Unlock Cost Savings: The Ultimate RFID Manufacturer Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rfid manufacturer
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing reliable RFID manufacturers can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With varying levels of technological advancement and market maturity across regions, understanding the nuances of RFID technology and its applications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the global RFID market by exploring the different types of RFID systems, their diverse applications across industries such as retail, logistics, and healthcare, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
International buyers often face challenges such as navigating complex supply chains, ensuring compliance with regional standards, and managing costs effectively. This guide empowers B2B buyers by providing actionable insights into evaluating potential manufacturers, comparing costs, and understanding the total cost of ownership associated with RFID solutions. By addressing these key areas, we aim to facilitate smarter sourcing strategies that align with your business goals.
Whether you are looking to enhance inventory management, improve asset tracking, or streamline supply chain operations, this guide equips you with the knowledge needed to make strategic decisions in the RFID market. With a focus on practical advice tailored to the unique needs of buyers from diverse regions, you will be well-prepared to leverage RFID technology for your organization’s success.
Understanding rfid manufacturer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Passive RFID Manufacturers | No internal power source; activated by reader signals | Inventory management, asset tracking | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Limited range and speed. |
| Active RFID Manufacturers | Battery-powered tags that transmit signals independently | Real-time tracking, logistics, and fleet management | Pros: Longer range; Cons: Higher cost and maintenance. |
| Semi-Passive RFID Manufacturers | Combine battery power with passive technology for better performance | Supply chain management, cold chain monitoring | Pros: Enhanced performance; Cons: More complex to implement. |
| RFID System Integrators | Provide complete solutions including hardware, software, and support | Custom implementations for diverse industries | Pros: Tailored solutions; Cons: Potentially higher upfront costs. |
| Specialty RFID Manufacturers | Focus on niche markets (e.g., medical, automotive, or retail) | Industry-specific applications | Pros: Expertise in specific areas; Cons: Limited product range. |
What are the Characteristics of Passive RFID Manufacturers?
Passive RFID manufacturers produce tags that do not have their own power source. Instead, they rely on electromagnetic energy emitted from RFID readers to activate and transmit data. This type of RFID is commonly used in applications such as inventory management and asset tracking, where cost-effectiveness is crucial. Buyers should consider the limited range and speed of passive RFID systems, which may not be suitable for all environments, particularly those requiring real-time data.
How Do Active RFID Manufacturers Differ?
Active RFID manufacturers create tags equipped with internal batteries, allowing them to transmit signals independently. This technology enables longer read ranges and faster data transmission, making it ideal for real-time tracking in logistics and fleet management. While the benefits include enhanced performance and reliability, buyers must weigh these advantages against the higher costs and maintenance associated with active RFID systems.
What Makes Semi-Passive RFID Manufacturers Unique?
Semi-passive RFID manufacturers offer a hybrid solution that combines the benefits of passive and active technologies. These tags have batteries that power onboard sensors, improving performance while still relying on external readers for communication. They are particularly effective in supply chain management and cold chain monitoring. Buyers should consider the complexity of implementation and potential costs but can benefit from enhanced performance in demanding applications.
Why Choose RFID System Integrators?
RFID system integrators provide a comprehensive service that includes hardware, software, and ongoing support, allowing businesses to implement tailored RFID solutions. They are essential for companies looking for custom implementations that fit specific operational needs across various industries. While integrators offer the advantage of expert guidance and customized solutions, buyers should be prepared for potentially higher upfront costs and longer implementation times.
What Should Buyers Know About Specialty RFID Manufacturers?
Specialty RFID manufacturers focus on specific industries, such as healthcare, automotive, or retail, providing tailored solutions that cater to unique market needs. These manufacturers bring valuable expertise and innovation to their respective fields, which can significantly enhance operational efficiency. However, buyers should be aware that these niche products may have a limited range of offerings, making it essential to evaluate whether their specific needs align with the manufacturer’s capabilities.
Related Video: RFID Antenna Series: Types of RFID Antennas | RFID Portal Antennas
Key Industrial Applications of rfid manufacturer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of RFID Manufacturer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | Inventory Management | Enhances accuracy in stock levels, reduces shrinkage | Compatibility with existing systems, read range, durability |
| Logistics and Supply Chain | Asset Tracking | Streamlines operations, improves visibility of goods in transit | Tags’ durability, environmental resistance, integration ease |
| Healthcare | Patient Tracking | Improves patient safety, reduces errors in medication dispensing | Compliance with health regulations, security features |
| Manufacturing | Quality Control | Ensures product traceability, enhances process efficiency | RFID tag durability, read accuracy, integration with ERP systems |
| Agriculture | Livestock Management | Facilitates tracking of livestock health and location | Tag robustness, environmental resistance, data management capabilities |
How is RFID Used in Retail for Inventory Management?
In the retail sector, RFID technology is instrumental in inventory management, allowing businesses to track stock levels in real-time. By employing RFID tags on products, retailers can automate the stock-taking process, significantly reducing human error and the time spent on manual counts. This technology also helps in minimizing shrinkage due to theft or misplacement, thus improving overall profitability. International buyers should consider the compatibility of RFID systems with existing inventory management solutions and assess the durability of tags for various retail environments.
What Role Does RFID Play in Logistics and Supply Chain Asset Tracking?
RFID manufacturers provide solutions that enhance asset tracking within logistics and supply chains. By utilizing RFID tags on shipping containers and pallets, businesses gain improved visibility into their inventory as it moves through the supply chain. This real-time tracking reduces delays and enhances operational efficiency, as companies can quickly locate assets and manage their logistics more effectively. When sourcing RFID solutions, buyers should evaluate the environmental resistance of tags, especially in harsh conditions, and the ease of integration with existing logistics software.
How is RFID Technology Beneficial in Healthcare Patient Tracking?
In the healthcare industry, RFID technology plays a critical role in patient tracking and safety. Hospitals can use RFID tags to monitor patient movements, ensuring that they receive the correct medications and treatments. This system minimizes the risk of errors and enhances patient care by providing healthcare professionals with accurate, real-time data. International buyers in the healthcare sector must prioritize compliance with health regulations and consider the security features of RFID systems to protect sensitive patient information.
How Does RFID Improve Quality Control in Manufacturing?
RFID technology is widely used in manufacturing for quality control purposes. By tagging products throughout the production process, manufacturers can ensure traceability and monitor quality at each stage. This capability not only enhances process efficiency but also allows for quick identification of defects, leading to faster resolutions and reduced waste. Buyers in the manufacturing sector should focus on the durability of RFID tags and their accuracy in read rates, as well as their ability to integrate seamlessly with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems.
In What Ways Does RFID Enhance Livestock Management in Agriculture?
In agriculture, RFID technology is utilized for livestock management, providing farmers with the ability to track animal health and location effectively. By tagging livestock with RFID, farmers can monitor feeding schedules, health records, and breeding cycles, thus improving overall herd management. This technology leads to better productivity and profitability in agricultural operations. Buyers from the agricultural sector should consider the robustness of RFID tags to withstand outdoor conditions and the data management capabilities of the RFID systems they choose.
Related Video: RFID Technology Explained
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rfid manufacturer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating High Costs of RFID Solutions
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of high upfront costs associated with implementing RFID systems. This can be particularly daunting for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in regions like Africa and South America, where budget constraints are common. Additionally, buyers may struggle to understand the total cost of ownership, which includes not only the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and ongoing operational costs. This lack of clarity can lead to hesitancy in adopting RFID technology, which is crucial for improving inventory management and operational efficiency.
The Solution: To mitigate these high costs, buyers should first conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis tailored to their specific needs. This includes identifying the key areas where RFID can provide the most value, such as reducing labor costs or minimizing stock discrepancies. Engaging with multiple RFID manufacturers to solicit quotes and understand their pricing structures can also help in negotiating better deals. Additionally, consider exploring flexible financing options, such as leasing agreements or pay-as-you-go models, which can reduce the financial burden at the outset. Lastly, working with manufacturers that provide strong post-installation support can help ensure that the technology is utilized effectively, maximizing return on investment.
Scenario 2: Understanding Complex RFID Technologies
The Problem: The world of RFID technology can be overwhelming, especially for international B2B buyers who may not have a technical background. With various types of RFID systems (active, passive, and semi-passive) and numerous frequency bands (LF, HF, UHF), making informed decisions can be challenging. This complexity can lead to the selection of inappropriate technologies, resulting in underperformance or failure to meet specific operational needs.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize working closely with knowledgeable RFID manufacturers who can provide comprehensive education about the different types of RFID technologies and their specific applications. Request detailed product specifications and case studies that demonstrate successful implementations in similar industries. Furthermore, consider participating in webinars or workshops offered by manufacturers to deepen understanding of RFID capabilities. When sourcing RFID solutions, focus on suppliers that offer customization options to align with unique business needs, ensuring that the chosen technology will deliver optimal performance.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compatibility with Existing Systems
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is ensuring that new RFID solutions are compatible with existing systems, such as ERP or inventory management software. This issue is particularly prevalent in Europe and the Middle East, where many companies have invested heavily in legacy systems. Incompatibility can lead to data silos, operational inefficiencies, and increased costs associated with system overhauls.
The Solution: To avoid compatibility issues, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their current systems before engaging with RFID manufacturers. This includes documenting existing software and hardware configurations to identify potential integration challenges. When approaching manufacturers, explicitly inquire about the compatibility of their RFID solutions with your existing systems. Many RFID providers have experience integrating their technology with various ERP solutions; therefore, seek out those that offer integration services or have partnerships with leading software providers. Additionally, consider running a pilot program to test compatibility before full-scale implementation. This approach not only minimizes risk but also allows for adjustments based on real-world data and feedback.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rfid manufacturer
When selecting materials for RFID manufacturing, it is crucial to consider the properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific applications of each material. This analysis focuses on four common materials used in RFID tags and devices: Polypropylene (PP), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Epoxy, and Metal. Each of these materials has distinct characteristics that can significantly impact performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
What Are the Key Properties of Polypropylene (PP) in RFID Manufacturing?
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent chemical resistance and lightweight nature. It can withstand temperatures up to 100°C and has a good balance of rigidity and flexibility. Its low moisture absorption rate makes it suitable for various environments, especially in humid conditions.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of PP is its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. However, it has limited UV resistance, which may lead to degradation when exposed to sunlight over extended periods. This limitation can affect its suitability for outdoor applications.
Impact on Application: PP is often used in RFID tags for logistics and inventory management due to its compatibility with various media, including cardboard and plastic. However, buyers should consider its outdoor use limitations.
How Does Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Benefit RFID Applications?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is another popular choice for RFID manufacturing, particularly in card applications. PVC is known for its durability and resistance to abrasion and chemicals, making it ideal for environments where tags may be subjected to wear and tear.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of PVC is its robustness, which allows for longer-lasting products. However, its production can be more complex and costly compared to PP. Additionally, PVC is less environmentally friendly, which may be a concern for buyers focused on sustainability.
Impact on Application: PVC is commonly used in access control cards and identification badges. Its durability makes it suitable for high-traffic areas, but international buyers should be aware of compliance with environmental regulations in their regions.
What Are the Advantages of Using Epoxy for RFID Manufacturing?
Epoxy resins are widely used in RFID applications due to their excellent adhesion properties and resistance to environmental factors, including moisture and chemicals. They can endure temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C, making them versatile for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of epoxy is its strong bonding capabilities and durability. However, the curing process can be time-consuming, and the material can be more expensive than other options. Additionally, the rigidity of epoxy may limit its use in flexible applications.
Impact on Application: Epoxy is often used in encapsulating RFID chips to protect them from environmental damage. Buyers should consider the specific application requirements, such as flexibility and temperature tolerance.
Why Choose Metal for RFID Tags and What Are Its Limitations?
Metal, particularly aluminum and stainless steel, is used in RFID applications where durability and robustness are paramount. Metal tags can withstand extreme conditions, including high temperatures and corrosive environments.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of metal is its strength and longevity. However, metal can interfere with signal transmission, which may limit its use in certain applications. Additionally, metal tags are generally more expensive to produce.
Impact on Application: Metal RFID tags are ideal for industrial applications, such as asset tracking in manufacturing. Buyers must ensure that their RFID readers are compatible with metal tags to avoid performance issues.
Summary Table of Material Selection for RFID Manufacturing
| Material | Typical Use Case for RFID Manufacturer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | Logistics and inventory management | Cost-effective and lightweight | Limited UV resistance | Low |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Access control cards and badges | Durable and abrasion-resistant | More complex production and less eco-friendly | Medium |
| Epoxy | Encapsulation of RFID chips | Strong adhesion and environmental resistance | Time-consuming curing process | High |
| Metal | Industrial asset tracking | Strong and long-lasting | Can interfere with signal transmission | High |
This material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the properties and implications of each material will facilitate informed decision-making tailored to specific applications and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rfid manufacturer
What Are the Main Stages in RFID Manufacturing Processes?
The manufacturing of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) devices involves several key stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and customer requirements. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers assess the capabilities and reliability of potential suppliers.
Material Preparation
The first step in RFID manufacturing is material preparation. This involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, including silicon chips, antennas, and substrates. The selection of materials directly impacts the performance and durability of the RFID tags. Suppliers should provide documentation on material certifications, ensuring compliance with international standards such as REACH and RoHS, which are crucial for buyers from Europe and other regions.

A stock image related to rfid manufacturer.
Forming Techniques Used in RFID Production
Once materials are prepared, the next phase is forming. This stage includes various techniques like die-cutting and injection molding to create the physical components of the RFID tags. Advanced technologies such as photolithography may also be used for creating micro-sized components. B2B buyers should inquire about the specific forming techniques employed by manufacturers, as these can affect the scalability and precision of the production process.
Assembly Process: How Are RFID Tags Assembled?
The assembly process involves integrating the RFID chip with the antenna and encapsulating the components. This is typically done using automated machinery to ensure high precision and efficiency. Manufacturers may also utilize manual assembly for specialized or complex products. It’s crucial for buyers to evaluate the assembly process, as it directly influences the reliability and performance of the RFID tags.
Finishing Touches: What Is Involved in RFID Tag Finishing?
The finishing stage includes applying protective coatings and conducting quality checks. Protective coatings can enhance the durability of RFID tags, making them suitable for harsh environments. This stage is essential for ensuring that the tags meet specific industry standards, such as those required for logistics and asset tracking. Buyers should confirm the types of finishing processes used and their relevance to the intended application of the RFID products.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Important for RFID Manufacturers?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of RFID devices to ensure that products meet specified standards and perform reliably in their intended environments. Understanding the QA practices can help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Which International Standards Should RFID Manufacturers Comply With?
Compliance with international standards is a critical factor in assessing the quality of RFID manufacturers. The most common standard is ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Other relevant standards may include CE marking for European markets and API standards for specific applications. Buyers should verify that the manufacturer holds the necessary certifications and can provide documentation to support compliance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in RFID Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints throughout the RFID manufacturing process are essential for maintaining product quality. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify and rectify issues before they escalate.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection checks the finished products against quality standards before shipment.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific QC checkpoints implemented by manufacturers and request reports or statistics that demonstrate their effectiveness.
Which Common Testing Methods Are Employed for RFID Tags?
Common testing methods for RFID tags include functionality tests, environmental tests, and performance tests. Functionality tests ensure that the tags can be read and write properly under various conditions. Environmental testing evaluates the tags’ durability under extreme temperatures, humidity, and exposure to chemicals. Performance tests assess the read range and speed of the RFID tags. Buyers should ask manufacturers for details on their testing procedures and results to gauge product reliability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial for international B2B buyers to mitigate risks associated with product performance and compliance.
What Steps Should Buyers Take for Supplier Audits?
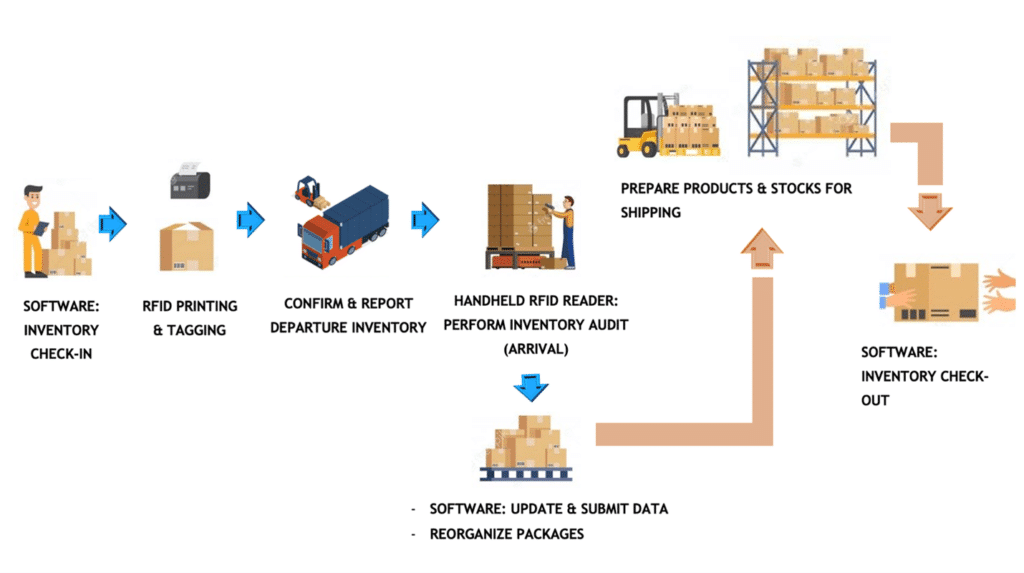
A stock image related to rfid manufacturer.
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to evaluate a manufacturer’s quality control processes. Buyers should consider scheduling regular on-site audits to assess manufacturing capabilities, QC practices, and adherence to standards. During these audits, buyers can review documentation, observe processes in action, and engage with staff to understand the company’s commitment to quality.
How Can Buyers Utilize Reports and Third-Party Inspections?
Buyers should request comprehensive quality reports from manufacturers, including data on defect rates and corrective actions taken. Engaging third-party inspection services can also provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturer’s processes and products. This approach is particularly important for buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where local market conditions may vary significantly from established markets in Europe.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Understanding the nuances of quality control can help international B2B buyers navigate the complexities of sourcing RFID products.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Quality Control?
Different regions may have varying standards and regulations that impact quality control processes. For example, European buyers must ensure that RFID products comply with CE marking requirements, while buyers from the Middle East may have specific certifications to consider. It’s essential for buyers to communicate their quality expectations clearly and ensure that manufacturers are equipped to meet these regional standards.
What Role Does Continuous Improvement Play in Quality Assurance?
Continuous improvement practices, such as Total Quality Management (TQM) or Six Sigma, can enhance the quality assurance processes within RFID manufacturing. Buyers should evaluate whether their potential suppliers implement such practices, as these can lead to better product quality and reduced defects over time.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices of RFID manufacturers, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers that meet their specific needs and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rfid manufacturer’
In the rapidly evolving landscape of RFID technology, international B2B buyers must navigate a multitude of factors when sourcing RFID manufacturers. This guide provides a practical checklist to ensure you make informed decisions that align with your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, it’s essential to clearly outline your technical requirements for the RFID solutions you seek. This includes the type of RFID technology (e.g., passive, active, or semi-passive), frequency bands, read range, and environmental conditions the devices must withstand. Having a detailed specification will help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers and ensure that the products meet your operational needs.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Manufacturers
Conduct thorough market research to identify potential RFID manufacturers that align with your specifications. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of candidates. Pay particular attention to manufacturers with a proven track record in your specific industry, as this can provide insights into their reliability and expertise.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that potential suppliers possess the necessary certifications and comply with international standards relevant to RFID manufacturing. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and specific RFID industry standards. This step is crucial as it not only assures product quality but also minimizes risks associated with non-compliance in your region.
Step 4: Request Product Samples for Testing
Before making a large-scale commitment, request samples of the RFID products you are interested in. Testing these samples in real-world conditions will allow you to assess their performance, durability, and compatibility with your existing systems. This step can save you from costly mistakes and ensure that the products meet your operational expectations.
Step 5: Check References and Customer Feedback
Reach out to previous clients or request case studies from potential manufacturers to gauge their reliability and customer service. This insight can be invaluable, especially in understanding how the manufacturer supports their products post-sale. Look for testimonials from businesses in your industry or region, as this will provide context to their performance.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve narrowed down your options, engage in discussions regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery timelines. Ensure that you understand the terms related to warranties, returns, and after-sales support. Effective negotiation can lead to more favorable terms and build a stronger partnership with your supplier.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
After selecting a manufacturer, focus on building a long-term relationship. Regular communication and collaboration can enhance your operational efficiency and ensure that you remain updated on new technologies and innovations. A strong partnership will also facilitate smoother negotiations for future orders.
By following this checklist, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing RFID manufacturers more effectively, ensuring that they choose a partner that meets their specific needs and fosters long-term success.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rfid manufacturer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in RFID Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure of RFID manufacturing is crucial for international B2B buyers aiming to make informed sourcing decisions. The primary components of cost include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as semiconductors, plastics, and metals, can significantly impact pricing. Fluctuations in the global market can lead to variances in material costs, which should be monitored closely.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can be a considerable part of the overall expenditure. Countries with lower labor costs may provide competitive pricing, but it’s essential to consider the quality and skill level of the workforce.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient overhead management can lead to lower prices for buyers.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for production molds and dies is significant, especially for customized RFID solutions. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs and their impact on the overall pricing structure.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the reliability of RFID products requires rigorous testing and quality assurance processes. The costs associated with QC can vary, affecting the final price.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can significantly influence the total cost, particularly for international buyers. Understanding the logistics costs, including customs and tariffs, is vital for accurate budgeting.
-
Margin: Manufacturers will typically apply a profit margin over their costs. This margin can vary based on competition, market demand, and the specific supplier’s pricing strategy.
How Do Price Influencers Impact RFID Manufacturing Costs?
Several factors influence pricing in the RFID manufacturing sector:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often attract discounts, reducing the per-unit cost. Buyers should evaluate their volume needs and consider negotiating MOQs for better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized RFID solutions may incur additional costs due to unique specifications. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against potential cost increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and compliance with industry standards can lead to increased costs. Buyers should assess whether the quality justifies the price, especially in industries where reliability is critical.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium due to their track record, while new entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The agreed terms for shipping and delivery can impact overall costs. Buyers should be familiar with different Incoterms to understand their responsibilities and potential hidden costs.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help International Buyers Secure Better Pricing?
B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can leverage several strategies to negotiate better pricing:
-
Research and Compare: Conduct thorough research on multiple suppliers to compare pricing structures and services. Understanding the market can strengthen your negotiation position.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the upfront costs but also the TCO, which includes maintenance, logistics, and potential downtime. This approach can highlight long-term savings.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a good rapport with suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing. Long-term partnerships often result in preferential pricing and service.
-
Be Transparent About Needs: Clearly communicate your requirements and constraints. Suppliers may be willing to adjust their pricing if they understand your budget limitations and order sizes.
-
Timing and Flexibility: Timing your orders during off-peak seasons can lead to better pricing. Additionally, being flexible with delivery schedules may help negotiate lower logistics costs.
Conclusion: Why Understanding Cost Structures and Pricing Influencers is Essential for B2B Buyers
For international B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure and pricing influencers in RFID manufacturing is vital. By leveraging this knowledge and employing strategic negotiation tactics, buyers can secure favorable pricing while ensuring product quality and reliability. Keep in mind that prices are indicative and can fluctuate based on various market conditions and supplier relationships.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rfid manufacturer With Other Solutions
When considering the adoption of RFID technology, it is essential for B2B buyers to evaluate not just RFID manufacturers but also alternative solutions that may offer similar benefits. This analysis provides insights into how RFID compares with other viable technologies, enabling informed decision-making tailored to specific business needs.
Comparison Table of RFID Manufacturer and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | RFID Manufacturer | Barcode Technology | NFC (Near Field Communication) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High accuracy in tracking | Moderate accuracy; prone to errors in poor conditions | High accuracy for short-range interactions |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; ongoing costs for tags | Lower initial cost; no maintenance required | Moderate cost; varies by application |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex; requires infrastructure setup | Simple; requires minimal training | Simple; user-friendly for consumers |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required for readers and software | Minimal; only scanner needed | Low; mainly device compatibility checks |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale inventory and asset management | Retail environments and shipping | Contactless payments and access control |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Barcode Technology as an Alternative to RFID?
Barcode Technology has been a staple in inventory management for decades. Its primary advantage is the lower cost of implementation and operation compared to RFID systems. Barcodes require minimal training and can be easily integrated into existing processes. However, they are limited by line-of-sight scanning requirements and can be less accurate in high-volume scenarios, particularly if labels are damaged or obscured. For businesses operating in environments where quick scanning is not critical, barcodes remain a reliable choice.
How Does NFC Offer Unique Benefits Compared to RFID?
NFC (Near Field Communication) technology is increasingly popular for applications like mobile payments and access control. Its advantages lie in its ease of use and the growing acceptance among consumers, making it ideal for businesses looking to enhance customer interactions. NFC allows for secure, contactless transactions and can facilitate two-way communication between devices. However, its range is significantly limited, typically requiring devices to be within a few centimeters of each other. For organizations focusing on customer engagement and secure transactions, NFC can be a valuable complement to RFID.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose Between RFID and Alternative Solutions?
Selecting the right solution depends on several factors, including the scale of operations, budget constraints, and specific business needs. RFID manufacturers offer robust solutions for extensive asset tracking and inventory management but come with higher costs and complexity. On the other hand, barcode technology provides a cost-effective and straightforward alternative for smaller operations, while NFC is ideal for enhancing customer interaction in retail and payment systems. B2B buyers should assess their operational requirements, budget, and growth potential to determine which technology aligns best with their strategic goals. By doing so, they can optimize their investment in tracking and management solutions.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rfid manufacturer
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of RFID Products?
When evaluating RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) manufacturers, understanding key technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some of the most important specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of RFID tags affects their durability and performance. Common materials include PVC, PET, and paper, each offering different levels of resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, heat, and chemicals. For instance, PVC tags are suitable for outdoor applications due to their weather resistance, while paper tags are often used for short-term applications. Choosing the right material grade ensures that the RFID solution will meet the specific operational needs of your business.
2. Read Range
The read range is the maximum distance at which an RFID reader can successfully communicate with a tag. This specification varies based on the type of RFID technology used (e.g., passive, active, or semi-passive). For example, active RFID tags can have a read range of up to 100 meters, making them ideal for tracking assets in large areas. Understanding the read range is vital for applications like inventory management or supply chain tracking, where distance can impact efficiency.
3. Frequency
RFID systems operate at different frequencies: low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), and ultra-high frequency (UHF). Each frequency has distinct advantages and limitations. For instance, LF RFID is less susceptible to interference but has a shorter read range, while UHF RFID offers faster read speeds and longer distances. Selecting the appropriate frequency is essential for ensuring optimal performance in your specific application.
4. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions and performance characteristics of RFID products. This specification is crucial in applications where precise fitting and alignment are necessary, such as in automated identification systems. Proper tolerance ensures reliable operation and minimizes the risk of tag failure or misreadings, which can lead to costly errors in inventory management or logistics.
5. Operating Temperature Range
The operating temperature range indicates the environmental conditions in which RFID devices can function effectively. Some RFID tags are designed for extreme temperatures, making them suitable for industrial applications, while others are more appropriate for office environments. Understanding the operating temperature range is important to ensure that RFID solutions remain functional and reliable under varying conditions.
Which Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Understand?
Familiarizing yourself with common trade terms in the RFID industry can streamline communication with manufacturers and enhance negotiation effectiveness. Here are some essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce components or equipment that are marketed by another company. In the RFID sector, an OEM may manufacture RFID tags or readers that are branded under a different name. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers assess quality and compatibility with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory planning. Manufacturers may set MOQs based on production costs and demand forecasts, and understanding these quantities can help buyers negotiate better terms or decide on alternative suppliers.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price and terms for specific products or services. It is a critical tool for B2B buyers looking to compare offers from multiple manufacturers. Providing detailed specifications in an RFQ can lead to more accurate quotes and better decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, reducing the risk of misunderstandings. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for international B2B buyers to ensure compliance and smooth logistics.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the goods are delivered. Understanding lead times is crucial for planning and inventory management, especially in industries where timely delivery is critical to operations.
Conclusion
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing RFID solutions. This knowledge not only enhances negotiation leverage but also ensures that selected products meet operational requirements effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rfid manufacturer Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the RFID Manufacturer Sector?
The RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) industry is witnessing significant growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing adoption across various sectors. Key global drivers include the escalating demand for supply chain transparency and efficiency, particularly in logistics, retail, and healthcare. International B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, such as Germany and Mexico, are increasingly looking for solutions that enhance inventory management, reduce theft, and improve operational efficiency.
Emerging trends in the RFID sector highlight the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technologies. This convergence allows for real-time data collection and analysis, providing businesses with actionable insights that enhance decision-making. Moreover, the push for automation in warehouses and manufacturing facilities is leading to a surge in demand for RFID systems that facilitate seamless tracking and monitoring of assets.
Additionally, the market is experiencing a shift towards more cost-effective and flexible solutions, such as RFID tags that can be easily integrated with existing systems. International buyers should also pay attention to regional market dynamics, as varying regulations and technological readiness can impact sourcing strategies. Countries in Africa and South America may present unique challenges and opportunities, necessitating localized approaches for successful implementation.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the RFID Manufacturing Sector?
Sustainability is becoming an integral part of sourcing decisions in the RFID sector, as businesses increasingly recognize the importance of ethical supply chains. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and materials used in RFID products is under scrutiny, prompting manufacturers to adopt greener practices. International B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, which can enhance their brand reputation and meet consumer demand for responsible sourcing.
Ethical sourcing practices include the use of recyclable materials in RFID tags and ensuring that manufacturing processes adhere to environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and adherence to RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to attract international buyers. These certifications not only assure compliance with environmental standards but also signal a manufacturer’s commitment to sustainable practices.
Moreover, the push for transparency in supply chains is driving RFID manufacturers to adopt technologies that allow for traceability of materials and components. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in Europe and the Middle East, where consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental and social implications of their purchases. By aligning with suppliers that prioritize sustainability, international B2B buyers can contribute to a circular economy while also enhancing their own market competitiveness.
What Is the Brief Evolution of RFID Technology Relevant to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of RFID technology dates back to the early 20th century, but it has gained significant traction in the past two decades. Initially used for military applications, RFID technology has expanded into commercial sectors, driven by the need for efficient inventory management and tracking solutions. The introduction of passive RFID tags, which do not require a power source, has made the technology more accessible and cost-effective for businesses.
In recent years, advancements in RFID technology have led to the development of more sophisticated systems that integrate with cloud computing and IoT. This progression allows for enhanced data analytics capabilities, providing B2B buyers with deeper insights into their supply chains. As the technology continues to evolve, international buyers must stay informed about innovations and trends that could impact their sourcing strategies, ensuring they leverage the full potential of RFID solutions for operational excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rfid manufacturer
-
How do I select the right RFID manufacturer for my business needs?
When choosing an RFID manufacturer, consider factors such as industry experience, technological capabilities, and customization options. Look for manufacturers that specialize in your specific application, whether it’s inventory management, asset tracking, or supply chain optimization. Additionally, review their client testimonials and case studies to gauge their reliability and performance. Engaging in a direct dialogue about your requirements can also help determine if they can meet your expectations. -
What are the key considerations for international shipping of RFID products?
When sourcing RFID products internationally, it’s essential to understand the logistics involved, including shipping costs, delivery times, and customs regulations. Ensure that the manufacturer offers reliable shipping partners and can provide documentation required for customs clearance. Additionally, clarify whether the manufacturer handles duties and taxes or if these are your responsibility. Understanding these aspects can help avoid unexpected delays and costs. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for RFID products?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for RFID products can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and product type. Generally, MOQs can range from 100 to 1,000 units. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with the manufacturer, as some may be flexible on MOQs for first-time orders or custom projects. Always consider your inventory management strategy to ensure that you can effectively handle the ordered quantities. -
How can I ensure the quality of RFID products from international manufacturers?
To ensure quality, request samples from potential manufacturers to evaluate their RFID products firsthand. Look for manufacturers with ISO certifications, as this indicates adherence to international quality standards. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes, including testing methods and defect rates. Establishing a clear communication channel for quality feedback post-delivery can also help maintain product standards. -
What payment terms should I expect when working with RFID manufacturers?
Payment terms can differ based on the manufacturer and your negotiation power. Common arrangements include a 30% deposit upfront and the remaining balance before shipment. Some manufacturers may offer credit terms for established buyers. It’s essential to clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., wire transfer, letters of credit) and any potential fees associated with international transactions. Understanding these terms can help you manage your cash flow effectively. -
Can RFID products be customized to meet specific business requirements?
Yes, many RFID manufacturers offer customization options to tailor products to your specific needs. This can include adjustments in tag size, frequency, memory capacity, and even the incorporation of your branding. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and ask for a timeline for development and production. This will help ensure that the end product aligns with your operational requirements. -
What are the common challenges in sourcing RFID products internationally?
Common challenges include navigating different regulatory environments, language barriers, and varying quality standards. Additionally, international shipping can lead to delays and increased costs due to customs procedures. To mitigate these issues, conduct thorough research on potential manufacturers, establish clear communication protocols, and consider working with local agents or consultants who understand the market dynamics in both your region and that of the manufacturer. -
How do I vet potential RFID suppliers effectively?
Vetting potential RFID suppliers involves several steps: check their business credentials, such as certifications and years in operation; review customer feedback and case studies; and request references from previous clients. Conduct virtual or in-person visits if possible, and evaluate their production capabilities and quality control measures. Additionally, consider their responsiveness and willingness to collaborate on your specific needs, as this can indicate their commitment to customer service.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rfid manufacturer
In the rapidly evolving landscape of RFID manufacturing, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal approach for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By prioritizing partnerships with reliable manufacturers, companies can enhance supply chain efficiencies, reduce operational costs, and ensure product quality. Understanding regional market dynamics and leveraging technology for real-time data can significantly improve decision-making processes.
As you navigate the complexities of sourcing RFID solutions, consider not only the price but also the total cost of ownership, including factors such as support services, customization capabilities, and compliance with international standards. Engaging with manufacturers that offer comprehensive support and innovative solutions will empower your organization to stay ahead of competitors.
Looking forward, the RFID market is poised for substantial growth, driven by advancements in IoT and automation. Now is the time for international B2B buyers to act strategically, forging partnerships that will facilitate long-term success and innovation. Embrace the opportunities presented by RFID technology to enhance operational efficiencies and drive business growth in your respective markets.