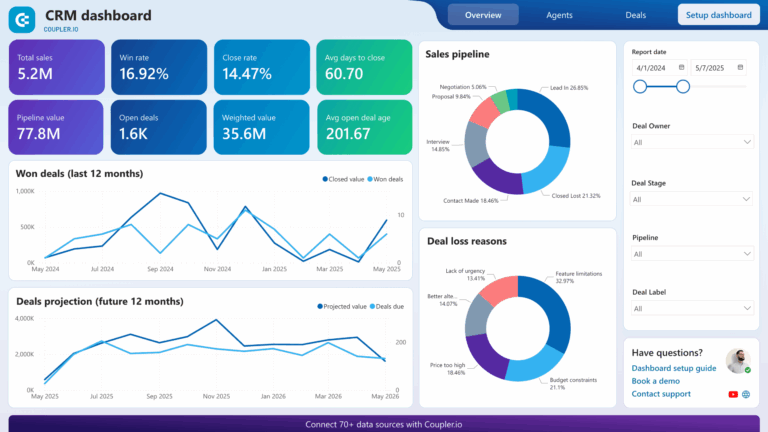
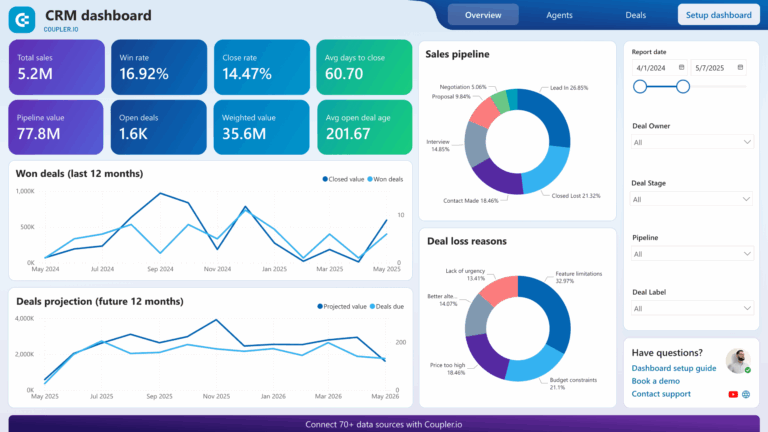
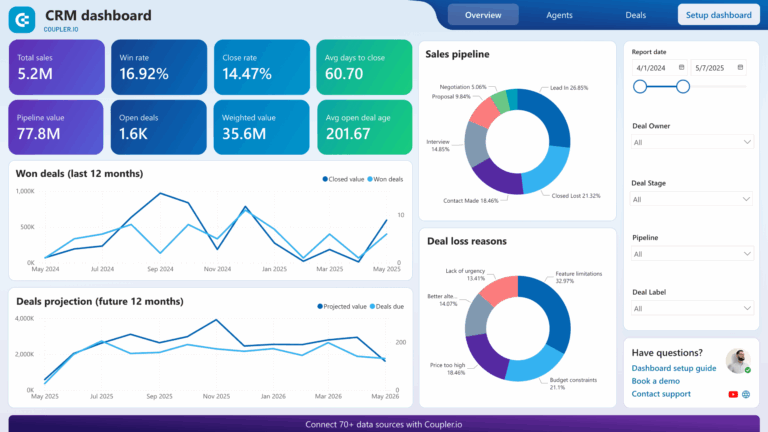
What Is a CRM System? A Complete Guide for Businesses (2025)
Introduction: Why Your Business Needs More Than a Spreadsheet
In the fast-paced world of business, managing customer data effectively is paramount to success. Many organizations, especially small to medium-sized enterprises, often resort to using spreadsheets and scattered notes to keep track of customer interactions, sales leads, and important information. While spreadsheets can serve as a temporary solution, they quickly become cumbersome as data grows, leading to confusion, errors, and missed opportunities. The inability to access real-time information can hinder decision-making and stall growth, ultimately impacting customer satisfaction and retention.
This is where Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems come into play. CRM is a strategy and technology designed to manage a company’s relationships and interactions with current and potential customers. The core purpose of a CRM is to streamline processes, enhance productivity, and improve customer relationships by centralizing and organizing customer data in one accessible platform. By consolidating information, a CRM allows businesses to have a 360-degree view of their customers, facilitating better communication and more personalized service.
This comprehensive guide is designed to help business owners, sales managers, and marketing professionals navigate the world of CRM systems. We will delve into what a CRM is, exploring its core features that go beyond mere data storage. Key benefits of adopting a CRM will be highlighted, including improved collaboration among teams, enhanced customer insights, and automation of repetitive tasks, which can save valuable time and resources.
Furthermore, we will provide an in-depth review of the top CRM platforms available in the market today. Each platform will be evaluated based on its features, pricing, and suitability for different business sizes and types. Finally, we will equip you with a guide to choosing the right CRM for your specific needs, ensuring that you make an informed decision that aligns with your business goals.
As you embark on this journey toward better customer relationship management, remember that transitioning from spreadsheets to a CRM system is not just a technological upgrade—it’s a strategic move that can transform how your business interacts with its customers, ultimately paving the way for sustained growth and success.
The Top 7 CRM Platforms of 2025
Top 10: CRM Platforms
In the article “Top 10: CRM Platforms” from Technology Magazine, a selection of cutting-edge customer relationship management systems is showcased, designed to help businesses of all sizes streamline their operations and enhance customer experience (CX). These platforms cater to diverse target audiences, including small businesses and sales teams, by offering robust features that drive growth and foster meaningful customer relationships, ultimately transforming the way companies interact with their clients.
- Website: technologymagazine.com
- Company Age: Approx. 22 years (domain registered in 2003)
Try The World’s #1 AI CRM
Salesforce, recognized as the world’s leading AI-powered CRM, provides businesses with comprehensive tools to enhance customer relationship management. Designed for sales teams and organizations of all sizes, it streamlines processes through automation, data analytics, and personalized engagement strategies. With features like predictive analytics and customizable dashboards, Salesforce empowers users to foster stronger customer connections and drive sales growth effectively, making it an ideal choice for companies aiming to enhance their customer interactions.
- Website: salesforce.com
- Company Age: Approx. 27 years (domain registered in 1998)
CRM software: the ultimate guide and 10 top AI
The article “CRM Software: The Ultimate Guide and 10 Top AI-Powered Solutions” on monday.com explores Freshsales CRM as an affordable and efficient solution for small to medium-sized businesses aiming to enhance lead management, customer engagement, and sales automation. With features like a robust sales pipeline, it targets sales teams seeking to streamline their processes and improve overall productivity through AI-driven insights and automation tools.
- Website: monday.com
- Company Age: Approx. 30 years (domain registered in 1995)
The Best Simple CRMs for 2025
In “The Best Simple CRMs for 2025,” Zendesk highlights user-friendly and straightforward CRM solutions tailored for small businesses. These easy-to-navigate platforms are designed to enhance customer relationship management without overwhelming users with complex features. Ideal for entrepreneurs and small teams looking to streamline their operations, these basic CRMs focus on facilitating growth and improving customer interactions, making them accessible for businesses of all sizes.
- Website: zendesk.es
What is a CRM System? A Deep Dive
Understanding CRM Systems
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are comprehensive tools designed to help businesses manage their interactions with current and potential customers. They centralize customer information, automate repetitive tasks, and provide insights that facilitate better decision-making and improved customer relationships. The evolution of CRM systems has led to diverse functionalities that cater to the specific needs of various industries and business sizes, from small startups to large enterprises.
The Goals of a CRM System
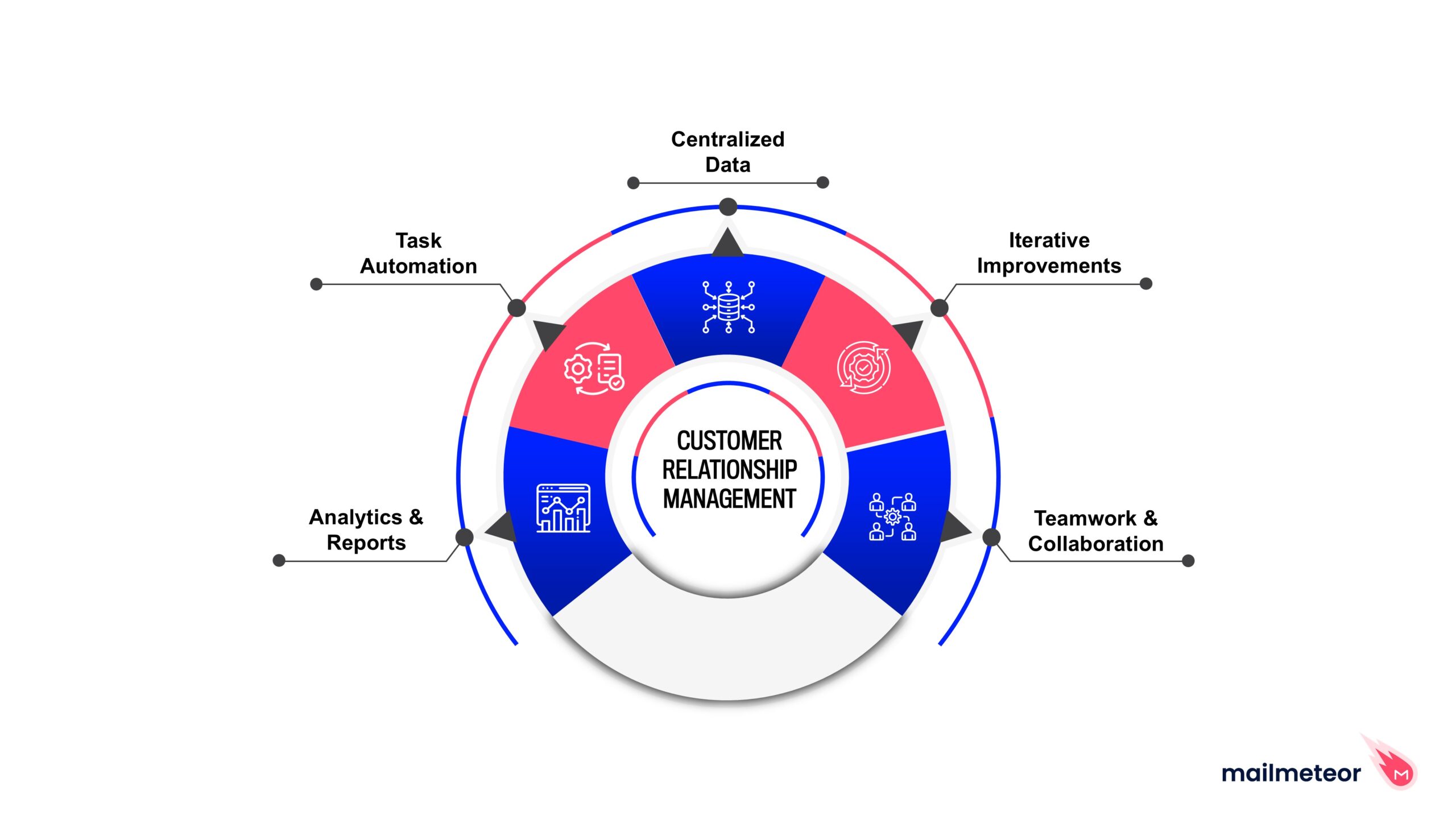
The primary goals of a CRM system can be categorized into several key areas:
-
Centralization of Customer Data: One of the core functions of a CRM system is to create a centralized database where all customer information is stored. This includes contact details, purchase history, communication logs, and preferences. By having all data in one place, businesses can ensure that every team member has access to the same information, reducing the chances of miscommunication and improving collaboration.
-
Automation of Tasks: CRM systems automate repetitive tasks such as sending follow-up emails, scheduling appointments, and updating customer records. This automation not only saves time but also allows employees to focus on higher-value activities, such as nurturing customer relationships and closing deals.
-
Enhanced Communication: A CRM system facilitates seamless communication among team members and departments. It provides tools for sharing information, tracking interactions, and managing workflows. This capability ensures that everyone is on the same page and can respond to customer inquiries or issues promptly.
-
Data Analysis and Reporting: Modern CRM systems are equipped with powerful analytics tools that enable businesses to analyze customer data and generate reports. These insights can help identify trends, measure performance, and inform strategic decisions. For example, sales teams can use CRM data to assess which products are selling well, while marketing teams can evaluate the effectiveness of campaigns.
-
Improved Customer Experience: Ultimately, the goal of a CRM system is to enhance the customer experience. By understanding customer needs and preferences, businesses can tailor their offerings and communications, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Who Uses a CRM?
CRM systems are versatile tools used across various departments within an organization. Each department leverages CRM functionalities to achieve specific objectives:
-
Sales Teams: Sales professionals use CRM systems to manage leads, track sales activities, and forecast revenue. They can access detailed customer profiles, view interaction history, and set reminders for follow-ups, enabling them to build stronger relationships with prospects and clients.
-
Marketing Teams: Marketing departments utilize CRM systems to segment their audience, track campaign performance, and manage marketing automation. By analyzing customer data, marketers can create targeted campaigns that resonate with specific segments, improving conversion rates and return on investment (ROI).
-
Customer Service Teams: Customer service representatives rely on CRM systems to access customer information quickly and efficiently. This access allows them to resolve issues more effectively, as they can view past interactions and understand the customer’s history with the company. Additionally, CRM systems often include features for managing support tickets and tracking service level agreements (SLAs).
-
Management: Executives and managers benefit from CRM systems by gaining insights into overall business performance. They can use reporting tools to monitor sales metrics, customer satisfaction scores, and team productivity, enabling them to make informed strategic decisions.
Why a Spreadsheet Isn’t Enough
While many businesses start with spreadsheets to manage customer data, relying solely on this method has significant drawbacks that can hinder growth and efficiency:
-
Limited Functionality: Spreadsheets lack the comprehensive features of a CRM system. They do not provide automation capabilities, reporting tools, or integration with other business applications. As a result, managing customer relationships becomes cumbersome and time-consuming.
-
Data Fragmentation: Spreadsheets often lead to data silos, where different teams maintain their own separate files. This fragmentation can result in inconsistencies, outdated information, and a lack of visibility into customer interactions across departments.
-
Collaboration Challenges: Collaboration becomes challenging with spreadsheets, especially when multiple team members need to access or update the same file. Version control issues can arise, leading to confusion and errors.
-
Scalability Issues: As businesses grow, managing customer data in spreadsheets becomes increasingly difficult. A CRM system is designed to scale with the organization, accommodating a growing customer base and expanding functionalities as needed.
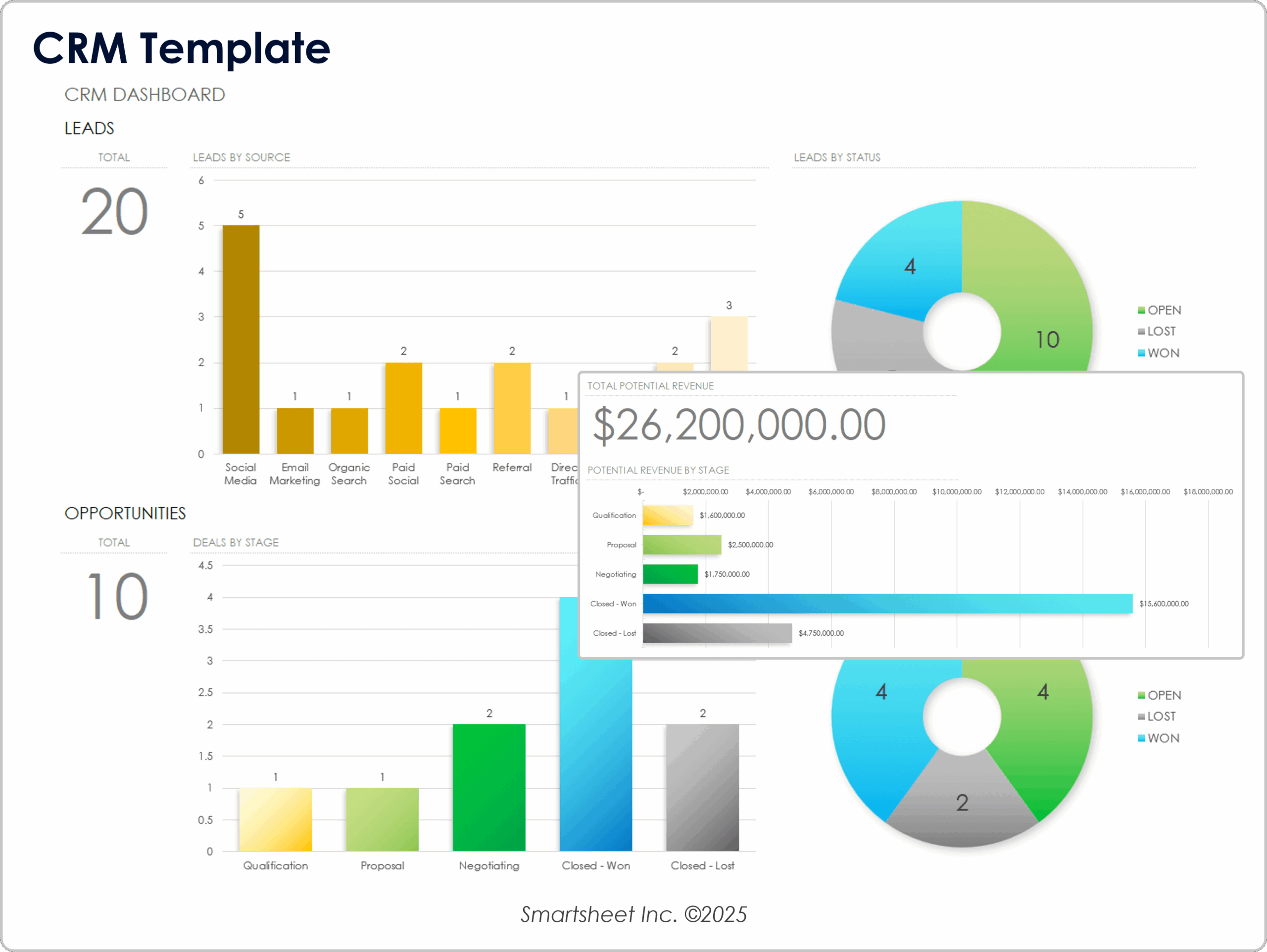
-
Lack of Insights: Spreadsheets provide limited analytical capabilities, making it difficult to derive actionable insights from customer data. In contrast, a CRM system offers advanced reporting and analytics features that can help businesses identify trends and make data-driven decisions.
Conclusion
In summary, a CRM system is an indispensable tool for modern businesses looking to enhance their customer relationships, streamline operations, and drive growth. By centralizing customer data, automating tasks, and providing valuable insights, CRM systems empower sales, marketing, and customer service teams to work more effectively and collaboratively. While spreadsheets may serve as a temporary solution, investing in a robust CRM system is essential for businesses aiming to thrive in today’s competitive landscape.
Core Features: What to Expect from a Modern CRM
Contact Management
Contact management is the foundational feature of any modern CRM system. It enables businesses to store, organize, and manage customer information in a centralized database. This includes essential details such as names, phone numbers, email addresses, company affiliations, and communication history.
How It Works
Modern CRMs use intuitive interfaces that allow users to easily input and access contact details. Information can be categorized by tags, custom fields, and segments, enabling users to filter and search for contacts based on various criteria. Additionally, many CRMs offer automated data entry through integrations with email and calendar applications, reducing the risk of human error.
Business Benefits
Effective contact management streamlines communication and enhances customer relationships. By having all pertinent information in one place, sales and support teams can provide personalized interactions, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty. Furthermore, a well-organized contact database aids in targeted marketing efforts, increasing conversion rates.
Lead and Opportunity Management
Lead and opportunity management features help businesses track potential customers throughout the sales funnel. This functionality allows users to capture leads from various sources, qualify them, and nurture them until they are ready to convert into paying customers.
How It Works
Modern CRMs enable users to create lead profiles that include information on their interests, behaviors, and interactions with the company. Users can assign leads to specific sales representatives, set follow-up tasks, and track the progress of each lead through stages of the sales process, such as qualification, proposal, and closing.
Business Benefits
By effectively managing leads and opportunities, businesses can optimize their sales efforts and improve conversion rates. This organized approach ensures that no lead falls through the cracks and that sales representatives focus their efforts on the most promising prospects. Additionally, the ability to analyze lead behavior can inform sales strategies and improve overall sales performance.
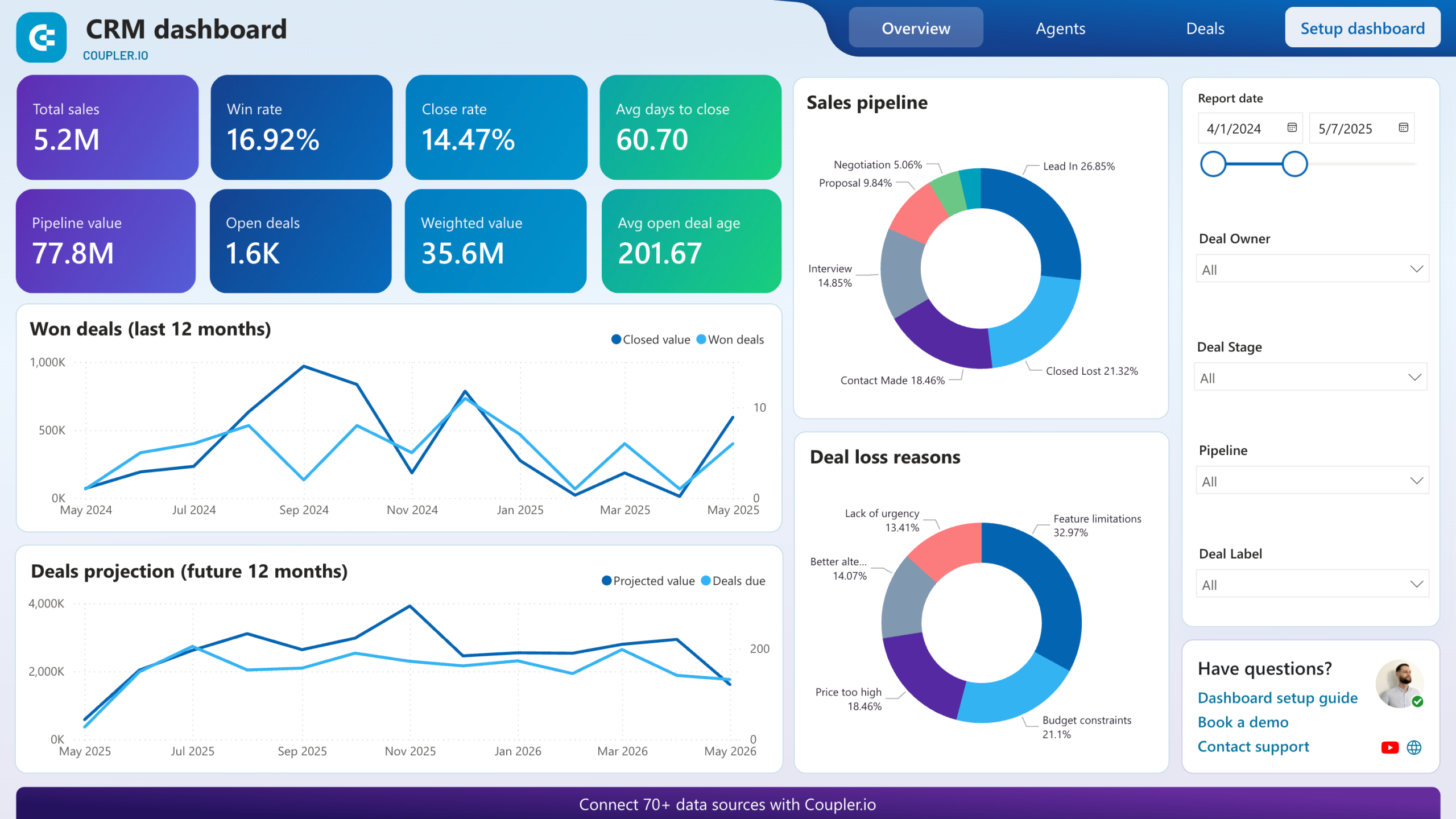
Sales Pipeline Visualization
Sales pipeline visualization provides a graphical representation of the sales process, allowing teams to see the status of leads and opportunities at a glance. This feature helps sales teams manage their workflow effectively and identify bottlenecks.
How It Works
Most modern CRMs offer customizable dashboards that visually depict the sales pipeline. Users can drag and drop opportunities between different stages (e.g., prospecting, negotiation, closed-won) and view metrics such as conversion rates and deal sizes. Some CRMs also include forecasting tools to project future sales based on current pipeline data.
Business Benefits
Sales pipeline visualization enhances team collaboration and accountability. By providing a clear view of where each opportunity stands, teams can prioritize their efforts and allocate resources more effectively. Additionally, real-time visibility into the pipeline allows for quicker decision-making and strategy adjustments, ultimately leading to increased sales efficiency.
Task and Activity Tracking
Task and activity tracking features allow users to record and manage interactions with leads and customers, including calls, emails, meetings, and follow-ups. This functionality ensures that all team members are aligned and that customer interactions are timely and relevant.
How It Works
Modern CRMs often include integrated calendars and task management tools, enabling users to schedule activities directly within the system. Users can set reminders, log completed tasks, and view a history of interactions with each contact. Some CRMs also offer automated follow-up reminders based on user-defined timelines.
Business Benefits
By keeping track of tasks and activities, businesses can enhance their customer engagement strategies. Timely follow-ups and personalized communication contribute to stronger relationships and higher customer satisfaction. Furthermore, this feature promotes accountability among team members, as everyone can see what tasks have been assigned and completed.
Marketing Automation
Marketing automation is a powerful feature that streamlines marketing efforts by automating repetitive tasks such as email campaigns, social media posting, and lead nurturing. This functionality allows marketing teams to focus on strategy rather than manual execution.
How It Works
Modern CRMs often integrate with marketing tools to provide comprehensive automation capabilities. Users can create automated workflows that trigger actions based on specific events, such as a lead signing up for a newsletter or downloading a resource. Additionally, CRMs can segment contacts based on behavior and preferences, allowing for targeted messaging.
Business Benefits
Implementing marketing automation leads to increased efficiency and improved marketing ROI. By automating tasks, businesses can ensure consistent communication with leads and customers, nurturing relationships without the need for constant manual intervention. Furthermore, data-driven insights gained from automation can inform future marketing strategies, optimizing campaigns for better results.
Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics features provide businesses with the tools to measure and analyze performance metrics across sales, marketing, and customer service. This functionality is crucial for understanding the effectiveness of strategies and making informed decisions.
How It Works
Modern CRMs come equipped with customizable reporting tools that allow users to generate real-time reports on various metrics, such as sales performance, lead conversion rates, and customer engagement. Users can create dashboards that visualize key performance indicators (KPIs) and filter data by different criteria for deeper insights.
Business Benefits
Access to comprehensive reporting and analytics enables businesses to track progress toward goals and identify areas for improvement. By leveraging data-driven insights, organizations can make informed decisions that enhance performance and drive growth. Additionally, regular reporting fosters accountability among team members, as they can easily see how their efforts contribute to overall business objectives.
Integrations
Integrations are a vital feature of modern CRMs, allowing them to connect with other software applications and systems. This capability enhances functionality and ensures that data flows seamlessly between platforms.
How It Works
Most CRMs offer a variety of pre-built integrations with popular applications, such as email clients, marketing platforms, accounting software, and customer support tools. Users can often customize integrations to meet their specific needs, ensuring that all relevant data is synchronized across systems.
Business Benefits
Integrations eliminate data silos, enabling teams to access all necessary information from a single platform. This interconnectedness enhances collaboration and ensures that everyone is working with the most current data. Furthermore, seamless integrations can improve operational efficiency by automating data transfer and reducing manual entry, allowing teams to focus on higher-value tasks.
Conclusion
In today’s competitive business landscape, a modern CRM system equipped with core features such as contact management, lead and opportunity management, sales pipeline visualization, task and activity tracking, marketing automation, reporting and analytics, and integrations is essential for driving growth and enhancing customer relationships. By understanding these features and their benefits, business owners, sales managers, and marketing professionals can make informed decisions when selecting a CRM that best fits their organizational needs.
The 3 Types of CRM Systems Explained
Understanding the Different Types of CRM Systems
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems come in various forms, each serving distinct purposes tailored to different business needs. The three primary types of CRM systems are Operational CRM, Analytical CRM, and Collaborative CRM. Below is a comparative table that highlights their core attributes, followed by a detailed exploration of each type.
| CRM Type | Primary Goal | Key Features | Best For (Department) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operational CRM | Streamline day-to-day customer interactions | Sales automation, customer service, marketing automation | Sales, Marketing, Customer Service |
| Analytical CRM | Analyze customer data to inform business decisions | Data mining, customer segmentation, reporting | Marketing, Sales, Executive Management |
| Collaborative CRM | Enhance communication and collaboration across teams | Shared databases, integrated communication tools | All Departments |
Operational CRM
Operational CRM focuses on the automation of customer-facing processes such as sales, marketing, and customer service. The primary goal is to improve efficiency by managing the day-to-day interactions between the business and its customers. This type of CRM allows organizations to streamline their operations, ensuring that sales and support teams can quickly access customer information and manage relationships effectively.
Key features of Operational CRM include sales automation tools that help manage leads and opportunities, marketing automation capabilities that enable targeted campaigns, and customer service tools that facilitate support interactions. For example, a retail company might use an Operational CRM like Salesforce to track customer purchases, manage inventory, and automate marketing emails based on customer behavior. This integrated approach not only enhances the customer experience but also increases productivity among sales and support staff.
Analytical CRM
Analytical CRM is designed to analyze customer data collected through various channels, providing insights that can drive strategic decision-making. The primary goal of Analytical CRM is to understand customer behavior, preferences, and trends, allowing businesses to tailor their offerings and improve overall customer satisfaction.
Key features of Analytical CRM include data mining capabilities, which help extract useful information from large datasets, customer segmentation tools that classify customers based on specific criteria, and reporting tools that visualize data for easier interpretation. For instance, a financial services firm might leverage an Analytical CRM like Zoho Analytics to segment its customers into groups based on their spending habits. This segmentation enables the firm to develop targeted marketing campaigns and personalized service offerings, ultimately leading to higher engagement and retention rates.
Collaborative CRM
Collaborative CRM emphasizes the importance of communication and information sharing among different departments within an organization. The primary goal is to enhance collaboration between sales, marketing, and customer service teams, ensuring a unified approach to customer relationship management. By breaking down silos, Collaborative CRM fosters a more cohesive understanding of customer needs and expectations.
Key features of Collaborative CRM include shared databases that provide real-time access to customer information across departments, integrated communication tools like chat and email for seamless interaction, and project management functionalities that support team collaboration. A practical example of Collaborative CRM in action is a software development company that utilizes a platform like HubSpot to share customer feedback between the development and marketing teams. This collaboration allows the company to refine its product offerings based on direct customer input, improving both product quality and customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Choosing the right type of CRM system is crucial for any business aiming to enhance its customer relationships and drive growth. Operational CRM is ideal for businesses focused on streamlining their customer interactions, Analytical CRM suits organizations looking to leverage data for strategic insights, and Collaborative CRM is best for those seeking to improve interdepartmental communication and teamwork. By understanding these different types of CRM systems, business owners and managers can make informed decisions that align with their specific operational goals and customer engagement strategies.
Key Business Benefits of Using a CRM
1. Centralized Customer Data
One of the primary advantages of implementing a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is the ability to centralize customer data. A CRM consolidates all customer information—such as contact details, interaction history, preferences, and feedback—into a single database. This central repository not only eliminates data silos but also enables team members across various departments to access and update customer records in real-time. As a result, businesses can provide more personalized and efficient service, as every team member has a comprehensive view of the customer’s journey. Moreover, having all relevant data in one location helps reduce errors, improves data accuracy, and streamlines onboarding for new employees who need to understand customer relationships quickly.
2. Improved Sales Productivity
CRM systems are designed to enhance sales productivity by automating routine tasks and providing tools that facilitate efficient sales processes. With features like lead management, pipeline tracking, and automated follow-ups, sales teams can focus more on selling rather than administrative duties. CRMs often include analytics and reporting capabilities that allow sales managers to track performance metrics, identify high-potential leads, and forecast sales more accurately. This improved visibility into the sales pipeline enables sales professionals to prioritize their efforts effectively, allocate resources where they are most needed, and ultimately close more deals in less time. By streamlining workflows and reducing time spent on manual tasks, CRMs can significantly boost overall sales productivity.
3. Enhanced Customer Retention
Another critical benefit of using a CRM is the enhancement of customer retention strategies. By analyzing customer interactions and feedback stored within the CRM, businesses can identify patterns and trends that inform their retention efforts. CRM systems enable companies to segment their customer base effectively, allowing for targeted marketing campaigns and personalized communication that resonate with specific customer groups. Additionally, CRMs often include tools for managing customer service interactions, ensuring that issues are resolved promptly and effectively. This level of engagement fosters stronger relationships, builds customer loyalty, and ultimately leads to a higher customer lifetime value. Companies that leverage CRM insights to enhance customer experiences are better positioned to retain their clientele and reduce churn rates.
4. Data-Driven Decision Making
In today’s fast-paced business environment, the ability to make informed decisions based on data is crucial for success. CRM systems provide valuable insights through analytics and reporting features that allow businesses to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and measure the effectiveness of their sales and marketing strategies. By harnessing this data, decision-makers can identify areas for improvement, allocate resources more efficiently, and adapt strategies in real-time to meet changing market demands. Furthermore, CRMs can facilitate A/B testing and campaign tracking, enabling businesses to assess which tactics yield the best results. Ultimately, data-driven decision-making supported by a CRM leads to more strategic planning, reduced risks, and improved business outcomes.
5. Scalable Growth
As businesses grow, managing customer relationships can become increasingly complex. A robust CRM system is designed to scale alongside the business, accommodating an expanding customer base and evolving business needs. Many CRM platforms offer tiered pricing and customizable features that allow businesses to add functionalities as they grow, ensuring that they are not overpaying for unnecessary features. This scalability also extends to user access; as teams expand, new users can be easily onboarded onto the platform without disrupting existing operations. By providing a flexible framework for managing customer relationships, CRMs enable businesses to adapt to growth opportunities while maintaining high levels of service and engagement. This adaptability is essential for sustaining competitive advantage in a dynamic marketplace.
Implementing a CRM system can bring numerous benefits to businesses of all sizes. From centralizing customer data to enhancing retention strategies, CRMs play a pivotal role in driving sales productivity and enabling data-driven decision-making. As businesses scale, the need for an adaptable and comprehensive solution becomes increasingly critical, making CRM systems an invaluable asset for fostering sustainable growth.
How to Choose the Right CRM: A 7-Step Buyer’s Guide
1. Define Your Business Goals and Needs
Before diving into the vast array of CRM options available, it’s crucial to clearly define your business goals and specific needs. Consider the following aspects:
Identify Core Objectives
- Sales Goals: Are you looking to increase sales, improve lead conversion rates, or enhance customer retention? Your CRM should align with these targets.
- Marketing Needs: Determine if you require features such as email marketing automation, campaign tracking, or customer segmentation.
- Customer Support: Assess if you need a system that integrates customer support tools for better service delivery.
Analyze Current Processes
- Workflow Assessment: Examine your current sales and marketing workflows. Identify bottlenecks or areas for improvement that a CRM could address.
- Data Management: Consider the types of customer data you currently manage and how a CRM can centralize this information for easier access and analysis.
2. Establish Your Budget
Once you have a clear understanding of your goals, it’s essential to establish a budget for your CRM investment. Here are some factors to consider:
Total Cost of Ownership
- Subscription Fees: Most CRM systems operate on a subscription model. Understand the pricing structure, including monthly or annual fees per user.
- Additional Costs: Account for additional costs such as onboarding, training, custom integrations, and ongoing support.
Cost vs. Value
- Feature Evaluation: Determine which features are critical for your business and ensure that the CRM you choose delivers sufficient value for its cost. Cheaper options may lack essential functionalities.
3. Consider Ease of Use and User Adoption
A CRM is only as effective as the people using it. Therefore, consider the user experience and adoption rates:
User Interface and Experience
- Intuitive Design: Look for a CRM that offers an intuitive interface, making it easy for users to navigate and utilize its features.
- Mobile Accessibility: If your team works remotely or on the go, ensure that the CRM has a robust mobile app.
Training and Support
- Onboarding Resources: Assess the availability of training materials, tutorials, and customer support to help your team get up to speed quickly.
- User Feedback: Engage your team in the selection process to gather feedback on usability and functionality preferences.
4. Check for Essential Integrations
A CRM should not operate in a vacuum. It’s vital that it integrates seamlessly with other tools your business relies on:
Identify Key Tools
- Marketing Platforms: Ensure compatibility with email marketing services, social media management tools, and other marketing platforms.
- Sales Tools: Look for integration options with tools like e-commerce platforms, accounting software, and customer support systems.
API Availability
- Custom Integrations: Check if the CRM provides API access for custom integrations, allowing you to connect with unique tools and systems your business may use.
5. Evaluate Scalability for Future Growth
As your business evolves, your CRM needs may change. Therefore, choose a solution that can grow with you:
Assess Growth Potential
- User Limits: Ensure the CRM can accommodate an increasing number of users as your team expands.
- Feature Upgrades: Look for a platform that offers tiered pricing or additional features that can be activated as your business needs become more complex.
Flexibility
- Customizable Features: A good CRM should allow customization of workflows, dashboards, and reporting capabilities to adapt to your changing requirements.
6. Request Demos and Start Free Trials
Before making a final decision, it’s essential to see the CRM in action. This step can significantly influence your choice:
Schedule Demos
- Vendor Presentations: Many CRM providers offer demo sessions. Use this opportunity to see how the system functions in real time and ask specific questions about features relevant to your business.
Utilize Free Trials
- Hands-On Experience: Take advantage of free trials to test the CRM within your team. This will give you insight into its usability and whether it meets your needs.
7. Read Reviews and Case Studies
Finally, gather insights from other users to make an informed decision. Researching reviews and case studies can provide valuable information:
User Reviews
- Feedback Platforms: Visit review sites such as G2, Capterra, or PCMag to read user experiences and ratings. Pay attention to recurring pros and cons mentioned by users.
Case Studies
- Success Stories: Look for case studies from businesses similar to yours. Understanding how they successfully implemented a CRM can provide insights into potential challenges and benefits.
Conclusion
Choosing the right CRM is a critical decision that can significantly impact your business operations. By following these seven steps—defining your business goals, establishing a budget, considering ease of use, checking for essential integrations, evaluating scalability, requesting demos, and reading reviews—you can confidently select a CRM system that meets your unique needs. Remember, this is not just a software purchase; it’s an investment in your business’s growth and customer relationships.
CRM vs. ERP: Understanding the Key Differences
Definitions
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are software solutions designed to help businesses manage interactions with current and potential customers. They centralize customer data, facilitate communication, and streamline sales and marketing processes, ultimately aiming to enhance customer satisfaction and retention.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, on the other hand, are integrated management tools that help organizations manage and automate core business processes across various departments, such as finance, human resources, supply chain, and manufacturing. ERP solutions provide a unified view of business operations, ensuring that different departments can access the same information and work towards common organizational goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | CRM (Customer-Facing) | ERP (Business Operations-Facing) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Managing customer relationships and interactions | Managing internal business processes and resources |
| Core Users | Sales teams, marketing professionals, customer service teams | Finance departments, HR managers, supply chain managers, operations teams |
| Key Processes | Sales automation, lead tracking, customer support, marketing campaigns | Financial management, inventory management, order processing, HR management |
| Main Goal | Improve customer engagement, increase sales, enhance customer satisfaction | Optimize business operations, improve efficiency, reduce costs |
| Data Handling | Centralizes customer data and interactions | Centralizes data across various business functions |
| Customization | Often tailored to fit specific sales and marketing needs | Customizable to fit various business processes and requirements |
| Implementation Time | Generally quicker to implement and integrate | Usually requires more time for deployment and integration due to its complexity |
| Cost Structure | Typically subscription-based, with tiered pricing | Often involves higher upfront costs and ongoing maintenance expenses |
Detailed Comparison
Primary Focus
The primary focus of CRM systems is to foster strong relationships with customers. They achieve this through features that help track customer interactions, manage sales pipelines, and personalize marketing efforts. In contrast, ERP systems focus on streamlining and optimizing internal processes across an organization. This includes everything from managing financial transactions to overseeing supply chain logistics.
Core Users
CRM systems are predominantly used by customer-facing teams such as sales, marketing, and customer service. These users rely on the software to enhance their interactions with clients, gather insights on customer behavior, and drive sales. ERP systems are used by internal stakeholders, including finance and HR departments, to manage operations, resources, and compliance across the organization.
Key Processes
CRMs facilitate processes like lead management, customer support, and targeted marketing campaigns. They help businesses understand customer needs and preferences, enabling tailored interactions. On the other hand, ERPs encompass a wider range of processes, including financial management, procurement, manufacturing, project management, and human resources, ensuring that all aspects of the business are interconnected and functioning smoothly.
Main Goal
The main goal of a CRM is to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty by improving engagement and communication. Businesses aim to increase sales and build lasting relationships with their customers. Conversely, the goal of an ERP system is to optimize business operations, reduce redundancies, and enhance efficiency. By integrating various business functions, ERPs help organizations operate more cohesively.
Data Handling
CRMs centralize customer data, allowing users to access customer profiles, purchase history, and interaction logs easily. This centralized information supports personalized marketing and customer service. ERPs centralize data across various business functions, providing a holistic view of operations. This integration helps in informed decision-making and improves overall business agility.
Customization
While both CRM and ERP systems offer customization, CRMs typically focus on features that cater specifically to sales and marketing needs. ERPs, being more complex, provide broader customization options to fit diverse business processes and workflows.
Implementation Time
Implementing a CRM system is often quicker than deploying an ERP system. Due to their focused nature, CRMs can be set up and integrated into existing workflows in a relatively short time. ERPs, however, require extensive planning and coordination across departments, which can lead to longer implementation timelines.
Cost Structure
CRM systems generally follow a subscription model with tiered pricing based on features and user count. This makes them accessible for businesses of all sizes. ERPs, however, often involve higher upfront costs due to their complexity and the need for extensive training and maintenance, making them a significant investment for organizations.
Conclusion
Deciding whether a business needs a CRM, an ERP, or both depends on its specific requirements and goals. If a business is primarily focused on improving customer relationships and sales processes, a CRM may suffice. However, for organizations that require comprehensive management of internal processes and resources, an ERP is essential. Many businesses benefit from utilizing both systems to enhance customer engagement while optimizing their operations. Integrating a CRM with an ERP can provide a unified view of both customer interactions and internal operations, driving overall business success.
Best Practices for Successful CRM Implementation
Getting Leadership Buy-In
One of the most critical steps in successfully implementing a CRM system is securing buy-in from leadership. A CRM implementation requires both financial investment and organizational commitment, which necessitates a strong endorsement from upper management.
1. Communicate the Benefits:
Leaders need to understand how a CRM system can directly impact the business’s bottom line. Present data and case studies that illustrate improved sales performance, enhanced customer satisfaction, and streamlined processes. Highlight how CRM can lead to increased efficiency and reduced operational costs.
2. Involve Leadership in the Selection Process:
Encourage leaders to participate in the evaluation and selection of the CRM system. This involvement ensures that they feel invested in the decision and helps align the CRM’s capabilities with the organization’s strategic goals.
3. Establish a CRM Champion:
Designate a senior executive as the CRM champion. This individual will advocate for the CRM initiative, address concerns, and facilitate communication between teams. A champion can significantly influence the success of the project by fostering a culture of CRM utilization across the organization.
Planning Your Data Migration
Data migration is a pivotal phase in CRM implementation. Poorly executed data migration can lead to inaccuracies and inconsistencies that undermine the system’s effectiveness.
1. Audit Existing Data:
Before migrating data, conduct a thorough audit of your existing databases. Identify which data is valuable and relevant, and determine what needs to be cleaned, archived, or discarded. This step helps ensure that only high-quality data is transferred to the new system.
2. Establish a Migration Strategy:
Develop a comprehensive data migration plan that outlines the steps for transferring data, including timelines, responsibilities, and methods for validating data accuracy post-migration. Consider whether the migration will be conducted in phases or all at once, depending on the complexity and volume of data.
3. Test the Migration Process:
Run a pilot migration with a small subset of data to identify potential issues before full-scale implementation. Testing allows you to refine your process and address any discrepancies that arise, ensuring a smoother transition when migrating all data.
Customizing the CRM to Your Process (Not the Other Way Around)
A common pitfall in CRM implementation is customizing the system to fit the software’s processes rather than tailoring it to your business’s unique workflows.
1. Analyze Existing Processes:
Before customization, map out your current processes and workflows. Identify pain points, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. This analysis will guide how you configure the CRM to enhance your operations rather than impose a one-size-fits-all approach.
2. Use Custom Fields and Features Wisely:
Leverage the customization capabilities of the CRM to create fields, dashboards, and reports that reflect your specific needs. However, avoid over-customization, which can complicate user experience and maintenance. Focus on essential features that drive productivity.
3. Involve End Users in Customization:
Engage end users in the customization process to ensure that the system aligns with their daily tasks. Their insights can help identify necessary features and streamline processes, leading to greater acceptance and usage of the CRM.
Effective User Training and Onboarding
Successful CRM implementation hinges on effective user training and onboarding. Even the most powerful CRM system will fail if users are not adequately prepared to utilize it.
1. Develop a Comprehensive Training Plan:
Create a structured training program that covers all aspects of the CRM system, including basic navigation, data entry, reporting, and specific features relevant to different user roles. Include both in-person and online training options to accommodate different learning styles.
2. Use Real-World Scenarios:
Incorporate real-world scenarios and case studies into the training sessions. This practical approach allows users to see how the CRM can be applied to their daily tasks, making the training more relevant and engaging.
3. Provide Ongoing Support:
Post-training support is crucial for reinforcing learning and addressing challenges. Establish a helpdesk or support channel where users can ask questions and receive assistance. Consider appointing CRM champions within teams to provide peer support and guidance.
Setting Clear KPIs to Measure Success
Establishing clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential for measuring the success of your CRM implementation. Without defined metrics, it becomes challenging to assess the effectiveness of the system.
1. Align KPIs with Business Objectives:
Identify KPIs that directly correlate with your organization’s goals, such as increased sales revenue, improved customer retention rates, or enhanced lead conversion ratios. Aligning KPIs with broader business objectives ensures that the CRM system supports overall strategy.
2. Use a Mix of Quantitative and Qualitative Metrics:
Incorporate both quantitative metrics (e.g., sales growth, customer acquisition costs) and qualitative metrics (e.g., user satisfaction, customer feedback) to gain a holistic view of CRM performance. This balanced approach helps identify areas for improvement and celebrate successes.
3. Regularly Review and Adjust KPIs:
Set a schedule for reviewing your KPIs to evaluate the CRM’s impact continuously. Be prepared to adjust your metrics as needed based on evolving business goals or market conditions. This adaptability ensures that your CRM remains aligned with your organization’s objectives.
Conclusion
Implementing a CRM system can yield significant benefits for your organization, but success depends on careful planning and execution. By securing leadership buy-in, planning data migration meticulously, customizing the system to fit your processes, providing effective training, and setting clear KPIs, you can avoid common pitfalls and maximize the value of your CRM investment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. ¿Qué es un CRM y cómo puede beneficiar a mi negocio?
Un CRM, o sistema de gestión de relaciones con clientes, es una herramienta que ayuda a las empresas a gestionar sus interacciones con clientes actuales y potenciales. Al centralizar la información del cliente, un CRM permite a las empresas automatizar tareas, mejorar la colaboración entre equipos y obtener insights valiosos para estrategias de marketing y ventas. Esto puede resultar en una mejor atención al cliente, mayores tasas de retención y un aumento en las ventas.
2. ¿Cuáles son las características clave que debo buscar en un CRM?
Al elegir un CRM, es importante considerar características como la gestión de contactos, automatización de ventas, informes y análisis, integración con otras herramientas, personalización de flujos de trabajo y soporte al cliente. Además, la capacidad de acceder a datos en tiempo real y la facilidad de uso son cruciales para garantizar que tu equipo adopte la herramienta sin problemas.
3. ¿Cuánto cuesta un CRM?
El costo de un CRM puede variar significativamente dependiendo de la funcionalidad y el tamaño de la empresa. Los precios pueden oscilar desde opciones gratuitas para pequeños equipos hasta soluciones más robustas que pueden costar cientos o incluso miles de dólares al mes. Es importante evaluar tu presupuesto y las características que realmente necesitas antes de tomar una decisión.
4. ¿Puede un CRM ser utilizado para B2C (Business to Consumer)?
Sí, un CRM puede ser muy efectivo para empresas B2C. Estas plataformas permiten gestionar interacciones con un gran número de clientes, segmentar audiencias, realizar campañas de marketing personalizadas y mejorar la experiencia del cliente. Un CRM bien implementado puede ayudar a aumentar la satisfacción del cliente y fomentar la lealtad a la marca.
5. ¿Cuánto tiempo toma implementar un CRM?
El tiempo de implementación de un CRM puede variar dependiendo de la complejidad del sistema y del tamaño de tu organización. En general, la implementación puede tomar desde unas pocas semanas hasta varios meses. Factores que influyen en el tiempo de implementación incluyen la personalización del sistema, la capacitación del personal y la migración de datos desde otros sistemas.
6. ¿Qué tipo de empresas se benefician más de un CRM?
Casi cualquier tipo de empresa puede beneficiarse de un CRM, desde pequeñas startups hasta grandes corporaciones. Sin embargo, las empresas que manejan un alto volumen de interacciones con clientes, como las del sector de ventas, servicios al cliente y marketing, suelen ver un impacto más significativo en la eficiencia y la satisfacción del cliente al utilizar un CRM.
7. ¿Qué tipo de soporte se ofrece con un CRM?
La mayoría de los proveedores de CRM ofrecen diferentes niveles de soporte, que pueden incluir asistencia telefónica, chat en vivo, y recursos en línea como tutoriales y foros. Algunos proveedores también ofrecen formación personalizada y consultoría para ayudar a las empresas a maximizar el uso de la herramienta. Es recomendable revisar las opciones de soporte antes de decidirte por un proveedor.
8. ¿Cómo se mide el éxito de un CRM?
El éxito de un CRM se puede medir a través de varios indicadores clave de rendimiento (KPI), como el aumento de las ventas, la mejora en la retención de clientes, la reducción del tiempo de respuesta al cliente y el aumento en la satisfacción del cliente. También es útil realizar encuestas internas para evaluar cómo los empleados están utilizando el CRM y si está ayudando a mejorar sus procesos laborales.
Conclusion: Taking the Next Step in Customer Management
The Importance of CRM in Modern Business
In today’s fast-paced business environment, a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system serves as a foundational tool for growth and success. By centralizing customer data, automating repetitive tasks, and providing valuable insights, CRMs empower businesses to enhance customer interactions, streamline operations, and drive sales performance. As you navigate the myriad of options available, it becomes crucial to select a CRM that aligns with your specific business needs—be it enhancing customer service, improving sales processes, or optimizing marketing efforts.
Aligning CRM Features with Business Needs
Choosing the right CRM is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Each business has unique processes, customer bases, and objectives. Small businesses may benefit from user-friendly solutions like HubSpot Smart CRM or Less Annoying CRM, while larger enterprises might require more robust options like Salesforce or Creatio for their advanced capabilities. Understanding your business’s specific requirements and challenges will guide you in selecting a system that not only meets your current needs but also scales as your business grows.
Taking Action: Evaluate Your Workflows
Now is the time to take action. Start by evaluating your current sales and marketing workflows. Identify bottlenecks, areas for improvement, and opportunities for automation. Engage your team in discussions about their needs and pain points, as their insights are invaluable in the selection process. By taking these proactive steps, you set the stage for implementing a CRM that will enhance customer management, foster collaboration, and ultimately drive business growth.
In conclusion, investing in the right CRM system is a strategic move that can significantly impact your business’s future. Empower yourself to make informed decisions that will transform how you manage customer relationships. Begin your journey today by assessing your current workflows and exploring CRM options that align with your vision for success.
Important Disclaimer
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information and reviews in this guide are for educational purposes, based on publicly available data. We are not affiliated with any software providers mentioned. Features and pricing change frequently. Always conduct your own due diligence and request a demo before committing to a CRM platform.