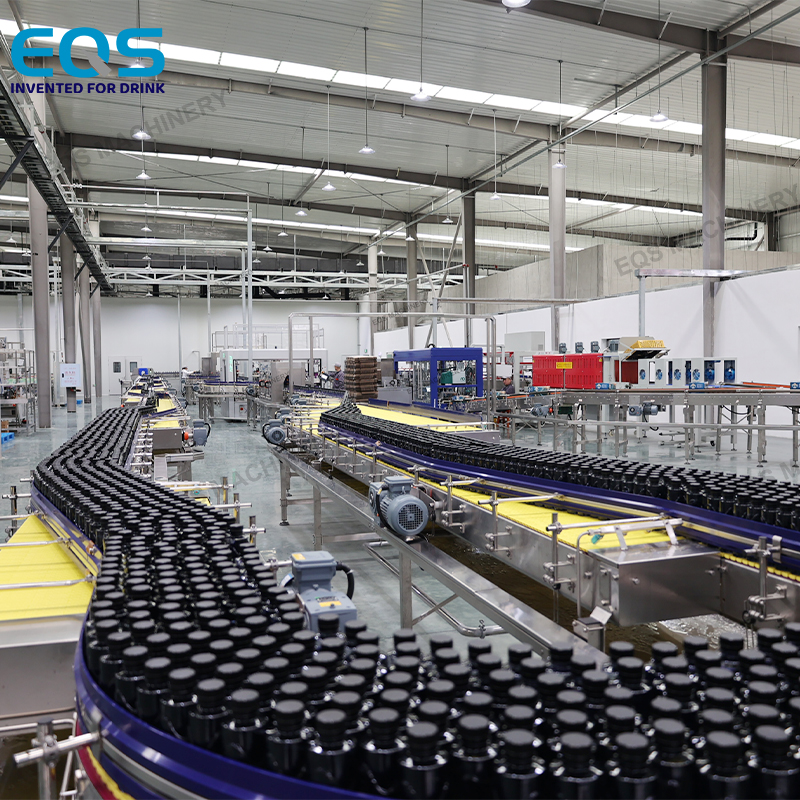
3. Integrated Combi Lines (Blow-Fill-Cap)
Moving beyond standalone blowing, the industry is shifting toward “Complete PET Filling Lines.” These systems integrate the blowing unit directly with the filler and capper into a single, compact block.
- Mechanism: By eliminating air conveyors between the blower and filler, these systems reduce the risk of bottle contamination and damage. They offer a “compact solution” that streamlines the process from raw preform to finished product.
- Best For: Greenfield projects or facilities with limited floor space looking for optimized solutions. They are particularly effective for lightweight bottles (which are hard to convey) and sensitive products requiring strict hygiene control.
- Market Relevance: As noted in recent implementations (e.g., the 14,000 BPH line for Uzdrowisko Busko-Zdrój), these comprehensive lines allow manufacturers to increase competitiveness by centralizing control and reducing energy overheads associated with multiple standalone machines.
Key Industrial Applications of pet bottle blowing machines
Key Industrial Applications of PET Bottle Blowing Machines
Modern PET blow molding technology has evolved beyond standard beverage packaging. For manufacturers in the USA and Europe, the versatility of these machines—capable of handling complex shapes and varying production speeds—makes them integral to several high-value sectors.
The following table outlines the primary industrial sectors utilizing PET blowing technology and the specific applications within each.
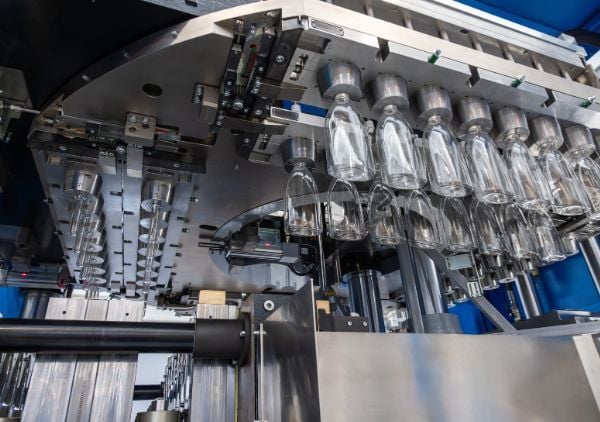
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Industry Application Matrix
| Industry Sector | Typical Applications | Critical Machine Capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Beverage (CSD & Water) | • Carbonated Soft Drinks (CSD) • Mineral & Spring Water • Energy Drinks |
High-Pressure Resistance: Machines must produce bottles capable of withstanding internal carbonation pressure. High Output: Required speeds often exceed 14,000 BPH for efficiency. |
| Liquid Dairy & Juices | • Fresh Milk & Yogurt Drinks • Cold-Pressed Juices • Smoothies |
Aseptic Technology: Critical for sensitive products requiring extended shelf life without preservatives. Light-blocking: Multi-layer preform handling to protect vitamin content. |
| Edible Oils & Sauces | • Sunflower & Olive Oil • Ketchup & Dressings • Vinegars |
Weight Precision: Handling heavier preforms for rigid containers. Handle Integration: Capability to blow complex shapes with integrated handles for large-volume containers (3L–5L). |
| Home & Personal Care | • Detergents & Softeners • Shampoos & Lotions • Dishwashing Liquids |
Design Flexibility: Focus on unique, non-cylindrical shapes (oval, rectangular) for brand differentiation. Orientation Precision: Ensuring neck orientation for pump/spray dispensers. |
| Chemical & Automotive | • Screen Wash Fluids • Sanitizers & Solvents • Motor Oils |
Durability: Production of bottles with thicker walls for chemical resistance and transport safety. Leak Integrity: High-precision neck finish molding to prevent leakage of hazardous fluids. |
Operational Benefits for Manufacturers
Implementing advanced PET blowing machinery offers distinct competitive advantages for B2B operators in competitive Western markets.
1. Unrestricted Design Flexibility (“Every Shape, Every Vision”)
Modern consumer markets demand distinct packaging to stand out on the shelf. Advanced blowing machines allow for the production of complex geometries beyond standard cylindrical bottles.
* Customization: Ability to switch molds quickly to produce unique shapes for marketing campaigns or seasonal products.
* Precision: High-fidelity replication of mold details, including embossed logos and ergonomic grips.
2. End-to-End Line Efficiency
As exemplified by integrated solutions (such as those handling up to 14,000 BPH), modern blow molding is rarely a standalone process.
* Integration: Machines are designed to sync perfectly with filling, labeling, and packaging units.
* Scalability: Equipment is available for various scales, from compact solutions for niche water brands (e.g., Uzdrowisko Busko-Zdrój) to mass-production lines.
3. Sustainability and Cost Reduction
With EU and US regulations tightening around plastic usage, modern machines are engineered to support “Lightweighting”—the process of reducing the amount of PET resin per bottle without compromising structural integrity.
* Material Savings: Advanced heating and blowing profiles reduce preform weight requirements.
* Energy Efficiency: Newer servo-driven systems reduce electricity consumption during the heating and blowing phases, lowering the total cost of ownership (TCO).
4. Hygiene and Safety Compliance
For food, dairy, and pharmaceutical applications, machine architecture prioritizes contamination control.
* Clean Design: Machines are constructed to minimize lubricant usage and prevent contamination of the bottle interior.
* Closed Loop Systems: Essential for maintaining the purity of water and sensitive beverages from the blowing stage through to capping.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pet bottle blowing machines’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘PET Bottle Blowing Machines’ & Their Solutions
1. Inconsistent Bottle Quality & High Rejection Rates
Scenario: A beverage manufacturer in Europe expands their product line to include lightweight 500ml water bottles. During the initial run, the quality control team flags a 15% rejection rate due to uneven wall thickness and “pearly” opacity in the neck area.
The Problem:
Achieving uniform wall thickness in PET bottles requires precise coordination between the heating of the preform and the mechanical stretching process. Older or less sophisticated machines often rely on pneumatic cylinders for stretching, which can suffer from inconsistent speed and pressure fluctuations. Additionally, standard infrared ovens may heat preforms unevenly, causing the material to stretch unpredictably—leading to weak spots, visual defects, and wasted material.
The Solution:
Servo-Driven Stretching & NIR Heating Technology.
Modern PET blowing machines, such as those engineered by SMF, replace pneumatic variability with servo-motor precision. Servo systems allow for exact control over the stretch rod’s speed and position (down to the millimeter), ensuring the preform is stretched exactly as designed every cycle.
* Near-Infrared (NIR) Lamps: Unlike standard IR, NIR lamps provide deeper, more uniform heat penetration into the preform wall, ensuring the plastic is perfectly malleable before blowing.
* Result: Rejection rates drop significantly (often below 0.1%), and manufacturers can confidently produce lightweight bottles without compromising structural integrity.
2. Excessive Energy Consumption
Scenario: A US-based bottling plant manager reviews the facility’s quarterly utility costs and identifies the compressed air system as the single largest expense. The high-pressure air required for the blowing stage is driving electricity bills up, threatening the product’s profit margin.
The Problem:
PET blow molding is inherently energy-intensive. The process requires high-pressure compressed air (often 30-40 bar) to shape the bottle, followed by low-pressure air for machine movement. In traditional systems, the high-pressure air used to blow the bottle is simply vented into the atmosphere after each cycle—a massive waste of potential energy. Furthermore, inefficient oven designs waste heat, requiring more electricity to keep preforms at the optimal temperature.
The Solution:
Air Recovery Systems & Eco-Ovens.
Advanced blowing machines now feature integrated Air Recovery Systems (ARS). These systems capture the exhaust air from the high-pressure blowing stage and recycle it to power the machine’s low-pressure pneumatic movements (like clamping and stretching) or route it to other factory equipment.
* Eco-Oven Design: Manufacturers like SMF utilize compact oven tunnels with ceramic reflectors to focus heat strictly on the preform, minimizing energy loss to the surroundings.
* Result: Energy consumption for compressed air can be reduced by up to 40-50%, directly improving the plant’s bottom line and sustainability profile.
3. Production Downtime During Format Changeovers
Scenario: A contract packer (co-packer) produces bottles for multiple clients, requiring frequent switches between 330ml juice bottles and 1L detergent containers. Each changeover currently takes 4 hours to cool down the machine, swap molds with heavy tools, and recalibrate, effectively killing half a day of production.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
The Problem:
In a high-mix production environment, flexibility is key. However, traditional blowing machines use bolted mold assemblies that are heavy, difficult to align, and require skilled technicians to swap. The “downtime cost” includes not just the lost production hours, but also the material wasted during the ramp-up phase while fine-tuning the new bottle parameters.
The Solution:
Quick-Change Mold Systems.
Leading manufacturers have standardized tool-less or semi-tool-less quick changeover systems. These smart mold designs allow operators to swap mold cavities in as little as 15–30 minutes.
* Smart Recipes: Modern HMIs (Human-Machine Interfaces) store “recipes” for each bottle format. Once the physical mold is swapped, the operator simply selects the corresponding profile, and the machine automatically adjusts heating zones and blowing pressures.
* Result: Changeover times are reduced by over 80%, allowing manufacturers to accept smaller, more diverse orders without sacrificing efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pet bottle blowing machines
Strategic Material Selection Guide for PET Bottle Blowing Machines
Selecting the correct resin and preform specifications is not merely a procurement decision; it is a critical operational variable that dictates machine efficiency, cycle times, and final product integrity. For manufacturers in the USA and Europe, where sustainability regulations and quality standards are stringent, understanding the interplay between raw materials and blowing machine capabilities is essential.
Modern blowing equipment—such as the high-precision lines manufactured by SMF—is designed to handle a variety of material inputs. However, optimizing production speed and minimizing rejection rates requires a strategic approach to material selection.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. Virgin PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate)
Virgin PET remains the industry standard for applications requiring high optical clarity and consistent Intrinsic Viscosity (IV).
* Machine Interaction: Virgin PET offers the most predictable processing window. High-speed linear and rotary machines can operate at maximum rated speeds (e.g., 14,000 BPH) with minimal adjustment to heating profiles.
* Strategic Fit: Ideal for premium beverage brands and pharmaceutical applications where aesthetic flaws or contamination risks are zero-tolerance issues.
2. Recycled PET (rPET)
Driven by the EU Single-Use Plastics Directive and US sustainability goals, rPET is rapidly becoming the dominant material choice.
* Processing Challenges: rPET often exhibits inconsistent IV levels and color variations compared to virgin resin. This can lead to uneven wall thickness if the blowing machine lacks advanced process controls.
* Machine Requirements: Successful rPET processing requires blowing machines equipped with precise, multi-zone heating systems (such as NIR or advanced IR lamps) that can adjust thermal penetration in real-time to compensate for material inconsistencies.
* Sustainability: Utilizing up to 100% rPET significantly reduces the carbon footprint but requires a machine capable of handling higher process temperatures without degrading the material.
3. Lightweight Preforms
Lightweighting is the primary method for reducing Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) and environmental impact.
* The Physics: Reducing the preform weight (e.g., shifting from 12g to 9g for a 500ml bottle) reduces the material available for stretching.
* Precision Blowing: This requires machines with servo-driven stretching rods and high-pressure air recovery systems. The machine must distribute the material perfectly evenly; otherwise, the bottle will suffer from “pearling” or structural weakness during top-load testing.
* SMF Context: For lines emphasizing “efficiency and cost-effectiveness,” lightweighting is the single most effective operational lever.
4. Barrier Additives and Multilayer Preforms
For sensitive products (juices, dairy, beer) requiring extended shelf life, standard PET is often insufficient regarding O2 and CO2 permeation.
* Material Composition: Includes oxygen scavengers (like Amosorb) or multilayer structures (PET/Nylon/PET).
* Processing Impact: These materials have different thermal absorption rates. The blowing machine must utilize specific heating profiles to prevent delamination (layer separation) or haze.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Comparative Analysis: Material Impact on Production
The following table outlines how different material choices impact machine parameters and operational goals.
| Material Type | Primary Application | Machine Processing Considerations | Sustainability Impact | Cost Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virgin PET | Water, CSD, Pharma | Low Complexity: Standard heating profiles; max cycle speeds achievable immediately. | Low | Medium (Market dependent) |
| rPET (25-50%) | Consumer Beverages | Medium Complexity: Requires minor heating adjustments; generally stable. | Medium | High (Tax incentives) |
| rPET (100%) | Eco-focused Brands | High Complexity: Requires advanced heating control and precise preform handling to avoid yellowing/haze. | High | Variable (Supply dependent) |
| Lightweight Preforms | High-Volume Water | High Precision: Demands servo-stretching and precise pressure control to prevent blowouts. | Medium | Highest (Material savings) |
| Barrier/Multilayer | Juice, Beer, Dairy | Thermal Sensitivity: Slower cycle times may be required to ensure proper heat soak without delamination. | Low (Harder to recycle) | Low (High material cost) |
Conclusion
To fully leverage the capabilities of modern blowing machinery—like those offered by SMF—manufacturers must align their material procurement with machine specifications. While virgin PET offers ease of use, the market trajectory in Europe and the US demands a shift toward rPET and lightweighting. Success in this transition relies on utilizing blowing machines with the adaptive technology necessary to process these variable materials without sacrificing speed or quality.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pet bottle blowing machines
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance
For buyers in the US and European markets, the value of a PET bottle blowing machine is defined by its Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and operational uptime. These metrics are directly determined by the rigor of the Original Equipment Manufacturer’s (OEM) fabrication and Quality Assurance (QA) protocols.
High-end manufacturers, such as those with decades of global implementation experience, utilize a precision-first approach to ensure machines meet the demands of carbonated and non-carbonated filling lines.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. The Manufacturing Lifecycle
The production of a PET blow molding machine typically follows a four-stage engineering cycle designed to minimize vibration, ensure mold alignment, and guarantee repetition accuracy.
Phase 1: Material Preparation and Sourcing
- Raw Material Selection: The machine frame is constructed from high-grade structural steel to absorb the kinetic energy generated during high-speed blowing (up to 14,000 BPH).
- Component Sourcing: Critical components (pneumatics, PLCs, servo motors) are sourced from Tier-1 suppliers. For European and American markets, this ensures component traceability and ease of spare parts procurement.
Phase 2: Precision Machining and Forming
- CNC Fabrication: Mold holders, blowing nozzles, and stretching rods undergo CNC machining to achieve tolerances within microns. This precision is vital for minimizing “reject rates” during bottle production.
- Surface Treatment: Components exposed to moisture or preform dust undergo anti-corrosion treatments (galvanization or powder coating) to meet food safety and hygiene standards.
Phase 3: Assembly and Integration
- Mechanical Assembly: Technicians assemble the clamping units and stretching mechanisms. Attention is paid to the alignment of the blowing station to prevent mold wear.
- Electrical & Pneumatic Integration: Installation of the “nervous system” of the machine. This includes high-pressure air recovery systems—a key feature for energy efficiency and environmental sustainability—and the integration of HMI panels.
2. Quality Assurance (QA) Protocols
Before a machine is crated for global shipping, it undergoes rigorous testing. Leading manufacturers do not rely on spot checks; they utilize comprehensive Factory Acceptance Tests (FAT).
| Test Protocol | Description | Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Dry Cycle Testing | Running the machine at full speed without preforms. | Verifies synchronization of servos and clamping mechanisms without load. |
| Hydrostatic Pressure Test | Testing the high-pressure blowing valves and piping (up to 40 bar). | Ensures zero leaks and safety under maximum operating pressure. |
| Mold Clamp Stability | Measuring the locking force of the mold carriers. | Prevents “parting lines” on finished bottles and ensures aesthetic quality. |
| 24-Hour Endurance Run | Continuous operation simulation. | Identifies potential overheating or software logic errors before commissioning. |
3. International Standards and Compliance
For machinery entering the USA and Europe, adherence to specific regulatory frameworks is non-negotiable. Top-tier manufacturers design their equipment to meet the following standards:
- ISO 9001:2015: Certification of the manufacturer’s quality management system, ensuring consistent production processes.
- CE Marking (Europe): Mandatory for the European Economic Area. It certifies that the machine meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection requirements (specifically the Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC).
- UL / ANSI (USA): Electrical components often require UL listing, and machine guarding must comply with ANSI standards to ensure operator safety in American facilities.
- HACCP Compatibility: For machines used in food and beverage (water, juices), the design must facilitate cleaning and prevent contamination, supporting the client’s HACCP protocols.
4. Commissioning and Final Validation
The manufacturing process concludes only after successful installation at the client’s site.
* On-site Optimization: Engineers adjust heating profiles and blowing pressures based on the client’s specific preform characteristics and environmental conditions (humidity/altitude).
* Efficiency Verification: The machine must demonstrate the promised efficiency (e.g., >95% operational efficiency) and low scrap rates before final handover is signed.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pet bottle blowing machines’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for PET Bottle Blowing Machines
Sourcing capital equipment for Western markets requires rigorous vetting. Buyers in the USA and Europe must prioritize energy efficiency, safety compliance (CE/UL), and total cost of ownership (TCO) over initial sticker price.
Use this checklist to structure your procurement process, ensuring alignment with production goals and regulatory standards.
Phase 1: Define Technical Requirements
Before engaging suppliers, quantify your internal production needs to avoid over-specification or capacity bottlenecks.
- Determine Output Capacity: Define required Bottles Per Hour (BPH).
- Note: Account for 85% OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness).
- Specify Bottle Characteristics:
- Volume range (e.g., 200ml to 5L).
- Neck finish standards (e.g., PCO 1881, 29/25).
- Shape complexity (standard cylinder vs. custom ergonomic designs).
- Identify Machine Type:
- Linear: Best for lower to medium speeds, frequent mold changes, and flexibility.
- Rotary: Best for high-speed, continuous mass production.
- Scope Integration Needs: Determine if you need a standalone blower or a complete line (Blower + Filler + Capper + Labeler).
- Reference: Vendors like SMF provide comprehensive lines, ensuring synchronization between blowing and filling stages.
Phase 2: Manufacturer Qualification
Filter vendors based on longevity, global footprint, and engineering capability.
| Criteria | Verification Step |
|---|---|
| Experience | Look for 20+ years in the industry (e.g., SMF has 25+ years). Avoid new market entrants with unproven track records. |
| Global Presence | Verify installations in regulated markets (USA/EU). Check if they have active machines in 50+ countries. |
| Manufacturing Origin | Distinguish between OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) and assemblers/traders. Visit the factory or request a virtual tour. |
| Engineering Support | Confirm the existence of an in-house design team for custom mold development and line layout optimization. |
Phase 3: Technical & Operational Assessment
Evaluate the machine’s efficiency and operational logic.
- Energy Efficiency (Sustainability):
- Does the machine utilize High-Pressure Air Recovery systems? (Target >30% recovery).
- Are the heating lamps infrared (NIR) with segmented control for precise heating profiles?
- Drive Systems:
- Prioritize all-electric servo motor systems over hydraulic systems for cleanliness (crucial for food/beverage) and precision.
- Changeover Speed:
- Request “Mold Changeover Time” data. For flexible production, this should be tool-free and under 30 minutes.
- Component Quality:
- Verify the brand of critical components (PLC, Pneumatics, Servos). Look for Tier 1 suppliers (e.g., Siemens, Mitsubishi, Festo) available locally in the US/EU.
Phase 4: Regulatory Compliance & Safety
For US and European markets, non-compliance is a legal and liability risk.
- Safety Certifications:
- Europe: Must carry a valid CE mark and Declaration of Conformity.
- USA: Request UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or CSA certification for electrical panels.
- Food Safety Standards:
- Ensure all contact parts are food-grade stainless steel (AISI 304/316).
- Verify lubrication systems are isolated from the molding zone to prevent contamination.
Phase 5: After-Sales & Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
The purchase price is only a fraction of the lifecycle cost.
- Service Availability:
- Does the vendor offer remote diagnostics/teleservice?
- Is there a local spare parts depot in your region (Europe/North America)?
- Training & Commissioning:
- Confirm the vendor provides on-site installation and operator training.
- Warranty Structure:
- Standard is 12 months, but negotiate for 24 months on core components (mold clamping units, PLCs).
- Reference Checks:
- Ask for contact details of 3 clients in your region running similar applications. Ask specifically about “unplanned downtime.”
Phase 6: Finalizing the Contract
- Performance Guarantee: Include a clause requiring a Site Acceptance Test (SAT) at full speed for 8 continuous hours before final payment.
- Lead Time: Define strict penalties for delivery delays.
- Incoterms: Clearly define shipping responsibility (typically FOB or CIF) and insurance coverage during transit.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pet bottle blowing machines Sourcing
The following section provides a comprehensive analysis of cost and pricing for sourcing PET bottle blowing machines, tailored for B2B buyers in the USA and Europe.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Sourcing
Sourcing industrial PET bottle blowing machinery requires a “Total Cost of Ownership” (TCO) approach. While the machine’s sticker price is the most visible expense, logistics, duties, auxiliary equipment, and operational labor often comprise 40-60% of the final diverse capital expenditure.
1. Machine Price Breakdown (2024/2025 Estimates)
Market prices vary significantly based on automation level, cavity count, and output speed (measured in Bottles Per Hour – BPH).
| Machine Type | Output (BPH) | Price Range (USD) | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semi-Automatic | 800 – 2,000 | $4,000 – $15,000 | Startups, lab testing, large containers (5 Gallon), or irregular shapes. |
| Automatic (Linear, 2-4 Cavity) | 2,000 – 6,000 | $20,000 – $55,000 | Small to medium beverage producers; standard water/juice bottles. |
| Automatic (Rotary/High-Speed) | 10,000 – 40,000+ | $150,000 – $500,000+ | High-volume mass production (water plants, major CSD brands). |
Note: Prices typically include the main blower and heater. Molds and auxiliary systems (compressors) are often quoted separately.
2. Sourcing Cost Structure
To negotiate effectively, buyers must understand the cost components driving the supplier’s price and the additional costs incurred during acquisition.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
A. Materials (Machine Construction)
The “Materials” cost in a sourcing context refers to the build quality which dictates longevity and price.
* Steel & Frame (20-30% of cost): High-end machines use stainless steel (SS304) to prevent corrosion, essential for food-grade compliance (FDA/CE). Cheaper alternatives use painted carbon steel, which risks rust over time.
* Components (30-40% of cost): The most critical cost driver.
* Premium: Festo/SMC pneumatics, Mitsubishi/Siemens PLC, Schneider electrics. Sourcing machines with these brands adds 15-20% to the price but ensures spare parts availability in the US and Europe.
* Standard: Domestic Chinese brands. Lower cost, but replacement parts may need to be shipped from Asia, causing downtime.
B. Labor (Manufacturing vs. Operational)
- Manufacturing Labor (Embedded in Price): Asian manufacturing labor rates allow for machine prices 30-50% lower than European counterparts. However, the gap is narrowing as skilled labor costs in manufacturing hubs (like Jiangsu and Zhejiang) rise.
- Operational Labor (Your Cost):
- Semi-Automatic: High labor cost. Requires 1-2 dedicated operators per shift to manually load preforms and remove bottles. In the US/EU, annual labor costs can exceed the machine price in <6 months.
- Fully Automatic: Low labor cost. One operator can oversee 3-4 machines.
C. Logistics & Duties
Shipping heavy machinery involves complex logistics. Prices below are estimates for 2025.
- Ocean Freight:
- Asia to US West Coast: ~$1,800 – $3,500 per 40ft container.
- Asia to Northern Europe: ~$2,000 – $4,000 per 40ft container.
- Trend: Rates are volatile due to geopolitical instability. Booking “Fixed Rate” contracts where possible is advised.
- Inland Trucking:
- USA: Average $3.00 – $5.00 per mile for standard flatbed; specialized rigging for heavy loads may cost extra.
- Import Duties & Taxes:
- USA (HS Code 8477.30): Standard duty is low (~3.1%), but Section 301 Tariffs for Chinese origin goods remain a critical factor, potentially adding 25% to the commercial invoice value. Verify current exclusions before shipping.
- Europe: Standard Third-Country Duty is approx. 1.7% – 2.2%. However, VAT (avg. 21%) is payable upon entry, which is a significant cash-flow consideration even if recoverable later.
3. The “Hidden” Costs of Sourcing
Failure to budget for these items is the most common cause of project overruns.
- High-Pressure Air System ($5,000 – $30,000): PET blowing requires 30-40 bar pressure. A standard shop compressor (7-10 bar) will not work. You must source a specialized high-pressure compressor, air dryer, and filters.
- Chiller ($3,000 – $10,000): Required to cool the molds and prevent bottle deformation.
- Molds ($500 – $3,000 per cavity): Molds are custom-machined. Complex designs (embossing, non-standard necks) increase cost. Always order a spare set of wear-parts for the mold.
- Installation & Commissioning: Technicians typically charge $200-$300/day plus flights and accommodation. For a standard automatic line, budget $5,000 – $10,000 for a 5-7 day setup.
4. Tips to Save Costs
- Standardize Preforms: Design your bottle around standard preform neck finishes (e.g., PCO 1881 for carbonated drinks, 29/25 for water). Custom neck finishes require expensive custom preform molds.
- Bundle Auxiliaries: Buying the compressor and chiller from the machine supplier often secures a “package discount” and ensures compatibility, reducing installation headaches.
- Spare Parts Kit: Negotiate a “2-year spare parts kit” (seals, valves, sensors) into the initial purchase price. It is cheaper to ship these inside the machine container than to air-freight them later during a breakdown.
- Energy Efficiency: For high-volume production, pay extra for Servo-driven clamping systems. They cost 10-15% more upfront but reduce electricity consumption by 30-40% compared to pneumatic systems, offering an ROI of 12-18 months in high-energy-cost regions like Europe.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pet bottle blowing machines With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing PET Bottle Blowing Machines With Other Solutions
For production managers and investors in the beverage and liquid packaging sectors, selecting the right machinery is a decision driven by Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), material properties, and supply chain logistics. While PET stretch blow molding is the dominant standard for water and CSD (Carbonated Soft Drinks), it is essential to evaluate how it compares to Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM) and Glass Bottle Manufacturing.
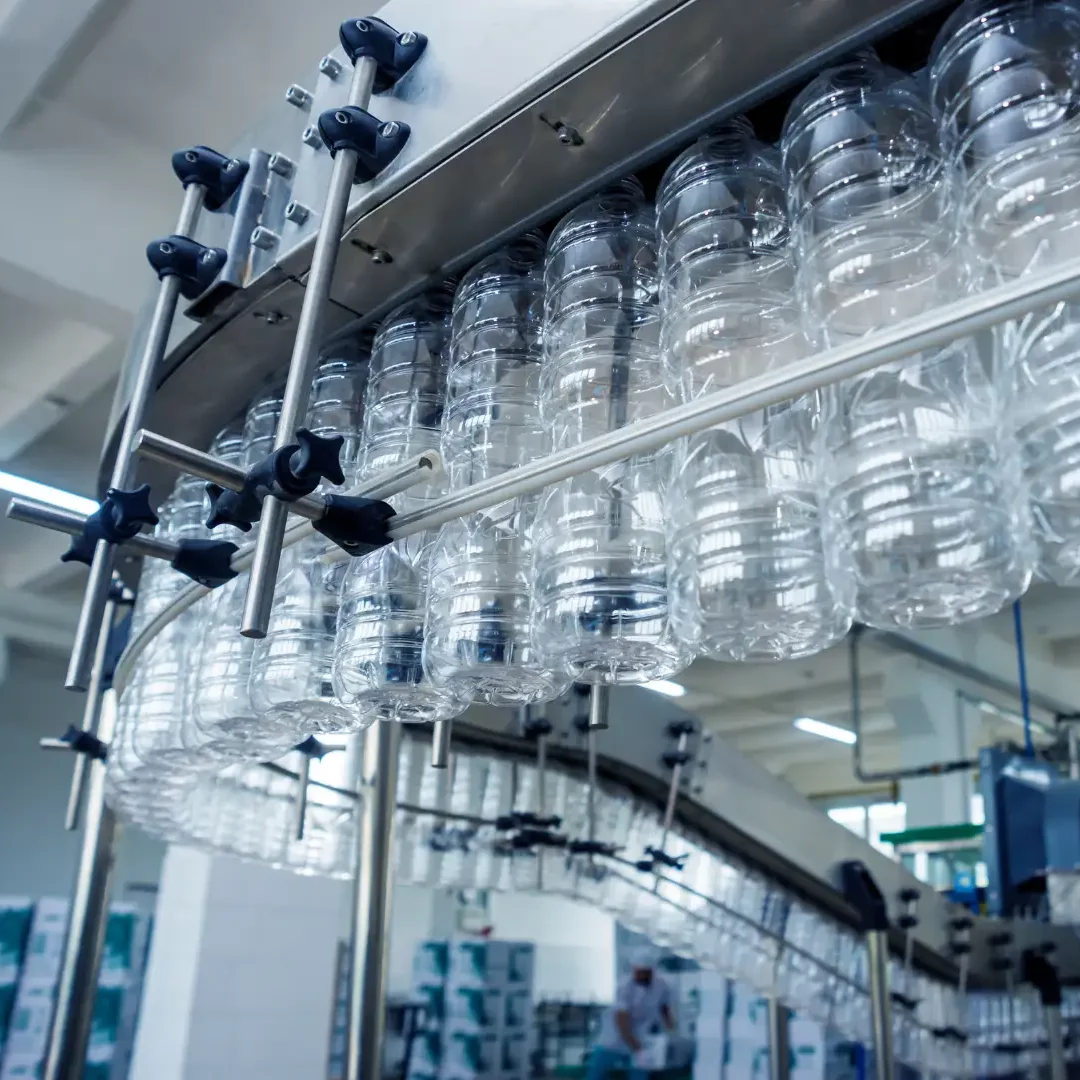

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
The following analysis compares these technologies based on production speed, design capabilities, and operational efficiency.
Comparative Overview
| Feature | PET Stretch Blow Molding | Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM) | Glass Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Materials | PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) | HDPE, PP, PVC | Silica Sand, Soda Ash, Limestone |
| Production Speed | High (Up to 80,000+ BPH) | Low to Medium | Medium |
| Product Weight | Ultra-lightweight | Medium to Heavy | Very Heavy |
| Design Flexibility | High clarity; limited handle integration | Opaque/Translucent; handles easily integrated | High; premium aesthetic |
| Energy Consumption | Moderate (Heating preforms) | High (Melting resin continuously) | Very High (Furnace operations) |
| Transport Costs | Low (Lightweight, non-brittle) | Medium | High (Heavy, fragile) |
detailed Analysis
1. PET Stretch Blow Molding vs. Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM)
Extrusion Blow Molding is frequently utilized for dairy, detergents, and industrial chemicals, often using HDPE or PP.
- Process Difference: PET blowing uses a preform that is reheated and stretched bi-axially. EBM extrudes a molten parison (tube) which is captured in a mold and blown.
- The Efficiency Gap: PET blowing machines generally offer significantly higher output rates per cavity compared to EBM. For high-volume beverage lines (e.g., water, juices), PET solutions provide superior throughput.
- Material usage: PET technology allows for extreme lightweighting without sacrificing tensile strength. EBM products typically require thicker walls to maintain structural integrity, leading to higher raw material consumption per unit.
- Application: Choose EBM if the container requires an integrated handle (e.g., milk jugs) or if the product is sensitive to UV light and requires opaque HDPE. Choose PET blowing for clarity, speed, and cost-effectiveness in high-volume production.
2. PET Stretch Blow Molding vs. Glass Manufacturing
Glass remains the traditional competitor in the premium alcohol and food preservation sectors.
- Logistics and Weight: A standard PET bottle can weigh 90% less than its glass equivalent. This disparity drastically affects logistics costs and carbon footprint during transport. SMF-style PET solutions focus on optimizing this weight reduction to maximize environmental and economic efficiency.
- Safety and Durability: PET is shatterproof, reducing loss rates during filling, capping, and transport. Glass requires specialized handling equipment to mitigate breakage hazards.
- Energy Intensity: Glass manufacturing requires furnaces running at over 1500°C, resulting in massive energy consumption. Modern PET blowing machines use focused infrared heating for preforms, which is significantly more energy-efficient and can be powered on/off more rapidly to match production shifts.
- Aesthetic: While glass offers a “premium” tactile feel, modern PET molding allows for intricate designs and high clarity that mimic glass at a fraction of the cost.
Strategic Conclusion
For manufacturers targeting the mass market in beverages, edible oils, and personal care, PET Stretch Blow Molding offers the optimal balance of speed, precision, and unit cost.
- Select Glass only if the product requires a hermetic seal for years of aging (e.g., wine) or relies heavily on a premium, heavy-weight tactile experience.
- Select EBM only if the container design necessitates an integral handle or utilizes polyolefins (HDPE/PP).
For standard liquid filling lines—ranging from water to carbonated drinks—PET blowing machinery provides the most scalable and efficient return on investment, aligning with modern requirements for lightweight, recyclable, and cost-effective packaging.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pet bottle blowing machines
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology
When sourcing PET bottle blowing machines for markets in the USA and Europe, buyers must evaluate specific technical metrics that dictate production efficiency and compatibility. Below are the critical technical properties and industry-standard trade terms used during procurement.
Key Technical Properties
1. Output Rate (BPH/CPH)
* Definition: Bottles Per Hour or Containers Per Hour.
* Significance: The primary metric for machine speed.
* Linear Machines: Typically range from 1,000 to 12,000 BPH. Ideal for SMEs or flexible production lines.
* Rotary Machines: High-speed solutions ranging from 10,000 to 80,000+ BPH.
* Buyer Note: Verify if the BPH rating is theoretical or based on a specific bottle size (usually 500ml).
2. Cavity Configuration
* Definition: The number of molding chambers available to blow bottles simultaneously.
* Significance: Directly correlates to output capacity. Common configurations range from 1-cavity (semi-auto) to 2-16 cavities (linear) and 20+ (rotary).
* Technical Spec: Look for “pitch” distance, which dictates the maximum bottle diameter the machine can handle.
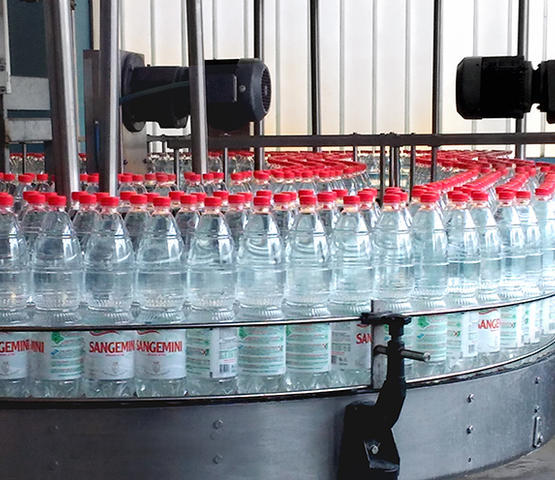

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
3. Maximum Bottle Volume and Neck Finish
* Volume: The range of capacity the machine can blow (e.g., 200ml to 2.5L for standard machines; 5L to 20L for large-format machines).
* Neck Finish: The specific standard of the preform neck (e.g., PCO 1810, PCO 1881, 29/25, 30/25).
* Buyer Note: Ensure the machine’s preform loader and heater mandrels are adjustable or compatible with your specific neck finish standard.
4. Clamping Force (kN)
* Definition: The force applied to keep the mold closed during the high-pressure blowing phase.
* Significance: Insufficient clamping force results in visible mold seams (parting lines) on the bottle, reducing aesthetic quality.
* Requirement: High-pressure applications (carbonated drinks) require higher clamping force than still water applications.
5. Air Pressure Requirements
* Low Pressure (Action): 7–10 bar. Used for machine mechanical movements (clamping, stretching).
* High Pressure (Blowing): 25–40 bar. Required to expand the preform into the mold shape.
* Efficiency: Modern machines utilize air recovery systems to recycle high-pressure exhaust air for low-pressure pneumatic actions, reducing energy consumption by up to 30%.
6. Heating System Efficiency
* Technology: Near Infrared (NIR) or Infrared (IR) lamps.
* Significance: The heating tunnel prepares the preform for stretching.
* Key Feature: Look for servo-driven stepping in the heating oven for precise temperature control and uniform wall thickness distribution.
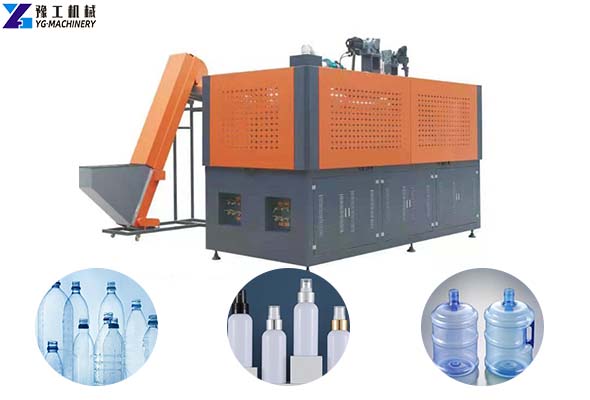

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Industry Trade Terminology
Understanding these terms is essential for negotiating contracts and technical specifications with manufacturers.
| Term | Definition | Context for Buyers |
|---|---|---|
| MOQ | Minimum Order Quantity | For capital machinery, the MOQ is typically 1 Unit. However, for spare parts or preforms, MOQs may be significantly higher. |
| OEM | Original Equipment Manufacturer | The supplier builds the machine according to your specific design requirements and branding. You own the IP of the custom design. |
| ODM | Original Design Manufacturer | The supplier sells their existing machine design under your brand name (White Labeling). Common for standard linear blowers. |
| FAT | Factory Acceptance Test | A trial run performed at the manufacturer’s facility before shipment. The buyer verifies the machine meets speed (BPH) and quality specs using their own preforms/molds. |
| SAT | Site Acceptance Test | Final testing performed at the buyer’s facility after installation and commissioning. This triggers the final payment release. |
| Cycle Time | Production Cycle Duration | The time (in seconds) it takes to complete one full blowing sequence. Lower cycle times equal higher efficiency. |
| Changeover Time | Mold/Format Switch Time | The time required to switch molds to produce a different bottle shape. “Tool-free” or “Quick-change” systems are preferred to minimize downtime. |
| Preform | PET Parison | The test-tube-shaped piece of plastic that is heated and blown into the final bottle. Machine compatibility is dictated by the preform’s neck size. |
Compliance and Standards (USA/EU Focus)
- CE Marking: Mandatory for machinery imported into the European Economic Area, certifying conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- UL / CSA: Electrical certification often required for machinery installation in the USA and Canada.
- HACCP/FDA: While the machine itself is not food, the surfaces touching the preform/bottle (air conveyors, molds) must be food-grade compliant.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pet bottle blowing machines Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the PET Bottle Blowing Machines Sector
The PET packaging machinery market is undergoing a significant transformation driven by strict environmental regulations in Europe and the United States, rising energy costs, and a demand for extreme production flexibility. For B2B buyers, sourcing decisions are no longer limited to hardware specifications; they now encompass total lifecycle efficiency, vendor partnership capability, and adaptability to recycled materials.
Historical Evolution: From Standalone Units to Integrated Ecosystems
Over the past 25 years, the PET blowing sector has matured from a fragmented market of standalone machine providers to a landscape dominated by integrated solution architects.
- The Early 2000s: The market focused primarily on mechanical output and speed. Machines were often sourced independently from filling and labeling units, leading to integration challenges and efficiency losses.
- The Shift to Precision: As exemplified by established manufacturers with over two decades of experience, the industry shifted toward servo-driven technologies. This transition allowed for “unlimited” bottle shapes and higher precision, reducing material waste.
- Current State (2025 and beyond): The modern standard is the Complete PET Filling Line. Manufacturers now demand turnkey solutions—from blowing to filling, labeling, and packaging—sourced from a single partner to ensure synchronization and accountability.
Key Market Trends Driving Procurement
Buyers in the USA and Europe are prioritizing the following operational metrics when evaluating blowing machinery:
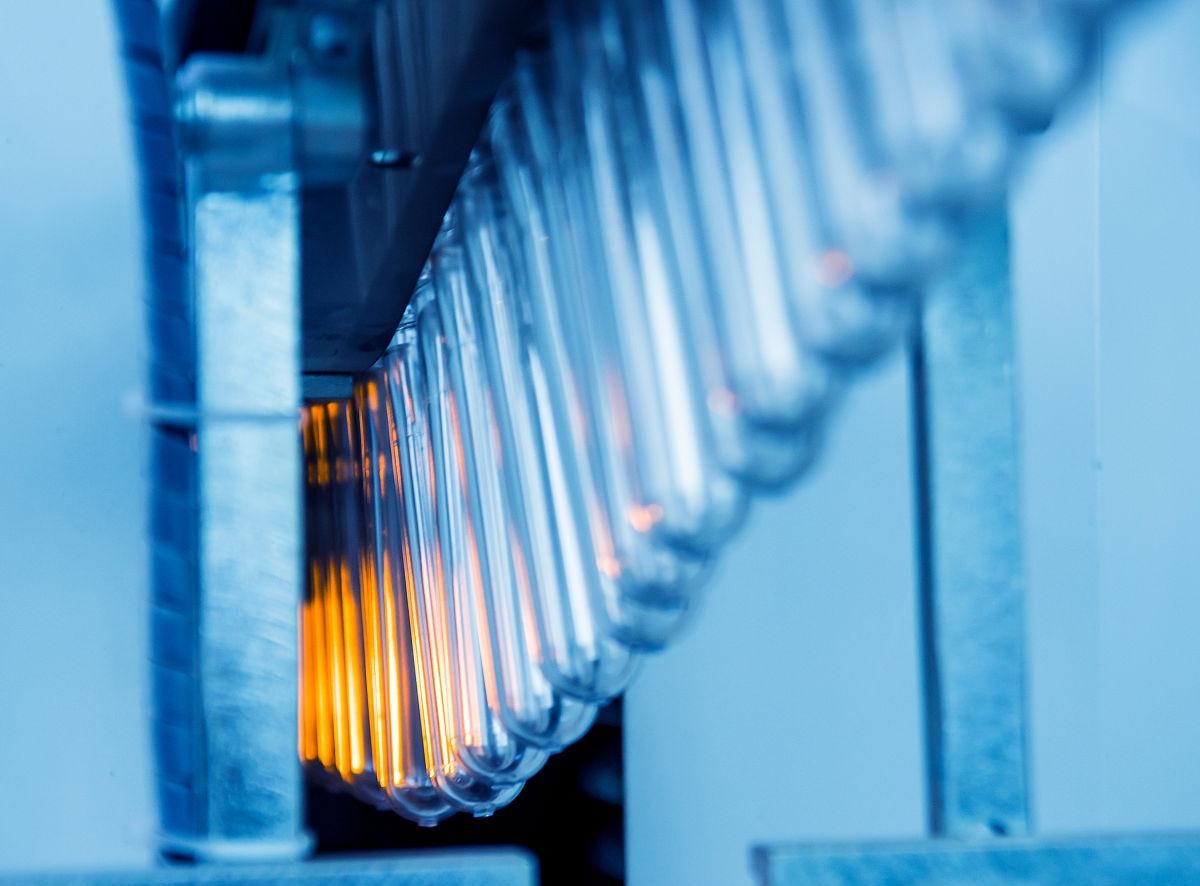

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. Holistic Line Efficiency
The demarcation between blowing and filling is vanishing. Modern sourcing favors suppliers capable of delivering compact, end-to-end solutions.
* Trend: Implementation of “Combi” or block systems where blowing and filling occur within a unified enclosure.
* Benefit: drastic reduction in footprint and elimination of air conveyors, reducing cross-contamination risks—a critical factor for beverage producers (e.g., water, juices).
2. Extreme Flexibility and SKU Proliferation
Marketing teams in Western markets constantly demand new bottle geometries to differentiate products on crowded shelves.
* Requirement: Machinery must handle rapid mold changes and diverse preform types without extended downtime.
* Sourcing implication: Buyers are selecting vendors who demonstrate design versatility (“Every shape, every vision”) rather than rigid standardization.
3. Global Reach with Local Support
With supply chains becoming increasingly volatile, the geographical footprint of the machinery OEM is critical.
* Trend: Preference for manufacturers with a presence in multiple markets (e.g., active in over 80 countries).
* Reasoning: This ensures that spare parts, commissioning expertise, and technical service are accessible regardless of the production facility’s location.
Sustainability as a Non-Negotiable Sourcing Criteria
In the European and American markets, sustainability has moved from a “nice-to-have” to a regulatory and operational necessity. Sourcing strategies must align with the following environmental pillars:
| Sustainability Pillar | Technical Implication for Machinery | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| rPET Compatibility | Heating ovens and blowing stations must be optimized to handle Recycled PET (rPET), which has different thermal properties than virgin PET. | Compliance with EU/US plastic tax regulations and corporate ESG goals. |
| Lightweighting | Precision blowing control to distribute material thinly yet evenly, maintaining structural integrity with less resin. | Direct reduction in raw material costs and shipping weight. |
| Energy Efficiency | Integration of near-infrared (NIR) heating lamps and air recovery systems to recycle high-pressure air. | Lower operational expenditure (OpEx) amidst fluctuating energy prices. |
Strategic Sourcing: The Partnership Model
The complexity of modern PET lines—such as the recent 2025 commissioning of high-capacity lines (14,000 BPH) for carbonated and non-carbonated water—requires a shift in vendor relationships.
Transactional sourcing is obsolete. Successful procurement strategies now focus on:
1. Consultative Design: Engaging manufacturers who assist in the design phase to optimize bottle geometry for both aesthetics and manufacturability.
2. Lifecycle Support: Prioritizing vendors offering commissioning, training, and long-term servicing.
3. Proven Reliability: vetting suppliers based on global implementation records across diverse continents to ensure the machinery can withstand rigorous industrial demands.
Conclusion for Buyers:
When sourcing PET bottle blowing machines, prioritize vendors that offer comprehensive, energy-efficient lines and demonstrate a history of partnership-based growth. The ability to process sustainable materials and adapt to changing consumer demands is now the primary indicator of long-term equipment ROI.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pet bottle blowing machines
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of PET Bottle Blowing Machines
1. Can PET blowing machines be integrated into existing filling lines, or must they be purchased as a complete system?
Modern PET technology providers offer flexible solutions. While turnkey solutions—incorporating blowing, filling, labeling, and packaging—maximize synchronization and efficiency, high-quality blowing machines can be integrated into existing production lines. Vendors like SMF specialize in both standalone units and complete filling lines, allowing manufacturers to scale or upgrade specific stages of production without replacing entire infrastructures.
2. How does the machine handle different bottle shapes and complex designs?
Advanced PET blow molding machines are designed to accommodate “every shape and every vision.” Manufacturers utilize precision-engineered molds to produce standard cylindrical bottles, complex geometric shapes, or custom branding designs. When selecting a machine, ensure the vendor offers comprehensive support in mold design and prototyping to guarantee the physical integrity of the bottle matches the visual concept.
3. What represents the standard “Total Cost of Ownership” (TCO) for these machines?
TCO extends beyond the initial purchase price to include energy consumption, maintenance, and operational efficiency. Premium machines are designed to be “cost-effective and environmentally friendly,” utilizing optimized heating and blowing processes to reduce electricity usage. Buyers should look for partners that offer optimized solutions to lower per-unit production costs over the machine’s lifecycle.
4. What is the typical production capacity range for modern PET blowing equipment?
Capacity varies significantly based on the machine model and bottle size. Solutions range from compact units for smaller operations to high-speed industrial lines. For example, recent implementations in the industry have demonstrated capacities reaching 14,000 bottles per hour (BPH) for both carbonated and non-carbonated beverages. Buyers should assess their current output requirements and future scalability needs when selecting a model.
5. How are international installation and technical support handled for US and European buyers?
For global manufacturers, selecting a vendor with a widespread presence is critical. Leading suppliers operate on multiple continents (serving over 80 countries) and provide full “commissioning and servicing” capabilities. This ensures that regardless of location—whether in the USA or Europe—manufacturers receive on-site installation support, operator training, and rapid response for maintenance to minimize downtime.
6. Can one machine produce bottles for both carbonated and non-carbonated beverages?
Yes. Versatile PET blow molding lines are capable of producing bottles for various applications, including still water, carbonated soft drinks (CSD), and functional beverages. The machine settings and molds can be adjusted to handle the different pressure requirements and preform weights necessary for carbonated versus non-carbonated containers.
7. What is the expected lifespan and reliability of high-precision blowing machines?
Machines designed with “maximum precision” and high-quality components are built for long-term industrial use. With over 25 years of engineering evolution in the sector, top-tier machines are constructed to withstand continuous operation. Reliability is further ensured through partnership-based maintenance schedules, where the manufacturer supports the client at every stage to prevent wear and tear from impacting production quality.
8. How does the vendor support the transition from bottle concept to mass production?
A full-service partner does not just sell hardware; they bring “visions to life.” This process typically involves:
* Consultation: Understanding the client’s aesthetic and functional needs.
* Design: Creating technical drawings and 3D models of the PET bottle.
* Prototyping: Testing the design for blow-ability and strength.
* Commissioning: Configuring the production line to manufacture the specific bottle efficiently.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pet bottle blowing machines
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook
Sourcing a PET bottle blowing machine is no longer a standalone equipment purchase; it is a critical infrastructure investment that dictates your facility’s agility and total cost of ownership (TCO). For manufacturers in the USA and Europe, the strategic focus must shift from initial capital expenditure to long-term operational efficiency, precision, and sustainability.
As 2025 approaches, the competitive advantage lies in partnering with suppliers who offer comprehensive technical depth rather than just hardware.
Key Outlook Drivers:
- Full-Line Integration: The industry is moving toward “complete line” solutions—integrating blowing, filling, and labeling—to eliminate compatibility bottlenecks and streamline maintenance.
- Adaptability: Machines must handle complex bottle shapes without limitations, allowing brands to pivot quickly to new packaging trends.
- Sustainability & Efficiency: With tightening environmental regulations, prioritizing energy-efficient systems that lower the carbon footprint per bottle is essential for compliance and cost reduction.
Strategic Recommendation:
Select a global partner with proven engineering expertise (25+ years) and a footprint in diverse markets. A vendor capable of delivering high-capacity solutions (e.g., 14,000 BPH) and customized support ensures your production line remains scalable, reliable, and future-proof against shifting market demands.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.