The Ultimate Guide to Gas Turbine Supplier (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for gas turbine supplier
Navigating the global market for gas turbine suppliers presents unique challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly when it comes to sourcing reliable and efficient energy solutions. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive for sustainable power generation, understanding the intricacies of gas turbine procurement becomes essential. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the various types of gas turbines, their applications in different sectors, and the key factors to consider when selecting a supplier.
In this resource, buyers will learn how to effectively vet suppliers, assess the cost implications of various turbine models, and ensure compliance with regional regulations. We delve into performance metrics, maintenance requirements, and the latest technological advancements that influence purchasing decisions. By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and a detailed understanding of the gas turbine landscape, this guide empowers them to make informed choices that align with their operational goals and budget constraints.
Whether you are a procurement officer in a manufacturing plant in Egypt or a project manager in the UK looking to enhance energy efficiency, this guide is tailored to meet your specific needs in the evolving global market for gas turbines.
Understanding gas turbine supplier Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy-Duty Gas Turbines | High efficiency, robust design for continuous operation | Power generation, industrial applications | Pros: High reliability, long operational life. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Aero-Derivative Gas Turbines | Lightweight, compact, and quick to start up | Peaking power plants, oil & gas industry | Pros: Fast deployment, flexible operation. Cons: Lower efficiency compared to heavy-duty models. |
| Micro Gas Turbines | Small size, low emissions, and modular design | Distributed generation, remote applications | Pros: Low capital cost, scalable. Cons: Limited power output, higher cost per kW. |
| Combined Cycle Gas Turbines (CCGT) | Utilizes waste heat for additional power generation | Large-scale power plants | Pros: High overall efficiency, reduced emissions. Cons: Complex infrastructure required. |
| Solar Hybrid Gas Turbines | Integrates solar energy to enhance efficiency | Renewable energy projects, remote areas | Pros: Sustainable, reduced fuel consumption. Cons: Initial setup complexity and cost. |
What Are Heavy-Duty Gas Turbines and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Heavy-duty gas turbines are known for their durability and efficiency, making them suitable for continuous operation in power generation and industrial applications. They are designed to handle high loads and offer long operational lifespans, which is crucial for businesses looking to minimize downtime. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and operational costs, alongside the initial investment.
How Do Aero-Derivative Gas Turbines Benefit B2B Applications?
Aero-derivative gas turbines are based on aircraft engine technology, providing a lightweight and compact solution that can start up quickly. This makes them ideal for peaking power plants and applications in the oil and gas industry where rapid response is essential. Buyers should consider the operational flexibility and quick deployment benefits, although they may face trade-offs in terms of efficiency compared to heavier models.
What Are Micro Gas Turbines and Their Key Considerations for Buyers?
Micro gas turbines are small, modular systems that offer low emissions and can be deployed in distributed generation scenarios. Their scalability makes them suitable for remote applications, particularly in areas lacking infrastructure. B2B buyers should assess the capital costs relative to the power output, as micro turbines may have a higher cost per kilowatt, but they provide an attractive solution for smaller-scale energy needs.
Why Choose Combined Cycle Gas Turbines (CCGT) for Large-Scale Projects?
Combined cycle gas turbines (CCGT) utilize both gas and steam turbines to maximize efficiency by converting waste heat into additional power. This technology is particularly advantageous for large-scale power generation, offering reduced emissions and operational costs. Buyers should consider the complexity of the required infrastructure and the initial investment against the long-term savings and environmental benefits.
How Do Solar Hybrid Gas Turbines Enhance Energy Efficiency?
Solar hybrid gas turbines incorporate solar energy to enhance overall efficiency and reduce fuel consumption. This innovative approach is particularly beneficial for renewable energy projects and remote areas where sustainability is a priority. B2B buyers must evaluate the complexity and cost of setting up such systems against their potential for long-term energy savings and environmental impact.
Related Video: How a Gas Turbine Works
Key Industrial Applications of gas turbine supplier
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of gas turbine supplier | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Generation | Combined Cycle Power Plants (CCPP) | Increased efficiency and reduced emissions | Compliance with local regulations and fuel availability |
| Oil & Gas | Gas Processing and Compression | Enhanced operational reliability and efficiency | Supplier’s experience in harsh environments and safety standards |
| Aerospace | Aircraft Engine Manufacturing | High thrust-to-weight ratio and fuel efficiency | Certifications and compliance with aviation standards |
| Marine | Marine Propulsion Systems | Reduced fuel consumption and lower emissions | Durability in saltwater conditions and maintenance support |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Cogeneration Systems for Process Heat and Power | Cost savings through energy recovery | Integration with existing systems and scalability options |
What Are the Key Applications of Gas Turbines in Power Generation?
Gas turbines are integral to Combined Cycle Power Plants (CCPP), which combine gas and steam turbines to optimize efficiency. This application is particularly vital for countries in Africa and the Middle East, where energy demand is surging. By utilizing gas turbines, these plants can produce electricity more efficiently, thus reducing operational costs and emissions. B2B buyers must consider the supplier’s compliance with local regulations and the availability of suitable fuel sources to ensure seamless operations.
How Are Gas Turbines Used in the Oil and Gas Sector?
In the oil and gas industry, gas turbines are employed for gas processing and compression. They provide the necessary power to compress natural gas for transportation and processing, ensuring that operations remain reliable even in challenging environments. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with proven experience in harsh conditions and robust safety standards, as these factors significantly influence operational reliability and efficiency.
What Role Do Gas Turbines Play in Aerospace Applications?
Gas turbines are essential in aircraft engine manufacturing due to their high thrust-to-weight ratio and fuel efficiency. This application is crucial for aerospace companies in Europe and South America, where competition demands advanced technology for performance and environmental compliance. When sourcing gas turbines for aerospace, businesses should ensure that suppliers have the necessary certifications and adhere to stringent aviation standards to guarantee safety and reliability.
How Are Gas Turbines Beneficial for Marine Applications?
In marine propulsion systems, gas turbines provide an effective solution for powering ships, offering reduced fuel consumption and lower emissions compared to traditional engines. This application is increasingly important for maritime businesses looking to enhance their environmental footprint. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their ability to provide durable solutions that withstand saltwater conditions and offer comprehensive maintenance support.
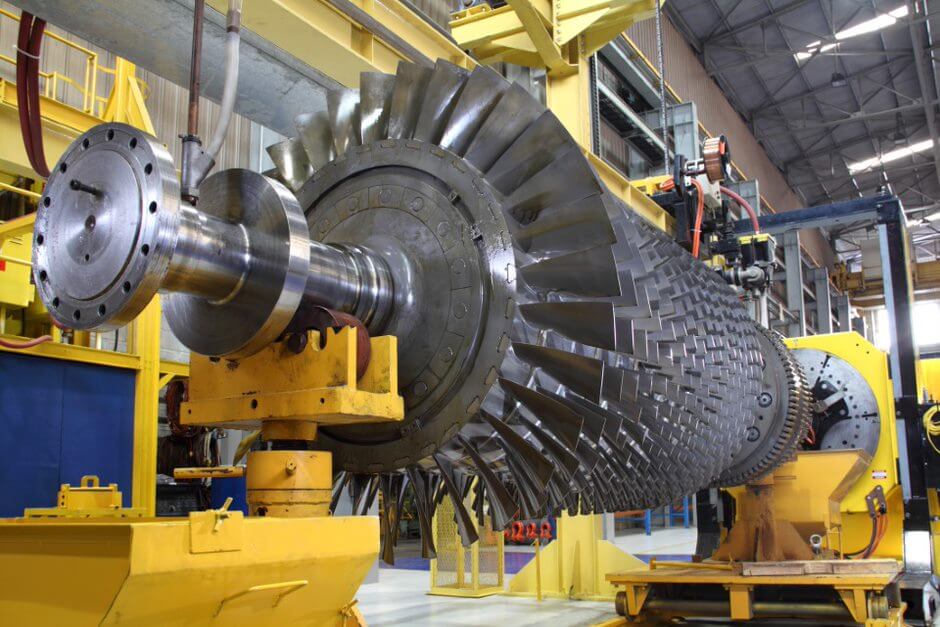

A stock image related to gas turbine supplier.
What Advantages Do Gas Turbines Offer in Industrial Manufacturing?
A stock image related to gas turbine supplier.
Gas turbines are utilized in cogeneration systems that produce both electricity and useful heat for industrial processes. This dual-use capability leads to significant cost savings through energy recovery, making it an attractive option for manufacturers in various regions, including Africa and Europe. When considering suppliers, businesses should focus on how well the turbines can integrate with existing systems and their scalability options to meet future energy demands.
Related Video: The Siemens SGT-800 A 50-MW-class industrial gas turbine
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘gas turbine supplier’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex Specifications for Gas Turbines
The Problem:
International B2B buyers often struggle with the intricate specifications and requirements when sourcing gas turbines. Different industries have varying needs regarding efficiency, emissions, and compatibility with existing systems. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America may find it particularly challenging due to limited local expertise and resources, leading to misunderstandings about the specifications needed for optimal performance. This misalignment can result in costly delays, increased operational expenses, and even project failures.
The Solution:
To effectively navigate these complexities, buyers should begin by conducting thorough research on the specific requirements of their projects. Engaging with industry experts or consultants who specialize in gas turbines can provide valuable insights into the specific needs of their operations. Additionally, buyers should prepare a detailed specification document that outlines their operational requirements, including expected performance metrics, environmental regulations, and integration capabilities with current systems.
Once the specifications are clearly defined, buyers should solicit proposals from multiple suppliers, ensuring that each proposal addresses the outlined specifications in detail. This not only facilitates comparison but also encourages suppliers to provide tailored solutions. It is crucial to ask targeted questions regarding the turbine’s efficiency ratings, maintenance schedules, and the supplier’s track record in similar projects to ensure alignment with operational goals.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Supply Chain Disruptions in Gas Turbine Procurement
The Problem:
Supply chain disruptions are a significant concern for B2B buyers, particularly in regions experiencing political instability or economic challenges. Buyers may face delays in receiving gas turbines, spare parts, or necessary support services. These disruptions can lead to project delays, increased costs, and a significant impact on operational efficiency, especially in critical industries like energy generation and manufacturing.
The Solution:
To mitigate the risks associated with supply chain disruptions, buyers should adopt a proactive sourcing strategy. This includes diversifying suppliers and establishing relationships with multiple manufacturers across different regions. By doing so, buyers can create a safety net that allows them to pivot to alternative sources if one supplier faces challenges.
Furthermore, implementing a robust inventory management system that tracks lead times and availability can help buyers anticipate potential shortages. Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers is essential for understanding the status of orders and any potential delays. Buyers should also consider negotiating contracts that include clauses for expedited shipping or alternative delivery methods during critical periods, ensuring that they remain agile in the face of disruptions.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with Regulatory Standards in Gas Turbine Use
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face significant challenges in ensuring that their gas turbines meet local and international regulatory standards. This is particularly true for buyers in regions like the Middle East and Europe, where regulations concerning emissions and operational efficiency are stringent. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines, operational shutdowns, and damage to the company’s reputation.
The Solution:
To ensure compliance, buyers should engage legal and environmental experts early in the procurement process. These experts can provide guidance on the relevant regulations and help buyers understand the implications of these standards on turbine selection and operation.
Buyers should also prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and regulatory compliance. Requesting documentation such as emissions certifications and performance reports can provide assurance that the selected gas turbines meet necessary standards.
Establishing a comprehensive compliance strategy that includes regular audits and assessments post-purchase can further enhance adherence to regulatory requirements. By integrating compliance checks into the operational framework, buyers can ensure ongoing compliance and mitigate risks associated with regulatory changes.
By addressing these common pain points, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, ultimately leading to more successful outcomes in their gas turbine projects.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for gas turbine supplier
When selecting materials for gas turbines, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including performance, cost, and compliance with industry standards. Below is a detailed analysis of four common materials used in gas turbine applications, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Superalloys in Gas Turbines?
Superalloys, particularly nickel-based superalloys, are extensively used in gas turbines due to their exceptional high-temperature strength and oxidation resistance. They can withstand temperatures exceeding 1,000°C and maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions. Their ability to resist creep deformation makes them ideal for turbine blades and other critical components.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of superalloys is their durability and performance at high temperatures, which significantly enhances turbine efficiency. However, they are costly to manufacture and process, leading to higher overall production costs. Additionally, the complexity of machining superalloys can pose manufacturing challenges.
Impact on Application: Superalloys are particularly suitable for high-pressure environments and aggressive media, making them essential for modern gas turbine designs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN when sourcing superalloys. Understanding local regulations regarding material sourcing and environmental impact is also crucial, especially in regions like the Middle East and Africa.
How Do Ceramic Matrix Composites Enhance Gas Turbine Performance?
Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMCs) are emerging as a favorable alternative for gas turbine components due to their lightweight and high-temperature capabilities. CMCs can operate at temperatures around 1,600°C, significantly reducing the weight of turbine components and improving fuel efficiency.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of CMCs is their ability to withstand extreme temperatures while being lighter than traditional materials. However, they can be more brittle than metals, which may limit their application in certain high-stress areas. The manufacturing processes for CMCs are also relatively complex and expensive.
Impact on Application: CMCs are particularly effective in reducing the overall weight of gas turbines, which can lead to improved performance and lower fuel consumption.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that CMCs meet regional compliance standards and assess the availability of suppliers capable of producing these advanced materials.
What Role Does Titanium Alloys Play in Gas Turbine Applications?
Titanium alloys are known for their excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for various turbine components, including casings and fan blades. They can operate effectively in moderate temperature ranges, typically up to 600°C.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of titanium alloys is their lightweight nature, which contributes to overall turbine efficiency. However, they can be more expensive than traditional steel alloys and may require specialized machining techniques, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Titanium alloys are particularly beneficial in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in aerospace gas turbines.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of titanium alloys required for their applications and ensure compliance with international standards, especially in Europe, where regulatory frameworks can be stringent.
How Do Steel Alloys Compare for Gas Turbine Components?
Steel alloys, particularly high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels, are commonly used in gas turbine applications due to their good mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness. They can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for structural components.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of steel alloys is their cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. However, they may not perform as well as superalloys or CMCs at higher temperatures, which can limit their application in high-performance turbines.
Impact on Application: Steel alloys are often used in components where high-temperature resistance is less critical, such as in turbine casings and support structures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the steel alloys used comply with local and international standards, and consider the availability of quality suppliers in their region.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Gas Turbine Suppliers
| Material | Typical Use Case for gas turbine supplier | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Superalloys | Turbine blades and high-stress components | Exceptional high-temperature strength | High manufacturing cost and complexity | High |
| Ceramic Matrix Composites | Lightweight turbine components | Lightweight and high-temperature capability | Brittle nature and complex manufacturing | High |
| Titanium Alloys | Fan blades and casings | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and specialized machining | Medium |
| Steel Alloys | Structural components | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Limited performance at high temperatures | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used in gas turbines, enabling informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for gas turbine supplier
What are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Gas Turbines?
The manufacturing process of gas turbines involves several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality components capable of withstanding extreme conditions. Understanding these stages is essential for international B2B buyers looking to assess potential suppliers.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Gas Turbines?
The first stage involves the careful selection and preparation of materials. Common materials used in gas turbine production include high-strength alloys, nickel-based superalloys, and ceramics. These materials are chosen for their ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
The preparation process includes:
– Material Inspection: Ensuring that the raw materials meet specified chemical and physical properties.
– Cutting and Shaping: Using techniques such as laser cutting or water jet cutting to create initial shapes for turbine components.
B2B buyers should inquire about the supplier’s sourcing practices and material certifications, as these can directly impact the performance and reliability of the gas turbines.
How Are Gas Turbine Components Formed?
Once materials are prepared, the next stage is forming, which typically involves several key techniques:
- Casting: Used for complex shapes like turbine blades. Investment casting provides high precision and surface finish.
- Forging: This process enhances the strength of the material through deformation at high temperatures.
- Machining: Precision machining processes such as CNC milling and turning ensure that components meet exact specifications.
Buyers should ask suppliers about their forming techniques and the machinery used, as these factors contribute significantly to the quality of the final product.
What Happens During Assembly of Gas Turbines?
The assembly process is crucial for integrating various components into a fully operational gas turbine. This stage includes:
- Sub-assembly: Components like combustion chambers, turbines, and compressors are assembled individually before final integration.
- Final Assembly: All sub-assemblies are combined, and the entire turbine is assembled. This step often involves specialized tools and fixtures to ensure precision alignment.
B2B buyers should verify the assembly methods and the experience of the workforce involved. Trained personnel can significantly reduce the risk of errors during assembly.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Gas Turbines?
Finishing processes are vital to enhance the durability and performance of gas turbines. Common finishing techniques include:
- Coating: Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) protect components from high temperatures and oxidation.
- Surface Treatment: Processes like shot peening improve fatigue resistance.
- Inspection and Testing: Final inspections ensure that all components meet quality standards before the turbines are shipped.
International buyers should inquire about the specific finishing techniques used and the expected performance improvements they offer.
How is Quality Assurance Maintained Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of gas turbines, ensuring that each component meets strict international standards and customer specifications.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Gas Turbine Manufacturing?
Several international standards guide quality assurance in gas turbine manufacturing, including:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS) that can enhance customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute provides standards specific to the oil and gas industry.
B2B buyers should verify that suppliers are certified to these standards, as they reflect the supplier’s commitment to quality.
What Are the Quality Control Checkpoints in Gas Turbine Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducting inspections during manufacturing to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished product before shipping.
Buyers should request information about the QC processes in place and the frequency of inspections.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Gas Turbines?
Testing is a vital aspect of the quality assurance process, ensuring that gas turbines perform as expected under operational conditions. Common testing methods include:
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing (UT) and radiographic testing (RT) identify internal defects without damaging the components.
- Performance Testing: Turbines are subjected to simulated operational conditions to verify performance metrics.
- Durability Testing: Components may undergo accelerated life testing to assess long-term performance.
B2B buyers should inquire about the types of testing performed and any certifications that validate the results.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify a Supplier’s Quality Control Practices?
Verifying a supplier’s QC practices is essential for B2B buyers to ensure they are partnering with a reliable manufacturer. Here are actionable steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits to evaluate the manufacturing processes, QC systems, and overall facility conditions.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their QC processes, including inspection reports and testing results.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to validate the supplier’s claims and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should also consider regional standards and certifications that may impact their procurement decisions.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating QC and certification nuances is particularly important for international buyers. Factors to consider include:
- Regional Regulations: Different regions may have varying compliance requirements, which can affect the certification process.
- Language Barriers: Ensure that documentation, including certification and quality reports, is available in a language that can be easily understood.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local business practices and communication styles can facilitate smoother negotiations and partnerships.
By being aware of these nuances, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting gas turbine suppliers.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices of gas turbine suppliers is crucial for international buyers. By focusing on material selection, manufacturing techniques, quality standards, and verification methods, buyers can ensure they partner with reliable suppliers that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘gas turbine supplier’
Introduction
Sourcing gas turbines is a critical decision for businesses seeking reliable and efficient energy solutions. This guide provides a practical checklist to assist B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, in navigating the complexities of selecting a suitable gas turbine supplier. By following these steps, you can ensure a well-informed procurement process that aligns with your operational needs and budgetary constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the first step in the sourcing process. Determine the required turbine capacity, efficiency ratings, and operational parameters that align with your project’s goals.
– Considerations: Identify specific fuel types, environmental regulations, and performance metrics that are crucial for your operations.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough market research to identify potential gas turbine suppliers. Utilize industry reports, online platforms, and trade shows to compile a list of candidates.
– Key Actions: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your region and those who specialize in your specific needs. Networking with industry contacts can also yield valuable recommendations.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Experience and Reputation
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Review their experience in the industry, focusing on their project portfolio and customer testimonials.
– What to Look For: Request case studies and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. This will provide insights into the supplier’s reliability, service quality, and support capabilities.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that potential suppliers hold the necessary certifications and comply with international standards. This step is vital for mitigating risks associated with quality and safety.
– Specifics: Check for ISO certifications, environmental compliance, and any industry-specific accreditations that demonstrate the supplier’s commitment to quality.
Step 5: Assess Financial Stability
Understanding the financial health of a supplier is essential to ensure they can meet long-term commitments. Assess their financial statements and credit ratings to gauge stability.
– Why This Matters: A financially stable supplier is more likely to invest in technology and service enhancements, which can benefit your operations.
Step 6: Request and Analyze Proposals
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed proposals that outline pricing, delivery timelines, and after-sales support.
– What to Analyze: Compare the total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and operational costs, rather than just the upfront price.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in negotiations to secure favorable terms that align with your budget and operational requirements.
– Focus Areas: Discuss warranty terms, service level agreements, and payment schedules to protect your interests and ensure accountability from the supplier.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement of gas turbines with confidence, ensuring they select a supplier that meets their technical, financial, and operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for gas turbine supplier Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Gas Turbine Supplier Pricing?
When sourcing gas turbines, international B2B buyers must understand the various cost components that contribute to the overall pricing structure. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: This encompasses the raw materials required for turbine construction, including metals, composites, and specialized alloys. The prices for these materials can fluctuate based on global market conditions and supply chain dynamics.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for manufacturing gas turbines, and labor costs can vary significantly by region. In countries with higher labor standards, such as those in Europe, costs may be elevated compared to regions in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling and equipment necessary for turbine production can represent a substantial initial investment. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs, especially when considering custom specifications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that gas turbines meet stringent quality standards incurs costs related to testing, inspections, and certifications. Buyers should assess the supplier’s QC processes to ensure compliance with international standards.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling of large gas turbines can be costly, especially for international shipments. Understanding the logistics costs, including potential tariffs and duties, is crucial for accurate budgeting.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on competition, demand, and supplier reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Gas Turbine Supplier Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of gas turbines significantly:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit prices due to economies of scale. B2B buyers should consider consolidating orders to negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and necessary certifications (e.g., ISO, ASME) can increase costs but may be essential for meeting regulatory standards in specific regions.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and financial stability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium, but they often provide assurance of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms defined by Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is critical. These terms dictate responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact overall costs.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Gas Turbine Sourcing?
To optimize sourcing decisions, international buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing and terms. Building a strong relationship can lead to more favorable terms, especially for long-term contracts.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtimes to assess the true value of the turbine over its lifespan.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Buyers from different regions should be aware of local economic conditions, currency fluctuations, and geopolitical factors that can influence pricing.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that quotes include a breakdown of costs, so you can better compare suppliers and understand where savings can be made.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Sourcing from local suppliers may reduce logistics costs and facilitate easier communication, which can be advantageous for ongoing support and maintenance.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of cost components and price influencers, coupled with strategic negotiation and analysis, can empower B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to make informed sourcing decisions in the gas turbine market.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing gas turbine supplier With Other Solutions
When considering energy solutions for industrial applications, B2B buyers often evaluate various options against gas turbines. Understanding the available alternatives is crucial for making informed decisions that align with operational goals and financial constraints. Here, we will compare gas turbines with two viable alternatives: reciprocating engines and renewable energy solutions like solar power.
| Comparison Aspect | Gas Turbine Supplier | Reciprocating Engine | Solar Power Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency and power output for large-scale applications | Moderate efficiency; best for smaller loads | Variable output; performance dependent on sunlight |
| Cost | High initial investment, but lower operating costs | Lower initial costs, higher fuel costs over time | High initial setup costs, low operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex installation requiring specialized skills | Easier to install and integrate | Requires significant space and planning for installation |
| Maintenance | Requires specialized maintenance; can be costly | Generally lower maintenance needs | Minimal maintenance once installed |
| Best Use Case | Large industrial applications needing high capacity | Backup power for facilities or smaller loads | Off-grid applications or large installations in sunny regions |
What Are the Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Reciprocating Engines?
Reciprocating engines offer a flexible alternative to gas turbines, particularly for smaller-scale applications. They are generally easier to install and integrate into existing systems, making them an attractive option for facilities that require backup power or smaller loads. However, they may incur higher fuel costs over time, especially if powered by diesel or natural gas. While their maintenance is typically less complex than that of gas turbines, the need for regular servicing still exists.
How Do Solar Power Solutions Compare to Gas Turbines?
Solar power systems present a sustainable alternative that is becoming increasingly popular. They have a low operational cost once installed, as they do not require fuel purchases. However, the initial investment can be substantial, and their efficiency is highly dependent on geographical location and weather conditions. Solar installations can also require significant planning and space, which may not be feasible for every B2B buyer. Moreover, energy output can be variable, necessitating backup solutions during cloudy days or at night.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Energy Solution?
Selecting the right energy solution hinges on understanding the specific operational requirements and constraints of your business. For large-scale operations requiring consistent and high output, gas turbines may be the best option despite their higher initial costs. In contrast, reciprocating engines could serve well for facilities needing backup power or smaller loads with easier installation. For businesses focused on sustainability and long-term cost savings, solar power could be a viable choice, provided they can accommodate the setup and variability in energy production. Ultimately, aligning the solution with your operational goals, budget, and future energy needs will ensure the best investment for your organization.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for gas turbine supplier
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Gas Turbines?
Understanding the technical specifications of gas turbines is critical for B2B buyers, especially when making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some key properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of gas turbine components, such as blades and casings, is paramount. Typically, high-performance alloys like Inconel and titanium are used due to their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments. Selecting the right material impacts the turbine’s efficiency and longevity, which is crucial for minimizing operational costs.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation in dimensions of turbine components. In gas turbines, tight tolerances are essential to ensure proper fitting and optimal performance. For instance, a small deviation in blade dimensions can lead to significant performance issues or even catastrophic failures. Understanding tolerance specifications allows buyers to ensure compatibility with existing systems.
3. Efficiency Rating
The efficiency rating indicates how effectively a gas turbine converts fuel into energy. This is usually expressed as a percentage, with higher ratings signifying better performance. Buyers should prioritize turbines with high efficiency ratings to achieve lower fuel costs and reduced emissions, aligning with global sustainability goals.
4. Pressure Ratio
The pressure ratio is the ratio of the pressure of the gas exiting the turbine to the pressure of the gas entering it. Higher pressure ratios typically mean more efficient turbines, as they can extract more energy from the fuel. Buyers should assess the pressure ratio to determine the turbine’s suitability for their specific applications.
5. Heat Rate
Heat rate measures the amount of fuel energy required to produce one unit of electricity, often expressed in BTU/kWh. A lower heat rate indicates a more efficient turbine. Understanding heat rate is vital for buyers looking to reduce operational costs and improve the environmental footprint of their energy generation.
What Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly enhance communication with suppliers and streamline procurement processes. Here are some common terms relevant to gas turbine suppliers:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of gas turbines, buying from an OEM ensures that you receive components that meet the original specifications and quality standards, crucial for maintaining warranty and performance.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ helps buyers manage their inventory and procurement costs effectively. It’s particularly important when sourcing spare parts for gas turbines, as it can influence the overall budget and lead times.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. This is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers. Clarity in the RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to understand shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks involved in transporting gas turbine components across borders, particularly in regions like Africa and South America.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the time taken from placing an order until its delivery. In the gas turbine industry, lead times can vary significantly based on the complexity of the parts and the supplier’s location. Understanding lead times helps buyers plan their projects more effectively, reducing downtime and ensuring timely operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that their investments in gas turbines lead to optimal performance and long-term operational success.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the gas turbine supplier Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Affecting Gas Turbine Suppliers?
The global gas turbine market is experiencing substantial growth driven by several factors. The demand for cleaner energy sources has surged, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Governments and businesses alike are increasingly investing in gas turbines as part of their energy transition strategies, capitalizing on their efficiency and lower carbon emissions compared to coal and oil. Emerging economies are particularly focused on enhancing their energy infrastructure, leading to a rise in demand for both new installations and upgrades of existing systems.
In addition to the push for cleaner energy, advancements in technology are reshaping the gas turbine landscape. Innovations such as digital twin technology, predictive maintenance, and IoT integration are becoming essential for optimizing performance and reducing operational costs. International B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that leverage these technologies, as they can provide enhanced reliability and efficiency. Furthermore, the ongoing geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions have highlighted the importance of diversifying sourcing strategies. Buyers must remain agile, considering local suppliers in addition to established global players to mitigate risks associated with supply chain vulnerabilities.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Gas Turbine Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are increasingly becoming critical factors in the gas turbine supplier sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of gas turbines are under scrutiny from both regulatory bodies and the public. B2B buyers are now more inclined to partner with suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, including the use of recycled materials and energy-efficient production methods.
Moreover, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and compliance with the Greenhouse Gas Protocol are becoming vital for suppliers aiming to attract international buyers. These certifications not only reflect a supplier’s dedication to reducing their environmental footprint but also enhance their marketability in regions where sustainability is prioritized. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, selecting suppliers with robust sustainability credentials can lead to a more resilient supply chain and contribute positively to corporate social responsibility goals.
What Historical Factors Have Shaped the Current Gas Turbine Market?
The evolution of the gas turbine market can be traced back to the mid-20th century when the technology was first developed for aviation purposes. As the energy crisis of the 1970s prompted a shift toward natural gas as a cleaner alternative, gas turbines began to gain prominence in power generation. Over the decades, continuous advancements in turbine efficiency and emissions control technologies have positioned gas turbines as a preferred choice for both industrial and commercial applications.
The global focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions has further accelerated the adoption of gas turbines, particularly in the wake of international climate agreements. Today, gas turbines are not only integral to power generation but also play a crucial role in supporting renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, by providing necessary backup power. As B2B buyers engage with suppliers, understanding this historical context can inform their purchasing decisions and strategic partnerships in the evolving energy landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of gas turbine supplier
1. How do I choose the right gas turbine supplier for my project?
Selecting the right gas turbine supplier involves evaluating several key factors. First, assess the supplier’s experience and expertise in your specific industry sector. Look for client testimonials and case studies that demonstrate their capability in handling projects similar to yours. It’s also crucial to consider their technological advancements and product range, as these can impact the efficiency and reliability of your operations. Lastly, ensure they offer comprehensive support, including maintenance services and spare parts availability, to minimize downtime.
2. What are the common payment terms offered by gas turbine suppliers?
Payment terms can vary significantly between suppliers. Generally, B2B transactions may involve options such as upfront payments, milestone payments based on project phases, or net 30 to net 90 days terms post-delivery. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow requirements and project timelines. Additionally, inquire about any available financing options, especially for large purchases, to ease budgetary pressures while ensuring timely delivery of equipment.
3. How do I ensure quality assurance when sourcing gas turbines internationally?
To ensure quality assurance, start by verifying the supplier’s certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Request detailed documentation about their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Conducting on-site inspections or audits, if feasible, can provide additional assurance of their capabilities. Moreover, consider establishing a clear Quality Assurance Agreement that outlines specifications, testing procedures, and acceptance criteria to mitigate risks of non-compliance.
4. What should I consider regarding minimum order quantities (MOQ) for gas turbines?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly influence your purchasing strategy. When sourcing gas turbines, clarify the supplier’s MOQ policies as they can vary widely. Some suppliers may offer flexible options for smaller projects, while others may impose strict MOQs that require bulk purchases. Consider your project needs and budget constraints, and negotiate terms that allow for scalability without overcommitting resources. Additionally, explore options for collaborative purchases with other buyers to meet MOQ requirements.
5. How can I effectively vet a gas turbine supplier before making a purchase?
Effective vetting of a gas turbine supplier involves multiple steps. Begin by researching their reputation in the market, looking for reviews from previous clients and industry analysts. Request references and follow up with them to gain insights into the supplier’s reliability and service quality. Examine their financial stability through credit checks or financial statements. Additionally, assess their compliance with international standards and regulations relevant to your project to ensure they meet safety and operational requirements.
6. What are the logistics considerations when importing gas turbines?
Logistics for importing gas turbines involves various critical factors, including transportation modes, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Choose a reputable freight forwarder experienced in handling heavy machinery to ensure safe transport. Understand the customs clearance process in your country and prepare the necessary documentation, such as invoices and certificates of origin. Additionally, factor in potential delays due to regulatory inspections or documentation issues and plan your supply chain accordingly to minimize disruptions.
7. How can I customize gas turbines to meet my specific operational needs?
Customization of gas turbines is often possible, depending on the supplier’s capabilities. Engage with the supplier early in the design process to discuss your specific operational requirements, such as efficiency, emissions control, and fuel type compatibility. Some suppliers may offer modular designs that allow for tailored configurations. Be prepared to provide detailed specifications and work collaboratively with the engineering teams to ensure the final product meets your performance expectations while adhering to regulatory standards.
8. What role does after-sales support play in choosing a gas turbine supplier?
After-sales support is a critical factor in selecting a gas turbine supplier, as it can greatly impact the longevity and efficiency of your investment. Assess the supplier’s maintenance services, availability of spare parts, and response times for technical support. A reliable after-sales service can help minimize downtime and ensure smooth operations. Additionally, inquire about training programs for your staff and regular updates on system performance, which can enhance your operational capabilities and efficiency over time.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for gas turbine supplier
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of gas turbines is essential for international B2B buyers looking to enhance operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. By understanding the diverse landscape of suppliers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, businesses can leverage competitive pricing, innovative technologies, and robust support services. It is critical to evaluate suppliers based on their capabilities, delivery timelines, and after-sales service to ensure long-term partnerships that can adapt to market changes.
How Can International Buyers Maximize Their Sourcing Strategy?
International buyers should prioritize building relationships with suppliers who demonstrate transparency and sustainability in their practices. Collaborating with suppliers that invest in research and development can lead to access to cutting-edge gas turbine technologies, which can significantly improve energy efficiency and reduce emissions. Furthermore, leveraging digital tools and platforms can streamline communication and foster collaboration, ultimately enhancing the procurement process.
As the energy landscape evolves, staying informed about market trends and technological advancements will be key for buyers in making informed decisions. Engage with industry experts and participate in relevant forums to share insights and best practices. By taking these proactive steps, international B2B buyers can position themselves advantageously in the competitive gas turbine market, paving the way for sustainable growth and innovation.